Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines
- 3.1 Latitude: Lines of Parallel
- 3.2 Longitude: Lines of Meridian
- 3.3 The Power of Latitude and Longitude: A Global Language
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions about Latitude and Longitude
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding and Using Latitude and Longitude
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines

The Earth, our home planet, is a vast and complex sphere. To comprehend its vastness and navigate its diverse landscapes, we rely on a system of imaginary lines known as latitude and longitude. These lines, etched onto maps and globes, serve as a universal language, allowing us to pinpoint locations with remarkable accuracy, enabling communication, exploration, and understanding of our world.
Latitude: Lines of Parallel
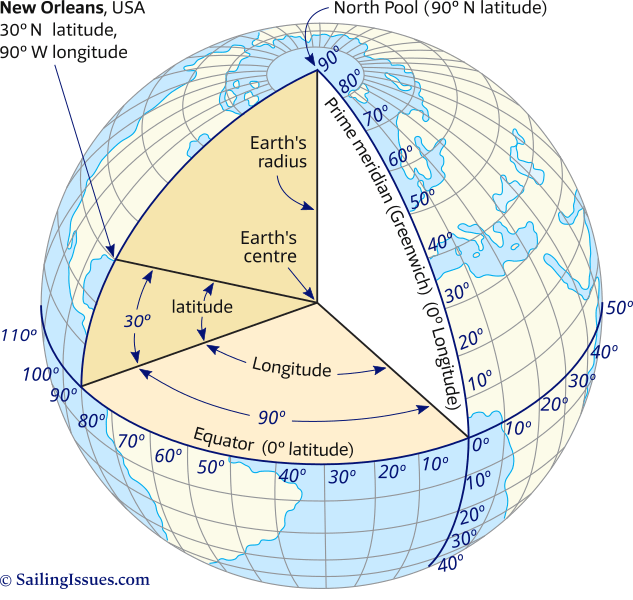
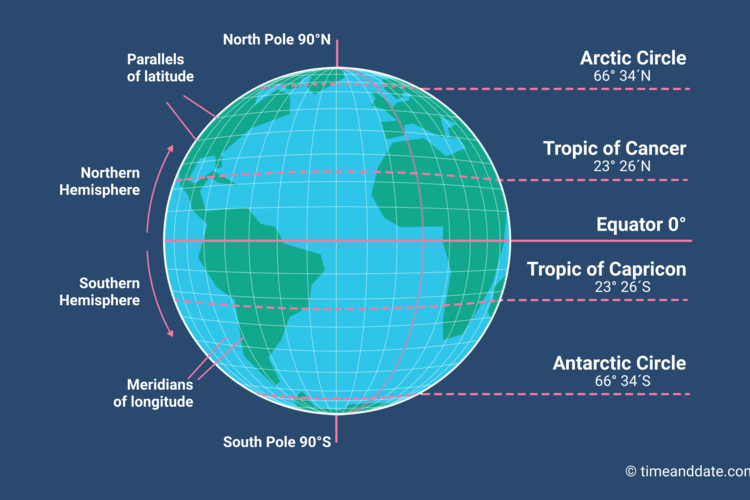
Imagine slicing the Earth like a giant orange, each slice representing a parallel circle running around the globe. These circles, known as lines of latitude, are measured in degrees, with the equator, the largest circle, serving as the zero-degree line. Each degree of latitude is further divided into 60 minutes, and each minute into 60 seconds, offering a granular level of precision.
As we move away from the equator, these circles become smaller, eventually converging at the North and South Poles, where latitude reaches its maximum value of 90 degrees. The lines of latitude are parallel to the equator and, therefore, are known as parallels.
Latitude plays a crucial role in determining climate. Regions closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight, leading to warmer temperatures, while areas near the poles experience colder climates due to their oblique angle of sunlight. Latitude also influences the duration of daylight hours, with locations near the equator experiencing consistent daylight hours throughout the year, while those closer to the poles experience significant variations in daylight duration.
Longitude: Lines of Meridian
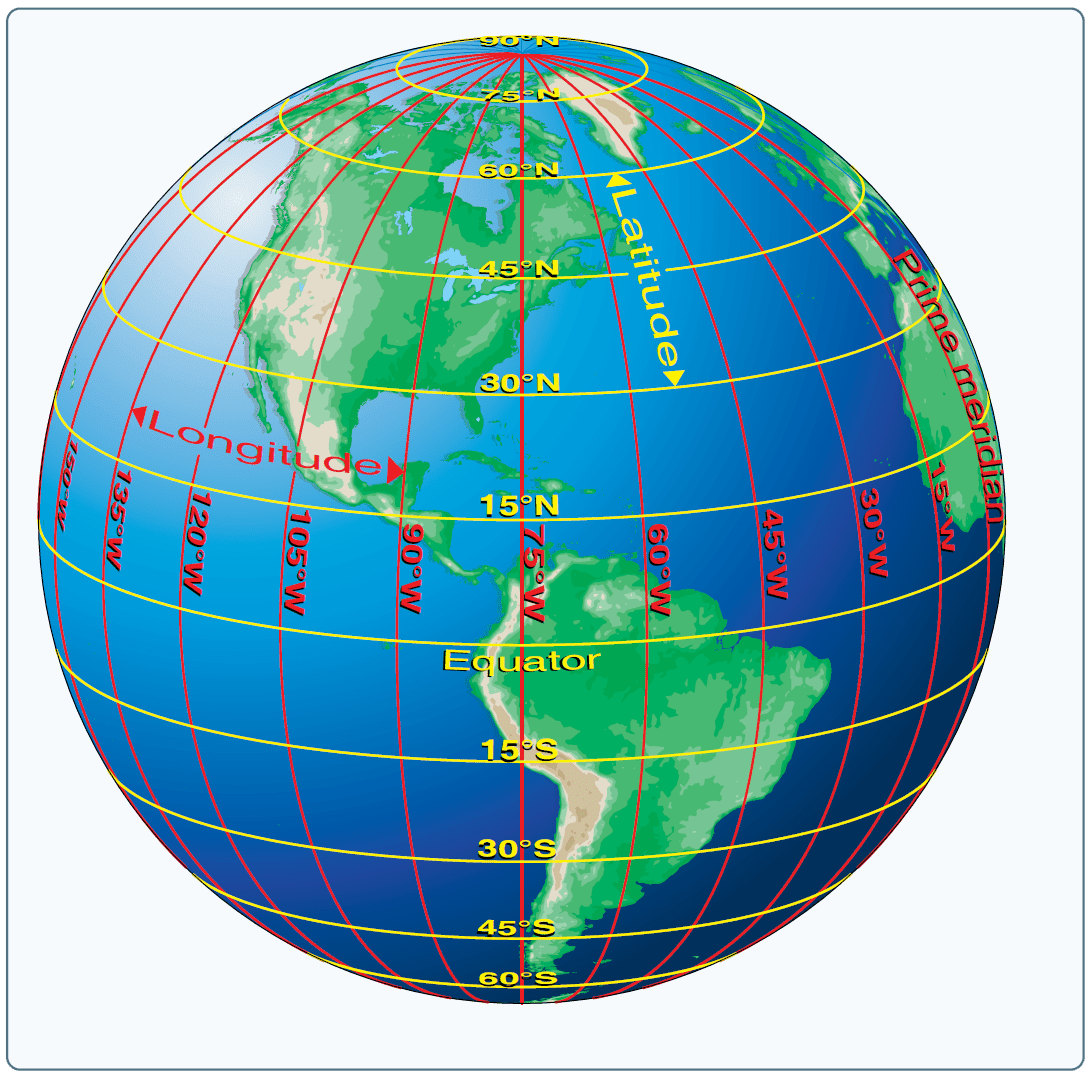
While latitude helps us understand the north-south position on the Earth, longitude provides the east-west dimension. Imagine drawing lines from the North Pole to the South Pole, each line representing a meridian. These lines converge at the poles and are perpendicular to the equator.
The prime meridian, passing through Greenwich, England, is designated as the zero-degree line of longitude. All other meridians are measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian, ranging from 0 to 180 degrees. Like latitude, longitude is also divided into minutes and seconds, offering fine-grained precision.
Longitude is essential for calculating time zones. The Earth rotates on its axis, completing a full rotation in 24 hours. This rotation, combined with the 360-degree system of longitude, allows us to divide the globe into 24 time zones, each spanning 15 degrees of longitude. As we move eastward, time advances, while moving westward results in time lagging behind.
The Power of Latitude and Longitude: A Global Language
The combination of latitude and longitude creates a grid system that uniquely identifies every point on Earth. This grid system, known as the geographic coordinate system, allows us to precisely pinpoint locations, communicate them effectively, and navigate with accuracy.
Here are some key benefits of using latitude and longitude:
