Navigating the World: Understanding the Grid of Longitude and Latitude
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding the Grid of Longitude and Latitude
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding the Grid of Longitude and Latitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding the Grid of Longitude and Latitude

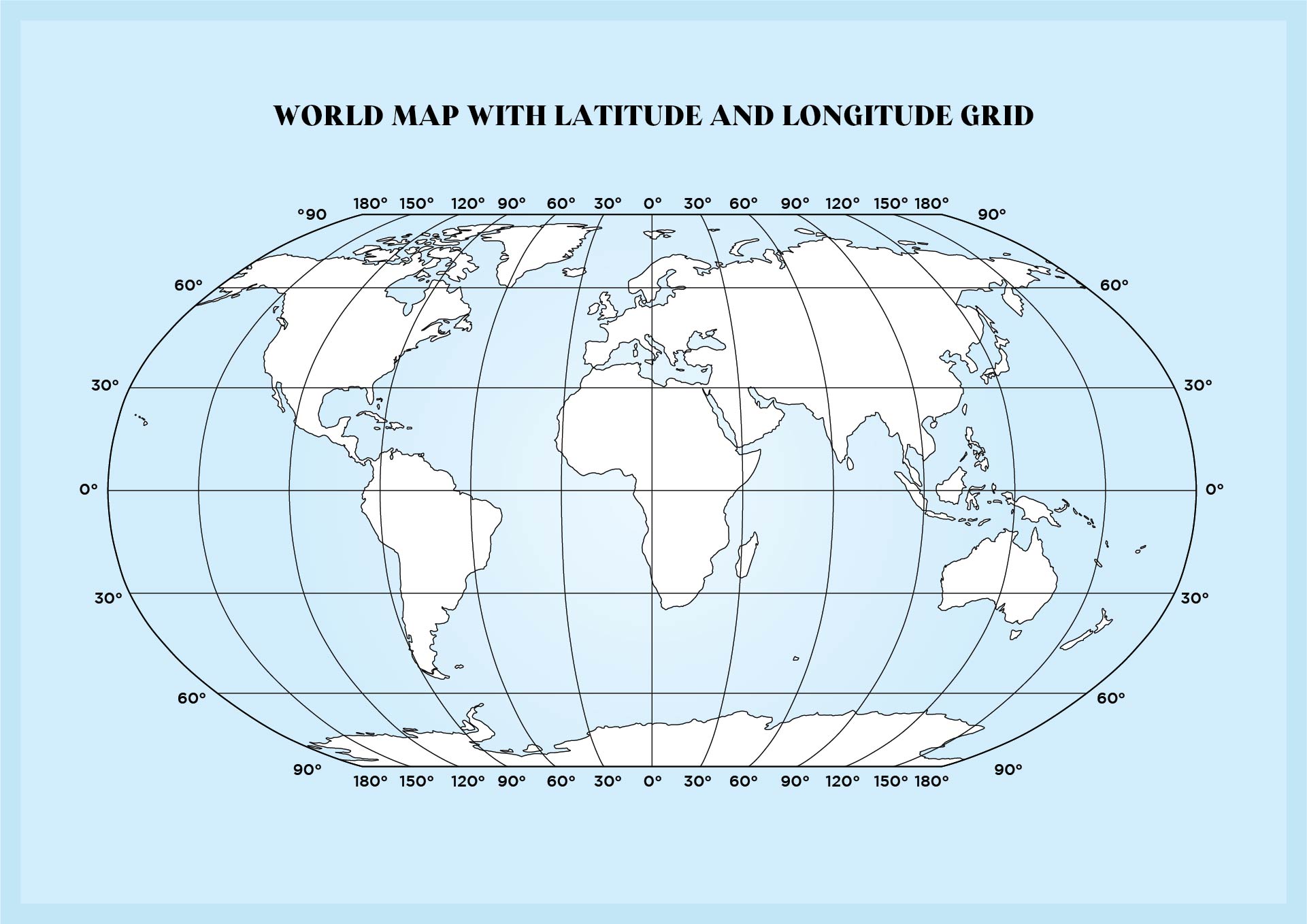
The Earth, a vast and complex sphere, presents a challenge when it comes to locating specific points. To overcome this, a system of imaginary lines, known as longitude and latitude, was devised. This grid system provides a universal framework for pinpointing any location on the planet, making it indispensable for navigation, mapping, and understanding global phenomena.
