Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude

The Earth, our home planet, is a vast and complex sphere. Navigating its surface, whether for exploration, trade, or simply understanding our place in the world, requires a system to pinpoint specific locations. This is where the concept of latitude and longitude comes into play, a fundamental tool in cartography and navigation that has been instrumental in shaping our understanding of the globe.
Latitude: Lines of Parallel
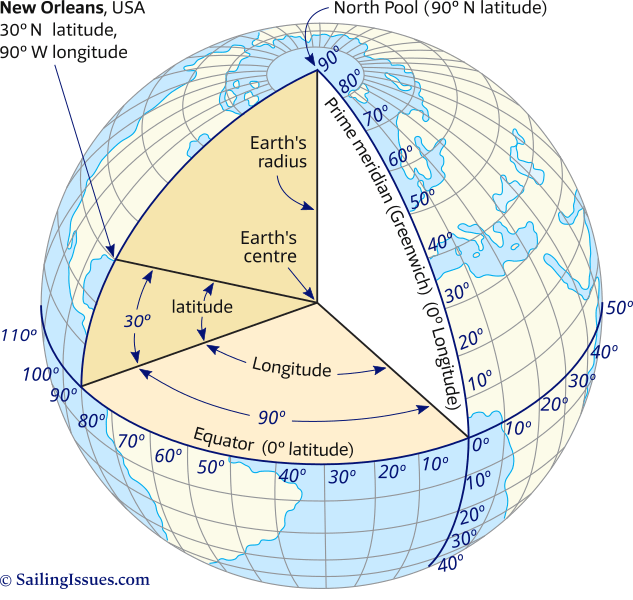
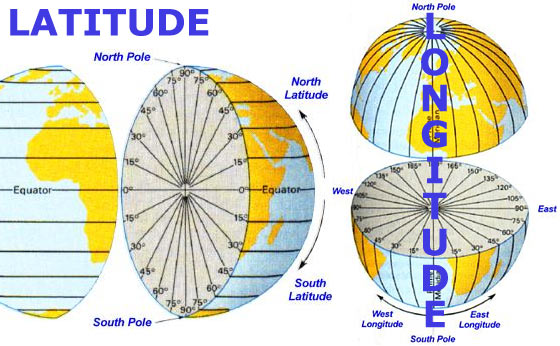
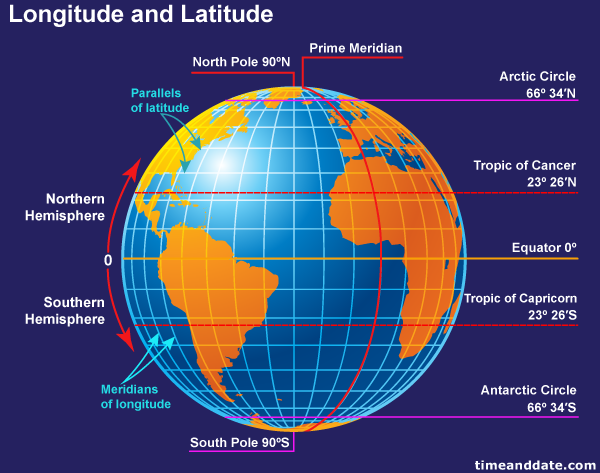
Latitude, often referred to as "parallels," are imaginary lines that circle the Earth parallel to the equator. The equator, the imaginary line that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, serves as the starting point for measuring latitude. Each degree of latitude represents approximately 111 kilometers (69 miles) of distance.
- Equator: The equator is designated as 0° latitude.
- North Pole: The North Pole is located at 90° North latitude.
- South Pole: The South Pole is located at 90° South latitude.
Locations north of the equator are assigned positive latitude values, while locations south of the equator are assigned negative latitude values.
Longitude: Lines of Meridian
Longitude, often called "meridians," are imaginary lines that run from the North Pole to the South Pole, perpendicular to the equator. They are used to measure the distance east or west of the prime meridian. The prime meridian, which runs through Greenwich, England, is designated as 0° longitude.