- Precise Location Identification: Latitude and longitude provide a standardized and universally recognized way to identify any location on Earth.
- Navigation and Exploration: These coordinates are essential for navigation, whether it be for ships at sea, aircraft in the sky, or individuals exploring remote areas.
- Mapping and Cartography: Latitude and longitude form the basis for map creation, enabling accurate representation of the Earth’s surface.
- Data Analysis and Research: Latitude and longitude are used extensively in various scientific disciplines, including geography, meteorology, and environmental studies.
- Global Communication and Collaboration: This system facilitates communication and collaboration among individuals and organizations across the globe, enabling shared understanding of locations and events.
Frequently Asked Questions about Latitude and Longitude
1. What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
Latitude measures the north-south position on Earth, while longitude measures the east-west position. Latitude lines are parallel to the equator, while longitude lines converge at the poles.
2. How are latitude and longitude measured?
Both latitude and longitude are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. The equator is 0 degrees latitude, while the prime meridian is 0 degrees longitude.
3. Why is the prime meridian located in Greenwich, England?
The prime meridian was initially established in Greenwich, England, due to its historical significance as a major maritime power and the prominence of its observatory.
4. How do latitude and longitude relate to time zones?
The Earth rotates on its axis, completing a full rotation in 24 hours. This rotation, combined with the 360-degree system of longitude, allows us to divide the globe into 24 time zones, each spanning 15 degrees of longitude.
5. Can latitude and longitude be used to determine altitude?
Latitude and longitude only indicate horizontal position. Altitude, or elevation, is measured separately, typically in meters or feet.
6. What are some real-world applications of latitude and longitude?
Latitude and longitude are used in navigation, mapping, weather forecasting, data analysis, and many other fields, enabling precise location identification, communication, and understanding of our world.
Tips for Understanding and Using Latitude and Longitude
- Visualize the Earth as a sphere: This will help you understand how latitude and longitude lines wrap around the globe.
- Use a globe or map: These tools provide a visual representation of the Earth and its grid system.
- Practice identifying locations using coordinates: Use online mapping tools or atlases to practice finding locations based on their latitude and longitude.
- Learn about the history of latitude and longitude: Understanding how these systems developed can enhance your appreciation for their significance.
- Explore the different applications of latitude and longitude: Research how these coordinates are used in various fields, from navigation to scientific research.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude are fundamental tools for understanding and navigating our world. They provide a universal language for location identification, enabling communication, exploration, and research across the globe. By understanding these lines and their applications, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our planet and the power of human ingenuity in mapping and understanding our vast world.
/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)



![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!