Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude

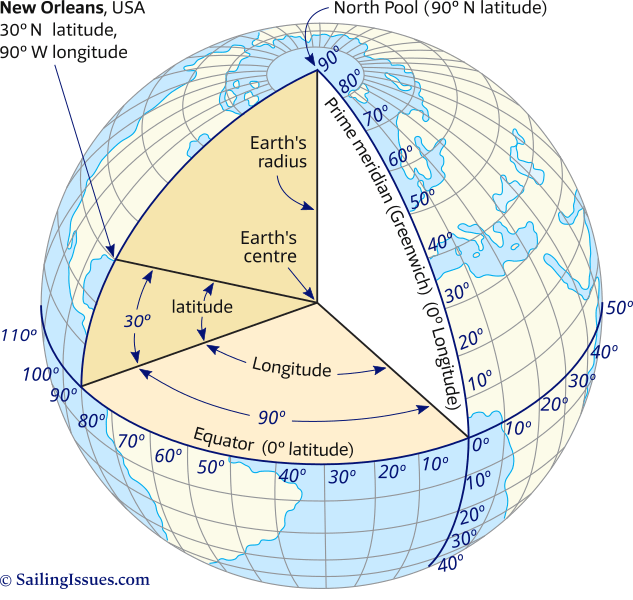
The Earth, a vast and complex sphere, presents a challenge when it comes to pinpointing specific locations. To overcome this, a system of imaginary lines was devised, forming a grid that allows us to identify any point on the planet with remarkable accuracy. This grid, known as the geographic coordinate system, is composed of latitude and longitude, two fundamental concepts that are essential for navigation, mapping, and understanding the Earth’s geography.
Latitude: Measuring North and South
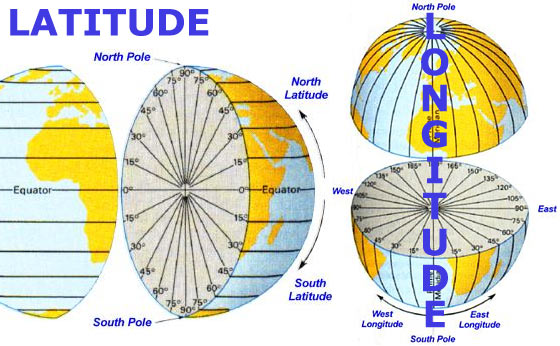
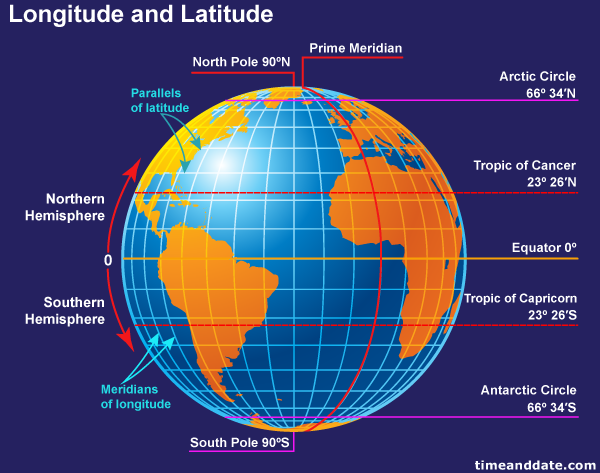
Latitude lines, also known as parallels, are imaginary circles that run parallel to the equator, which is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, dividing the planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Each latitude line represents a specific distance north or south of the equator, measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
- Equator: The equator is the largest latitude line, with a circumference of approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles). It marks the zero-degree latitude.
- Northern Hemisphere: Latitude lines north of the equator are assigned positive values, ranging from 0 degrees at the equator to 90 degrees at the North Pole.
- Southern Hemisphere: Latitude lines south of the equator are assigned negative values, ranging from 0 degrees at the equator to -90 degrees at the South Pole.
Imagine slicing the Earth like an orange. Each slice represents a specific latitude, with the equator being the largest slice and the poles being the smallest. The distance between two consecutive latitude lines is approximately 111 kilometers (69 miles), although this distance varies slightly due to the Earth’s oblate spheroid shape.
Longitude: Measuring East and West
Longitude lines, also known as meridians, are imaginary lines that run from the North Pole to the South Pole, intersecting at the poles and forming semi-circles. Each longitude line represents a specific distance east or west of the prime meridian, which is an imaginary line that passes through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England, and is designated as 0 degrees longitude.