- Prime Meridian: The prime meridian is designated as 0° longitude.
- International Date Line: The International Date Line, located roughly 180° longitude from the prime meridian, marks the boundary between calendar days.
Locations east of the prime meridian are assigned positive longitude values, while locations west of the prime meridian are assigned negative longitude values.
The Power of Intersection: Pinpointing Locations
The beauty of latitude and longitude lies in their ability to intersect and define a unique point on the Earth’s surface. By combining a specific latitude value with a specific longitude value, we can pinpoint any location on the globe.
Examples:
- New York City: 40.7128° N, 74.0060° W
- Sydney, Australia: -33.8688° S, 151.2093° E
- Tokyo, Japan: 35.6895° N, 139.6917° E
Applications of Latitude and Longitude
The concept of latitude and longitude has far-reaching applications, impacting various aspects of our lives:
- Navigation: Latitude and longitude are fundamental to navigation, enabling ships, aircraft, and even satellites to determine their precise location and plot their course.
- Mapping and Cartography: Latitude and longitude form the basis of map projections, allowing us to represent the Earth’s curved surface on a flat map.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS utilizes latitude and longitude to store, analyze, and visualize spatial data, providing insights into various geographic phenomena.
- Global Positioning System (GPS): GPS satellites constantly transmit signals that contain latitude and longitude information, allowing GPS receivers to determine their location.
- Weather Forecasting: Latitude and longitude are crucial for tracking weather patterns and forecasting weather conditions.
- Astronomy: Latitude and longitude are essential for understanding the position of celestial objects in the sky.
Importance and Benefits of Latitude and Longitude
The significance of latitude and longitude lies in their ability to provide a universal system for:
- Standardization: Latitude and longitude offer a standardized method for describing locations, eliminating ambiguity and facilitating communication.
- Precision: The system enables precise location identification, allowing for accurate measurements and analysis.
- Global Coverage: Latitude and longitude apply to all locations on Earth, facilitating global communication and understanding.
- Interoperability: The system allows for seamless integration with various technologies, including navigation systems, maps, and GIS platforms.
FAQs on Latitude and Longitude
1. What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
Latitude measures the distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the distance east or west of the prime meridian.
2. How are latitude and longitude measured?
Latitude and longitude are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. A full circle is divided into 360 degrees. Each degree is further divided into 60 minutes, and each minute is divided into 60 seconds.
3. How do I use latitude and longitude to find a location?
By combining a specific latitude value with a specific longitude value, you can identify a unique point on the Earth’s surface. This information can be used in navigation systems, maps, and GIS platforms to locate a specific place.
4. What is the importance of the equator and the prime meridian?
The equator is the starting point for measuring latitude, while the prime meridian is the starting point for measuring longitude. These lines serve as reference points for the global coordinate system.
5. Can latitude and longitude change over time?
While latitude remains relatively constant, longitude can change slightly due to the Earth’s tectonic plate movements. However, these changes are minimal and typically not significant for everyday purposes.
Tips for Understanding Latitude and Longitude
- Visualize the Earth as a sphere: Imagine the equator as a belt around the Earth and the prime meridian as a line running from the North Pole to the South Pole.
- Use a globe or an online map: These tools can help you visualize the relationship between latitude and longitude and how they intersect to define locations.
- Practice converting degrees, minutes, and seconds: Familiarize yourself with the units of measurement used for latitude and longitude.
- Explore online resources: There are numerous websites and applications that provide interactive maps and tools for understanding and using latitude and longitude.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude, an ingenious system of coordinates, have revolutionized our understanding of the Earth’s surface. They provide a standardized, precise, and universal method for locating any point on the globe, facilitating navigation, mapping, and countless other applications. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of latitude and longitude will only grow, further enhancing our ability to explore, understand, and interact with our planet.

/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!