The Foundation: Latitude and Longitude Explained
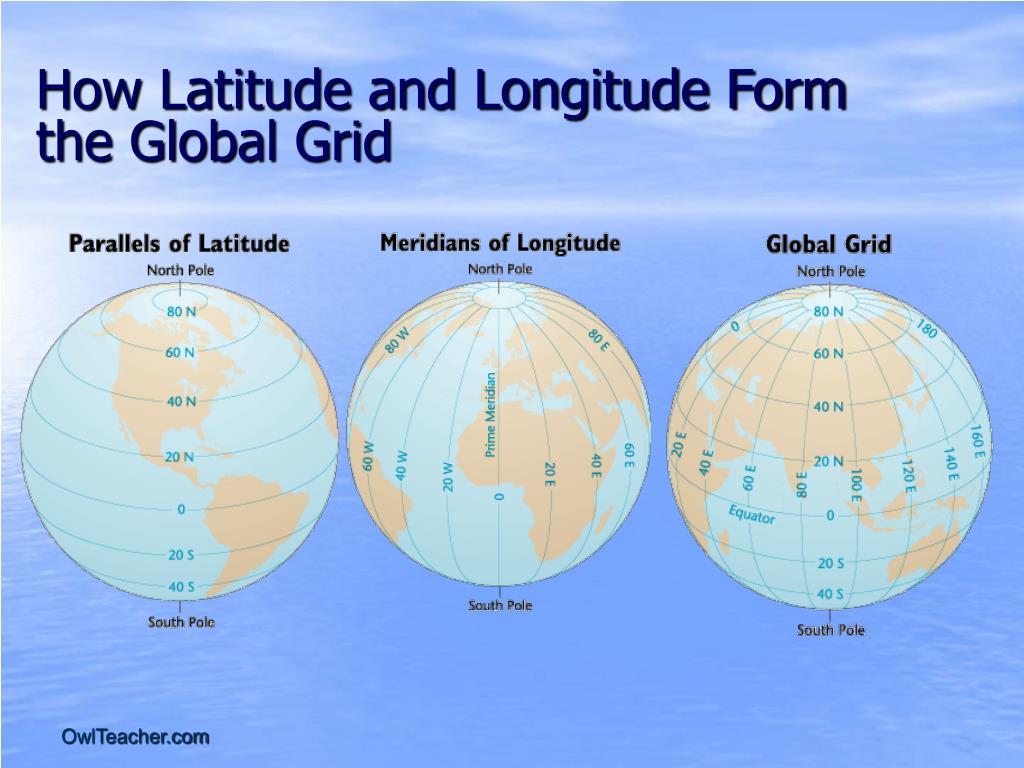
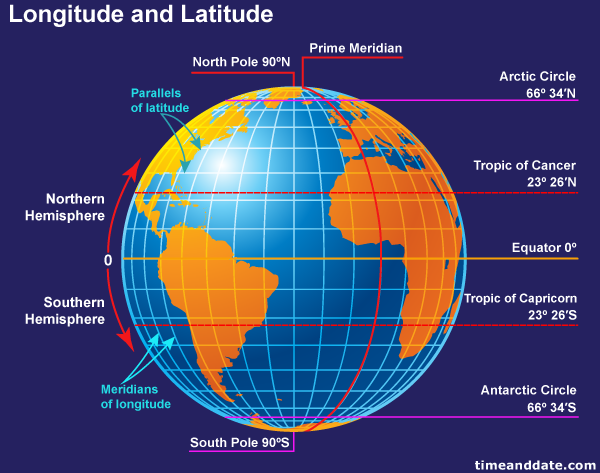
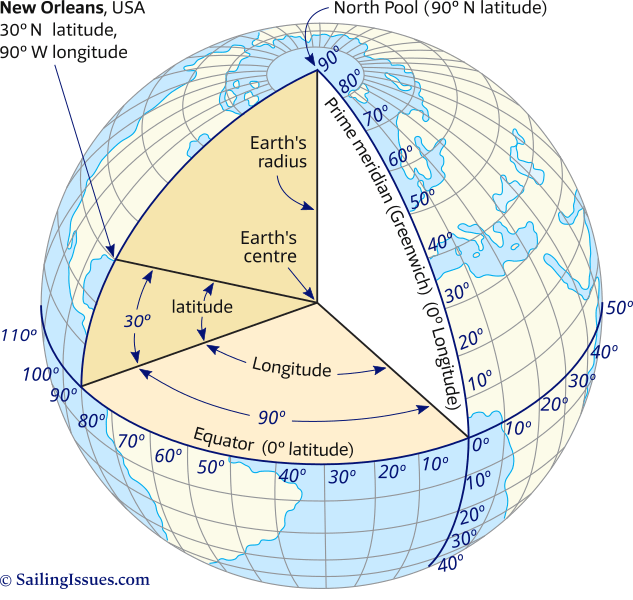
Latitude, often referred to as parallels, are imaginary circles that run horizontally around the Earth, parallel to the equator. They measure the angular distance, in degrees, north or south of the equator, which is assigned a latitude of 0°. The equator divides the Earth into the Northern Hemisphere (positive latitudes) and the Southern Hemisphere (negative latitudes). The North Pole sits at 90° N, and the South Pole at 90° S.
