Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps

Maps, those invaluable tools of exploration and understanding, rely on a fundamental system of coordinates to pinpoint locations across the globe: latitude and longitude. These two measurements, interwoven like threads on a tapestry, provide a precise framework for identifying any point on Earth’s surface.
Latitude: The Angular Distance from the Equator
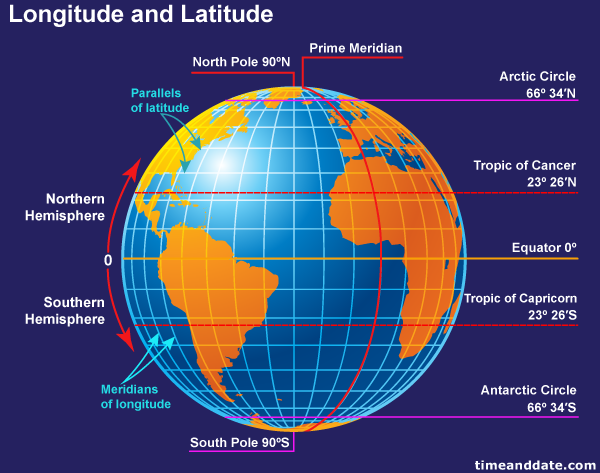
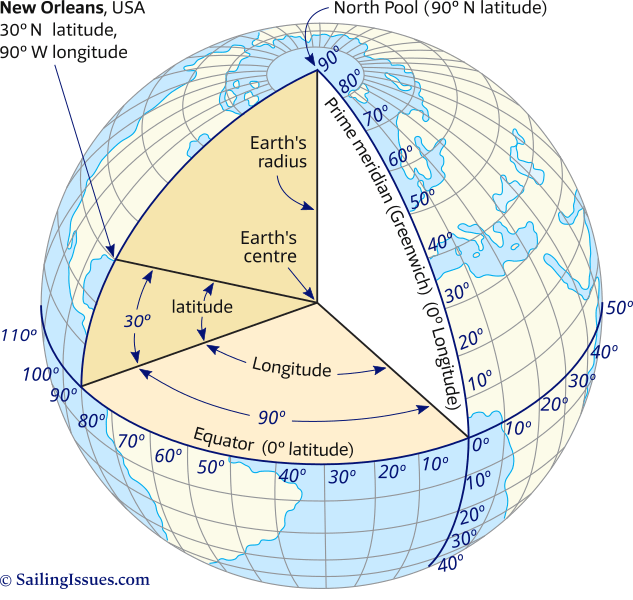
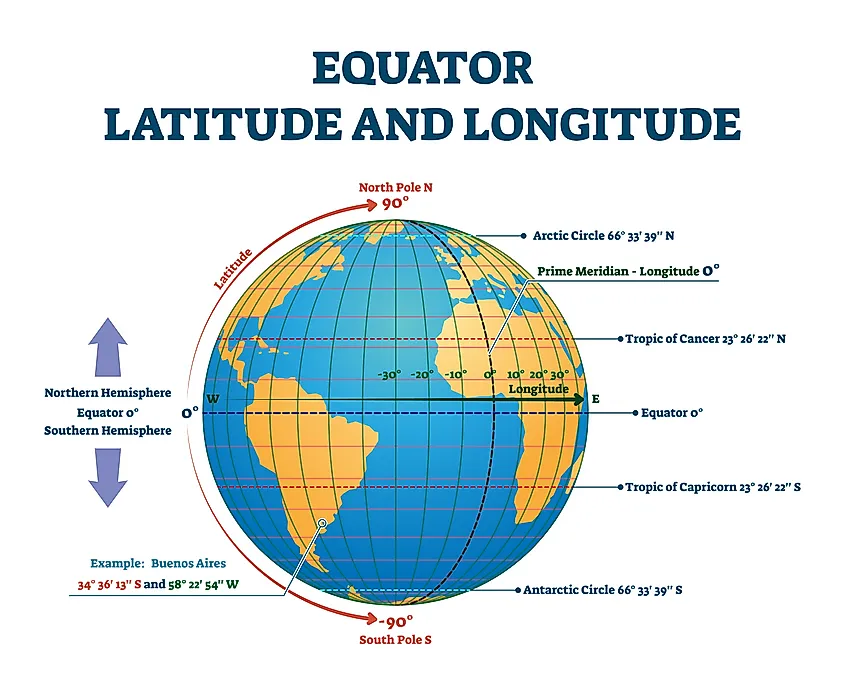
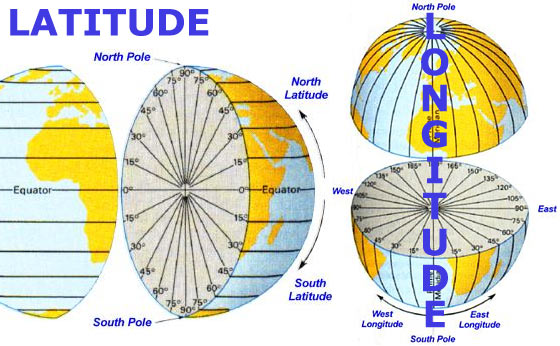
Imagine a series of imaginary circles, parallel to the equator, encircling the Earth. These circles, known as parallels, represent lines of latitude. Latitude measures the angular distance, in degrees, north or south of the equator. The equator itself is designated as 0 degrees latitude, while the North Pole sits at 90 degrees North and the South Pole at 90 degrees South.
