Navigating the World: The Power of Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating the World: The Power of Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: The Power of Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: The Power of Latitude and Longitude

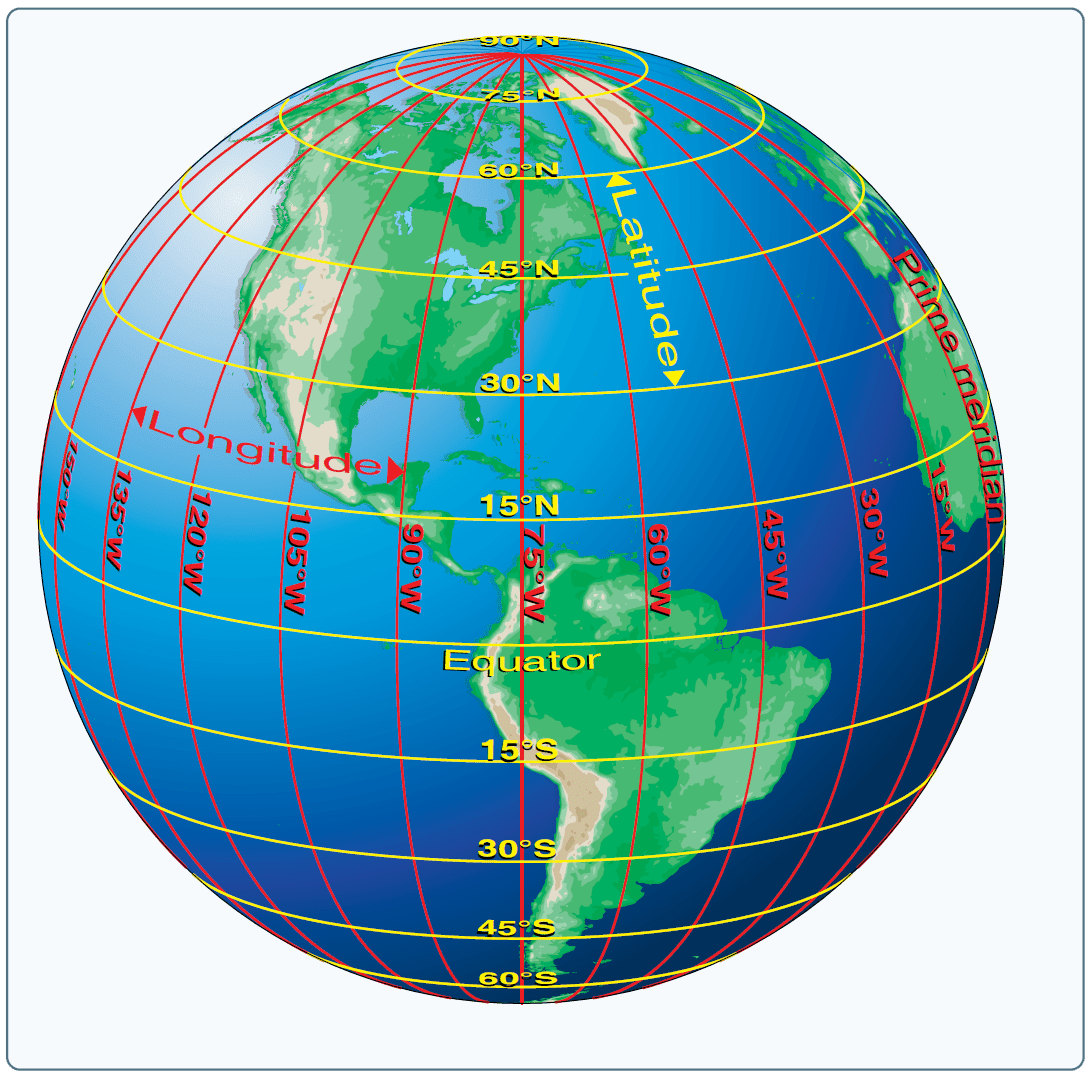
The Earth, a vast and complex sphere, holds within it countless locations, each with its own unique story. To navigate this intricate tapestry of places, we rely on a powerful tool: a system of coordinates known as latitude and longitude. This seemingly simple system, based on a grid of imaginary lines, provides a precise and universal method for pinpointing any point on the globe, unlocking a wealth of information and opportunities.
A Framework of Lines: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Imagine the Earth sliced into two halves by a plane passing through the equator, the imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude. This plane divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Latitude, measured in degrees north or south of the equator, defines a location’s position relative to this central line. For instance, the North Pole sits at 90 degrees north, while the South Pole sits at 90 degrees south.
Now, visualize another set of imaginary lines, this time running vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, intersecting the equator at various points. These lines, known as lines of longitude, are measured in degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian, an arbitrary line that passes through Greenwich, England. The Prime Meridian serves as the zero-degree longitude reference point.
Together, latitude and longitude create a grid system that covers the entire Earth. Every point on the globe can be identified by its unique combination of latitude and longitude coordinates. This system, known as the geographic coordinate system, forms the foundation for global navigation and mapping.
