Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude, Longitude, and Map Quest
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude, Longitude, and Map Quest
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude, Longitude, and Map Quest. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude, Longitude, and Map Quest

The ability to locate oneself and navigate the vast expanse of the Earth has been a fundamental human pursuit since the dawn of civilization. From ancient sailors charting courses by the stars to modern travelers relying on GPS technology, understanding our position on the globe has been paramount for exploration, communication, and understanding the world around us. This understanding rests on the foundation of two key concepts: latitude and longitude.
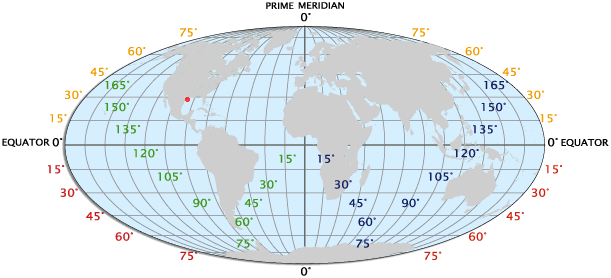
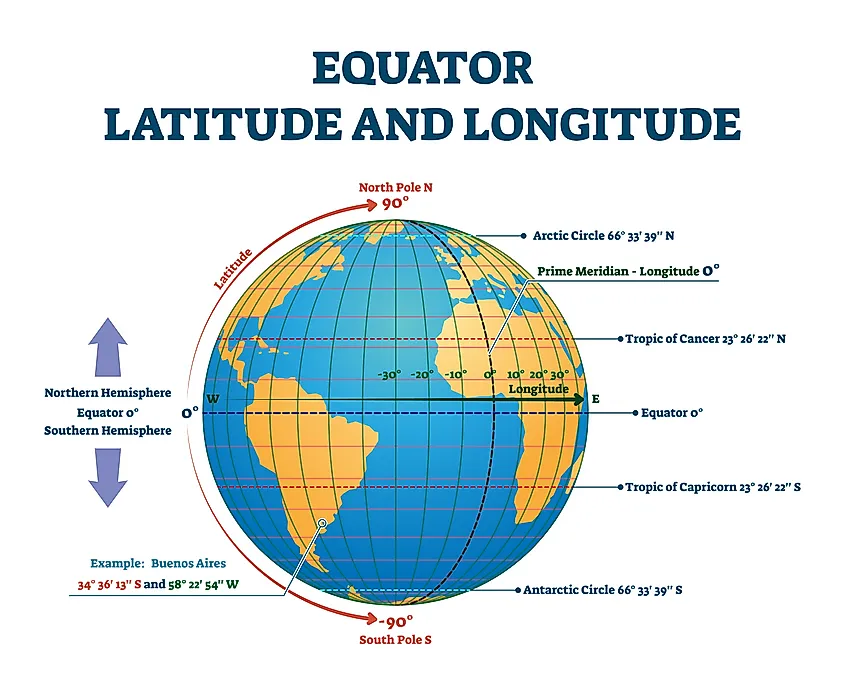
Latitude: The Angular Distance from the Equator
Latitude is an angular measurement that defines a location’s position north or south of the equator, an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees. The equator divides the Earth into two hemispheres: the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. Latitude is measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds, ranging from 0 degrees at the equator to 90 degrees at the North Pole and the South Pole.
Longitude: The Angular Distance from the Prime Meridian
Longitude, on the other hand, measures a location’s position east or west of the prime meridian, another imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole and passes through Greenwich, England. The prime meridian serves as the starting point for measuring longitude, which is also measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. Lines of longitude, known as meridians, converge at the poles and run parallel to each other.
The Power of Latitude and Longitude: Mapping the World
Latitude and longitude, together, form the basis of the geographic coordinate system, a system that allows for the precise location of any point on Earth. By combining the latitude and longitude coordinates, one can pinpoint a location on a map or globe. This system is essential for various applications, including:
- Navigation: Latitude and longitude are crucial for navigation, allowing sailors, pilots, and drivers to determine their position and plot their courses.