Each degree of latitude is further subdivided into 60 minutes (‘), and each minute into 60 seconds ("). This meticulous division allows for incredibly precise location identification. For instance, a location at 40 degrees 30’ 15" North, signifies a point 40 degrees and 30 minutes north of the equator, and 15 seconds north of the 30th minute mark.
Longitude: The Angular Distance from the Prime Meridian
Now, imagine another set of imaginary circles, running from the North Pole to the South Pole, intersecting the equator at right angles. These circles, known as meridians, represent lines of longitude. Longitude measures the angular distance, in degrees, east or west of the prime meridian.
The prime meridian, arbitrarily chosen to pass through Greenwich, England, is designated as 0 degrees longitude. Locations east of the prime meridian are given positive values, while those west are given negative values. The international date line, located roughly 180 degrees from the prime meridian, marks the transition between calendar days.
The Power of Intersection: Finding Your Place
The beauty of latitude and longitude lies in their ability to pinpoint a precise location through their intersection. Each point on Earth has a unique combination of latitude and longitude, like a unique address in a global grid system. This intersection creates a system of coordinates, expressed as "latitude, longitude," which allows for accurate and unambiguous identification of any location.
Benefits of Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Beyond simply pinpointing locations, understanding latitude and longitude unlocks a wealth of insights:
- Navigation: These coordinates are the foundation for navigation systems like GPS, enabling accurate direction finding and route planning.
- Mapping and Geospatial Analysis: Latitude and longitude form the basis for creating maps, analyzing geographic data, and understanding spatial relationships.
- Climate and Weather Patterns: Latitude plays a significant role in determining climate patterns, influencing temperature, precipitation, and seasonal variations.
- Time Zones: Longitude influences time zones, as the Earth rotates on its axis, creating a difference in solar time at different longitudes.
- Understanding Global Phenomena: Latitude and longitude are essential for understanding global phenomena like ocean currents, wind patterns, and plate tectonics.
Reading Latitude and Longitude on a Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify the Grid System: Most maps use a grid system with lines of latitude and longitude. The lines of latitude are horizontal, while the lines of longitude are vertical.
- Locate the Equator and Prime Meridian: The equator is the horizontal line running through the center of the map, marking 0 degrees latitude. The prime meridian is the vertical line running through the center of the map, marking 0 degrees longitude.
- Find the Latitude and Longitude of a Point: To find the latitude of a point, follow a vertical line from the point to the nearest line of latitude. The number on the line of latitude represents the latitude of the point. To find the longitude, follow a horizontal line from the point to the nearest line of longitude. The number on the line of longitude represents the longitude of the point.
- Remember the Directions: Latitude is measured north or south of the equator, while longitude is measured east or west of the prime meridian.
FAQs about Latitude and Longitude
Q: Why is the prime meridian located at Greenwich, England?
A: The location of the prime meridian at Greenwich is a historical convention, adopted in the late 19th century. Before then, different countries used their own prime meridians. The choice of Greenwich was primarily due to the prominence of the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, which had already established a system of timekeeping and astronomical observations.
Q: How does latitude influence climate?
A: Latitude affects climate primarily due to the angle at which sunlight strikes the Earth’s surface. Regions closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight, leading to warmer temperatures. As latitude increases, the angle of the sun becomes more oblique, resulting in less direct sunlight and cooler temperatures.
Q: Can latitude and longitude be used to pinpoint locations in space?
A: While latitude and longitude are specific to Earth’s surface, similar coordinate systems are used to pinpoint locations in space. These systems, however, employ different reference points and measurements.
Tips for Reading Latitude and Longitude on a Map
- Use a ruler or protractor: This can help you accurately measure the distance between a point and the nearest line of latitude or longitude.
- Pay attention to the scale: The scale of the map indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground. This is essential for accurately interpreting the coordinates.
- Practice: The more you practice reading latitude and longitude on a map, the more familiar you will become with the system and the easier it will be to locate points with precision.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude, seemingly abstract concepts, are the foundation of our understanding of the Earth’s surface. They provide a framework for navigation, mapping, and understanding global phenomena. By mastering the art of reading these coordinates, we unlock a deeper appreciation for our planet’s intricate geography and the interconnectedness of all its parts. Whether you’re navigating a vast ocean or exploring the intricacies of a local map, understanding latitude and longitude is key to unlocking the secrets of our world.
/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!