Longitude, also known as meridians, are imaginary lines that run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, intersecting the equator at right angles. They measure the angular distance, in degrees, east or west of the prime meridian, which passes through Greenwich, England, and is assigned a longitude of 0°. The prime meridian divides the Earth into the Eastern Hemisphere (positive longitudes) and the Western Hemisphere (negative longitudes).
The Importance of the Grid: Benefits of Longitude and Latitude
The grid system of longitude and latitude offers numerous advantages, making it a cornerstone of geography and navigation:
-
Precise Location Identification: Longitude and latitude provide a unique coordinate for every point on Earth. This allows for accurate location identification and communication, vital for navigation, mapping, and data analysis.
-
Global Standardization: The grid system is universally accepted, enabling consistent communication and data sharing across different cultures and languages. This standardization facilitates global cooperation in various fields, including scientific research, disaster relief, and international trade.
-
Navigation and Travel: Navigational tools like GPS (Global Positioning System) rely heavily on longitude and latitude coordinates to pinpoint locations and guide travelers. This system enables efficient and safe travel by air, sea, and land.
-
Mapping and Cartography: The grid system is fundamental to map creation. By using longitude and latitude, cartographers can accurately represent the Earth’s surface on maps, facilitating spatial analysis and understanding geographic relationships.
-
Scientific Research: Longitude and latitude are crucial for various scientific disciplines. For instance, meteorologists use the grid system to track weather patterns, oceanographers study ocean currents, and geologists analyze tectonic plate movements.
-
Environmental Monitoring: The grid system is essential for monitoring environmental changes, such as deforestation, pollution levels, and climate patterns. This data is vital for informing policy decisions and promoting sustainable practices.
Beyond the Basics: Delving Deeper into the Grid System
While the basic concept of longitude and latitude is relatively simple, understanding its nuances and applications requires further exploration:
-
Time Zones: Longitude plays a crucial role in defining time zones. As the Earth rotates, different locations experience sunrise and sunset at varying times. The grid system enables the division of the Earth into 24 time zones, each spanning 15 degrees of longitude.
-
Map Projections: Representing the spherical Earth on a flat map requires distortion. Various map projections have been developed to minimize distortion, each with its own strengths and limitations. Understanding the projection used for a particular map is crucial for interpreting its data accurately.
-
Geospatial Data: Longitude and latitude are fundamental to geospatial data, which encompasses information linked to specific locations on Earth. This data is used in diverse applications, including urban planning, disaster management, and resource management.
-
Advanced Navigation Techniques: Modern navigation systems utilize advanced techniques, such as GPS and inertial navigation systems, to determine precise locations and track movements. These systems rely on the underlying principles of longitude and latitude.
Addressing Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How are longitude and latitude measured?
A: Longitude and latitude are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. Each degree is divided into 60 minutes, and each minute into 60 seconds. The equator and the prime meridian are assigned 0° values, and the measurements increase towards the poles.
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude measures angular distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures angular distance east or west of the prime meridian. Latitude lines run horizontally, while longitude lines run vertically.
Q: How do I find the latitude and longitude of a specific location?
A: You can use online mapping services, GPS devices, or specialized software to determine the latitude and longitude of any location.
Q: Why is the prime meridian located at Greenwich, England?
A: The prime meridian was chosen arbitrarily, and Greenwich was selected due to its historical significance as a center of navigation and scientific research.
Q: What are the applications of longitude and latitude in everyday life?
A: Longitude and latitude are used in various everyday applications, including:
- Navigation apps: These apps use GPS to determine your location based on longitude and latitude coordinates.
- Weather forecasts: Weather reports often include longitude and latitude coordinates to identify specific locations.
- Social media: Many social media platforms allow users to tag locations using latitude and longitude coordinates.
- Online shopping: Online retailers use longitude and latitude to determine your location for delivery purposes.
Tips for Using Longitude and Latitude
- Understanding the Grid: Familiarize yourself with the basic principles of longitude and latitude, including their definitions, measurements, and how they are used together.
- Interpreting Map Projections: Be aware of the projection used for a particular map, as it can affect the accuracy of measurements and spatial relationships.
- Using Online Tools: Utilize online mapping services and GPS devices to determine latitude and longitude coordinates and explore geographic data.
- Applying the System: Consider how longitude and latitude can be used in your own work or personal life, from navigating to understanding environmental issues.
Conclusion
The grid system of longitude and latitude is a fundamental tool for understanding and navigating the world. Its ability to pinpoint locations, standardize global communication, and facilitate diverse applications makes it indispensable for numerous fields. By understanding the principles of longitude and latitude, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our planet and the power of spatial information. From exploring new places to conducting scientific research, the grid system continues to play a vital role in shaping our understanding and interaction with the Earth.


/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding the Grid of Longitude and Latitude. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!