- Cartography: Mapmakers rely on latitude and longitude to accurately represent the Earth’s surface on maps.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software uses latitude and longitude to analyze and visualize spatial data, enabling researchers and planners to study patterns and trends across the globe.
- Satellite Navigation: GPS systems use latitude and longitude to determine the location of satellites and receivers, providing precise location information for various applications, such as navigation, mapping, and tracking.
MapQuest: A Digital Compass for the Modern World
MapQuest, a prominent online mapping service, utilizes latitude and longitude to provide users with detailed maps, directions, and location information. The platform uses these coordinates to:
- Identify user location: When a user enters their address or uses their device’s GPS, MapQuest uses latitude and longitude to determine their precise location.
- Generate directions: MapQuest uses latitude and longitude to calculate the shortest and most efficient routes between two points, providing turn-by-turn directions.
- Display maps: MapQuest leverages latitude and longitude to accurately depict geographical features, roads, landmarks, and other points of interest on its maps.
- Search for locations: Users can search for locations by name or address, and MapQuest uses latitude and longitude to display the location’s exact coordinates on the map.
Beyond Navigation: The Value of Latitude and Longitude in a Digital Age
The importance of latitude and longitude extends beyond navigation and mapping. These coordinates play a crucial role in various fields, including:
- Weather forecasting: Meteorologists use latitude and longitude to track weather patterns and predict weather events.
- Environmental monitoring: Scientists use latitude and longitude to monitor environmental changes, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change.
- Data analysis: Researchers use latitude and longitude to analyze data related to population density, economic activity, and social trends.
- Emergency response: Emergency services use latitude and longitude to locate incidents and dispatch resources efficiently.
FAQs: Demystifying Latitude and Longitude
1. What are the differences between latitude and longitude?
Latitude measures a location’s position north or south of the equator, while longitude measures a location’s position east or west of the prime meridian. Latitude lines are parallel to the equator, while longitude lines converge at the poles.
2. How do latitude and longitude affect climate?
Latitude plays a significant role in determining a region’s climate. Locations closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight and have warmer temperatures, while locations farther from the equator experience colder temperatures.
3. Can latitude and longitude be used to track animals?
Yes, latitude and longitude can be used to track animals through the use of GPS collars or other tracking devices. This information can help researchers understand animal movements, migration patterns, and habitat use.
4. How accurate are latitude and longitude coordinates?
The accuracy of latitude and longitude coordinates depends on the technology used. GPS systems provide highly accurate location information, while older methods, such as triangulation, may have lower accuracy.
5. How do latitude and longitude relate to time zones?
Longitude plays a role in determining time zones. The Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each corresponding to a 15-degree longitude band. As you travel east, you enter a new time zone every 15 degrees of longitude, and the time advances by one hour.
Tips for Using Latitude and Longitude Effectively
- Understand the units of measurement: Latitude and longitude are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. Ensure you are using the correct units when entering coordinates into mapping software or devices.
- Use reliable sources: When obtaining latitude and longitude coordinates, rely on reputable sources, such as online mapping services or government agencies.
- Be aware of limitations: Latitude and longitude coordinates may not always be precise, especially in areas with poor GPS coverage or complex terrain.
- Consider the scale: The accuracy of latitude and longitude coordinates depends on the scale of the map or application. Smaller scales provide more detail and higher accuracy.
- Use the correct format: Latitude and longitude coordinates are typically expressed in decimal degrees or degrees, minutes, and seconds. Ensure you are using the correct format for the software or device you are using.
Conclusion: A Global Framework for Understanding Our World
Latitude and longitude form the foundation of our understanding of the Earth’s geography. These angular measurements provide a precise system for locating points on the globe, enabling navigation, mapping, data analysis, and countless other applications. From ancient explorers charting unknown territories to modern-day travelers navigating bustling cities, latitude and longitude have played a vital role in shaping our world. As technology continues to advance, these fundamental concepts will continue to be essential for understanding and interacting with our planet.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude, Longitude, and Map Quest. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!