- Prime Meridian: The prime meridian divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
- Eastern Hemisphere: Longitude lines east of the prime meridian are assigned positive values, ranging from 0 degrees at the prime meridian to 180 degrees at the International Date Line.
- Western Hemisphere: Longitude lines west of the prime meridian are assigned negative values, ranging from 0 degrees at the prime meridian to -180 degrees at the International Date Line.
The International Date Line, located at approximately 180 degrees longitude, is an imaginary line where the date changes. When traveling eastward across the line, the date is advanced by one day; when traveling westward, the date is reversed.
Coordinates: Pinpointing Locations
The combination of latitude and longitude forms a unique coordinate pair that identifies a specific point on Earth’s surface. These coordinates are expressed in degrees, minutes, and seconds, with latitude listed first, followed by longitude, separated by a comma. For example, the coordinates of the Eiffel Tower in Paris, France, are 48°51’29.9" N, 2°17’40.2" E.
- Degrees: The primary unit of measurement for latitude and longitude.
- Minutes: Subdivisions of a degree, with 60 minutes in each degree.
- Seconds: Subdivisions of a minute, with 60 seconds in each minute.
The use of degrees, minutes, and seconds provides a highly precise way of representing locations on Earth. However, for ease of use, decimal degrees are often employed, where the minutes and seconds are converted to decimal fractions of a degree.
Importance and Benefits of Latitude and Longitude
The geographic coordinate system, with its reliance on latitude and longitude, plays a crucial role in various aspects of modern life:
- Navigation: Latitude and longitude are essential for accurate navigation by sea, air, and land. GPS systems, used in cars, smartphones, and other devices, rely on this coordinate system to determine location and provide directions.
- Mapping: Maps, whether digital or paper-based, utilize latitude and longitude to represent locations accurately. This allows for the creation of detailed maps that depict geographical features, cities, roads, and other points of interest.
- Scientific Research: Latitude and longitude are fundamental in scientific research, particularly in fields like geography, geology, and meteorology. They enable researchers to study and analyze spatial patterns, track environmental changes, and understand the distribution of natural phenomena.
- Communication: Latitude and longitude are used in communication systems, such as radio and satellite communication, to identify and locate transmitting and receiving stations.
- Emergency Response: In emergency situations, like search and rescue operations, latitude and longitude are crucial for providing accurate location information to responders.
FAQs about Latitude and Longitude
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude measures the distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the distance east or west of the prime meridian.
Q: Why are the North and South Poles located at 90 degrees latitude?
A: The poles are located at 90 degrees latitude because they are the furthest points from the equator, representing the extremities of the Earth’s north-south axis.
Q: What is the difference between the International Date Line and the prime meridian?
A: The prime meridian is the zero-degree longitude line, dividing the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. The International Date Line, located at approximately 180 degrees longitude, marks the point where the date changes.
Q: Can latitude and longitude be used to pinpoint any location on Earth?
A: Yes, latitude and longitude can be used to pinpoint any location on Earth’s surface with remarkable accuracy.
Q: How are latitude and longitude measured?
A: Latitude and longitude are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. Degrees are the primary unit of measurement, with 60 minutes in each degree and 60 seconds in each minute.
Q: What are some examples of how latitude and longitude are used in everyday life?
A: Latitude and longitude are used in GPS navigation, mapping, weather forecasting, and communication systems.
Tips for Understanding Latitude and Longitude
- Visualize the Earth as a sphere: This will help you understand how latitude and longitude lines wrap around the planet.
- Use a globe or online map: These tools can provide a visual representation of the geographic coordinate system.
- Practice identifying locations using coordinates: This will help you become familiar with the system and its application.
- Explore the relationship between latitude and climate: Latitude plays a significant role in determining climate patterns.
- Learn about the history of navigation and the development of the geographic coordinate system: This will provide context and appreciation for the importance of latitude and longitude.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude are essential concepts that form the foundation of the geographic coordinate system, providing a powerful tool for pinpointing locations on Earth. This system is integral to navigation, mapping, scientific research, communication, and many other aspects of modern life. By understanding the principles of latitude and longitude, we gain a deeper understanding of our planet and its complexities, enabling us to navigate, explore, and engage with the world in a more informed and meaningful way.

/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!