Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines on Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines on Maps

Maps, the visual representations of our world, have been instrumental in human exploration, navigation, and understanding of our planet. Central to their functionality are latitude and longitude lines, an intricate grid system that allows for precise location identification. This article delves into the nature of these lines, their historical significance, and their enduring importance in modern navigation and geographical analysis.
The Foundation of Geographical Precision: Latitude and Longitude
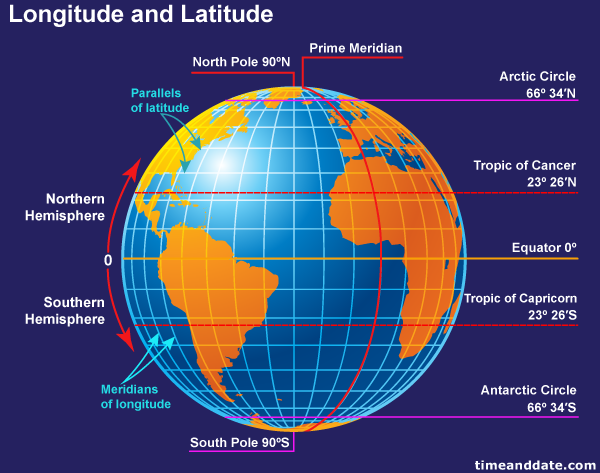
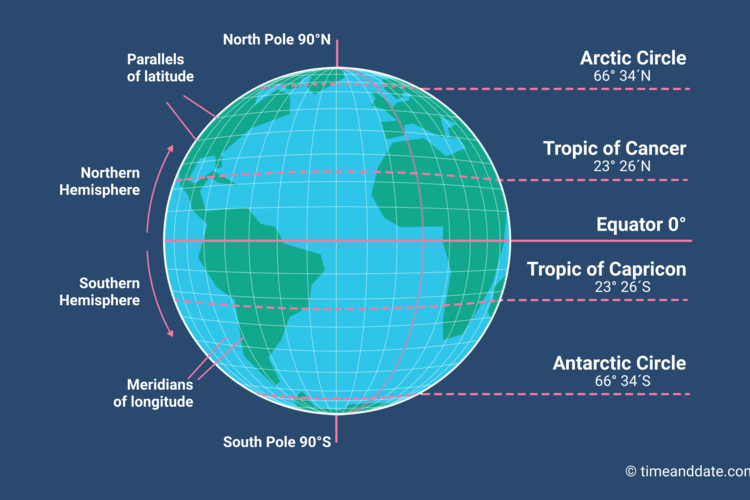
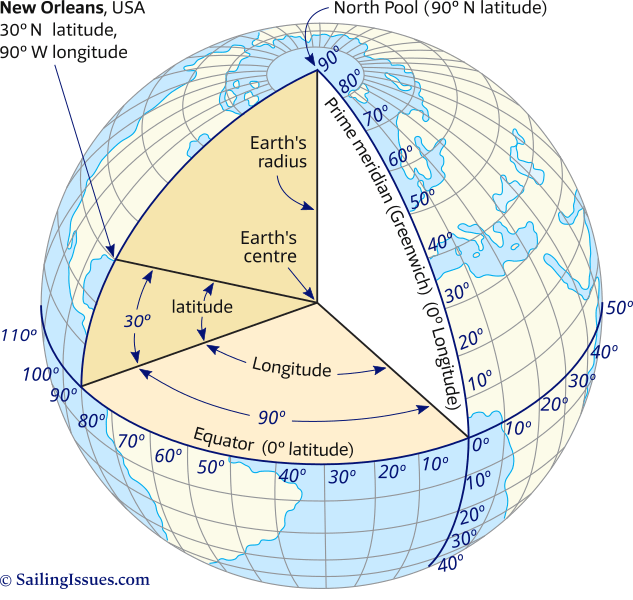
Latitude and longitude lines form a spherical coordinate system that overlays the Earth, dividing it into a network of intersecting lines. Imagine a vast, invisible grid encompassing the globe, providing a framework for pinpointing any location with remarkable accuracy.
Latitude: Measuring North and South
Latitude lines, also known as parallels, run horizontally around the Earth, parallel to the equator. The equator, positioned at 0 degrees latitude, is an imaginary circle that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Latitude is measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds, ranging from 0 degrees at the equator to 90 degrees at the North and South Poles. Each degree of latitude is approximately 69 miles (111 kilometers) apart.
Longitude: Measuring East and West
Longitude lines, also known as meridians, run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, intersecting the equator at right angles. The prime meridian, situated at 0 degrees longitude, passes through Greenwich, England, and serves as the reference point for measuring longitude. Longitude is also measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds, ranging from 0 degrees at the prime meridian to 180 degrees east or west. The distance between each degree of longitude varies depending on the latitude, converging at the poles.
Historical Significance: From Ancient Observations to Modern Navigation
The concept of latitude and longitude has roots in ancient civilizations. Early astronomers recognized the Earth’s spherical shape and observed the celestial bodies, leading to the development of rudimentary methods for determining latitude. The ancient Greeks, for instance, used the angle of the sun at noon to estimate their latitude.
The development of the compass and the invention of the sextant in the 16th century revolutionized navigation. These instruments allowed mariners to determine their latitude and longitude with greater accuracy, leading to significant advancements in exploration and trade. The ability to navigate precisely across vast oceans paved the way for European expansion and the discovery of new lands.
Modern Applications: Beyond Traditional Navigation
Today, latitude and longitude lines remain indispensable in various fields beyond traditional navigation. Their application extends to:
- Global Positioning System (GPS): GPS satellites constantly transmit signals containing latitude and longitude coordinates, enabling precise location determination for navigation, mapping, and tracking.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software utilizes latitude and longitude coordinates to analyze and visualize spatial data, enabling the study of environmental patterns, urban planning, and resource management.
- Cartography: Mapmakers rely on latitude and longitude lines to create accurate and detailed maps, incorporating topographic features, political boundaries, and other geographical information.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use latitude and longitude lines to pinpoint celestial objects in the sky, facilitating observation and research.
- Meteorology: Weather forecasting models utilize latitude and longitude coordinates to analyze atmospheric conditions and predict weather patterns.
FAQs
Q: Why is the equator at 0 degrees latitude?
A: The equator is at 0 degrees latitude because it serves as the reference point for measuring latitude north and south. It is the largest circle of latitude on the Earth, dividing the planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
Q: Why is the prime meridian at 0 degrees longitude?
A: The prime meridian is at 0 degrees longitude because it serves as the reference point for measuring longitude east and west. Its location at Greenwich, England, was established by international agreement in the 19th century.
Q: How are latitude and longitude coordinates expressed?
A: Latitude and longitude coordinates are typically expressed as decimal degrees, with latitude written first followed by longitude. For example, the coordinates of the Empire State Building in New York City are approximately 40.7484° N, 73.9857° W.
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude measures the distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the distance east or west of the prime meridian.
Tips
- Utilize online mapping tools: Websites and mobile applications provide interactive maps that allow users to explore the world, search for locations, and obtain latitude and longitude coordinates.
- Familiarize yourself with map projections: Different map projections distort the Earth’s surface to varying degrees, affecting the accuracy of distance and area measurements. Understanding the limitations of a particular projection is crucial for accurate interpretation.
- Consider the purpose of the map: The choice of map projection and scale depends on the intended use. For example, a map designed for navigation might emphasize accuracy in distance and direction, while a map for thematic analysis might prioritize visual representation of specific data.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude lines, a fundamental framework for geographical precision, have played a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the world. From ancient celestial observations to modern technological advancements, these lines continue to be essential tools for navigation, mapping, and scientific exploration. By understanding the nature and significance of latitude and longitude, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate complexities of our planet and the remarkable ingenuity of human endeavor.

![]()



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude Lines on Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!