Beyond the Grid: The Significance of Latitude and Longitude
The significance of latitude and longitude extends far beyond simply pinpointing locations. It forms the bedrock for a multitude of applications, impacting our lives in ways we may not even realize.
1. Navigation and Travel:
-
Seafaring and Aviation: Latitude and longitude have been instrumental in maritime navigation for centuries. Sailors use these coordinates to plot courses, navigate treacherous waters, and ensure safe passage. In aviation, pilots rely on these coordinates for flight planning, air traffic control, and precise landing maneuvers.
-
GPS Systems: The Global Positioning System (GPS) relies on a network of satellites that transmit signals containing precise latitude and longitude data. By receiving these signals, GPS devices can determine a user’s location with remarkable accuracy, enabling navigation, mapping, and location-based services.
2. Mapping and Geographic Information Systems (GIS):
-
Creating Maps: Latitude and longitude are the foundation for creating maps of all scales, from small-scale neighborhood maps to global atlases. These coordinates allow for accurate representation of locations and their relative positions, providing crucial information for understanding the world around us.
-
GIS Analysis: GIS systems use latitude and longitude to analyze spatial data, enabling us to identify patterns, relationships, and trends across different geographic areas. This allows for informed decision-making in various fields, including urban planning, environmental management, and resource allocation.
3. Data Management and Analysis:
-
Location-Based Data: Latitude and longitude are essential for tagging and analyzing location-based data. This information can be used to track movement, monitor environmental conditions, analyze population distribution, and understand the spatial patterns of various phenomena.
-
Geospatial Databases: Latitude and longitude are used to store and manage geospatial data in databases, enabling efficient retrieval, analysis, and visualization of location-specific information.
4. Scientific Research and Environmental Monitoring:
-
Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists use latitude and longitude to track weather patterns, predict storms, and issue alerts. These coordinates are crucial for understanding the movement and intensity of weather systems, ensuring public safety and informed decision-making.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Latitude and longitude are used to track environmental changes, monitor pollution levels, and study the impact of climate change. This data is vital for understanding and mitigating environmental threats, ensuring the health of our planet.
5. Social and Economic Development:
-
Urban Planning: Latitude and longitude are used to plan urban development, manage infrastructure, and allocate resources effectively. By understanding the spatial distribution of populations, amenities, and resources, planners can create more efficient and sustainable cities.
-
Economic Development: Latitude and longitude are used to analyze economic activity, identify investment opportunities, and track the growth of businesses. This data can inform policies and strategies for promoting economic development and improving quality of life.
FAQs on Latitude and Longitude
1. How are latitude and longitude measured?
Latitude and longitude are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. Degrees are the primary unit of measurement, with 360 degrees forming a complete circle. Each degree is further divided into 60 minutes, and each minute into 60 seconds.
2. What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
Latitude measures a location’s distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures a location’s distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
3. Why is the Prime Meridian at Greenwich, England?
The Prime Meridian was chosen arbitrarily at Greenwich, England, in the 19th century. This choice was largely due to the prominence of the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, which served as a leading center for astronomical research.
4. Can latitude and longitude be negative?
Yes, latitude can be negative, indicating locations south of the equator. Similarly, longitude can be negative, indicating locations west of the Prime Meridian.
5. How accurate are latitude and longitude measurements?
The accuracy of latitude and longitude measurements depends on the technology used. GPS systems can provide accuracy down to a few meters, while older methods, such as celestial navigation, may have lower accuracy.
6. What are the benefits of using latitude and longitude?
Latitude and longitude provide a universal and precise system for pinpointing locations, enabling navigation, mapping, data analysis, scientific research, and many other applications.
7. Are there any limitations to using latitude and longitude?
While latitude and longitude are incredibly powerful tools, they have some limitations. For instance, they do not account for the Earth’s curvature, which can lead to inaccuracies in long distances. Additionally, they do not provide information about elevation, which is crucial for some applications.
Tips for Working with Latitude and Longitude
1. Understand the Units of Measurement: Always ensure you are working with the correct units of measurement, whether degrees, minutes, or seconds.
2. Use Appropriate Tools: Utilize specialized software and tools designed for working with latitude and longitude, such as GIS software or online mapping platforms.
3. Consider Data Accuracy: Be aware of the accuracy of your data source and the potential for errors in latitude and longitude measurements.
4. Visualize the Data: Use maps and other visualization tools to gain a better understanding of the spatial relationships between different locations.
5. Be Aware of Geographic Context: Always consider the geographic context of your data, including factors like elevation, terrain, and proximity to water bodies.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude, a seemingly simple system of coordinates, are the foundation for a vast array of applications that impact our lives in countless ways. They enable us to navigate the world, create maps, analyze data, conduct scientific research, and make informed decisions. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of latitude and longitude is only likely to grow, further shaping our understanding of the world and our place within it.



/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: The Power of Latitude and Longitude. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!