Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude

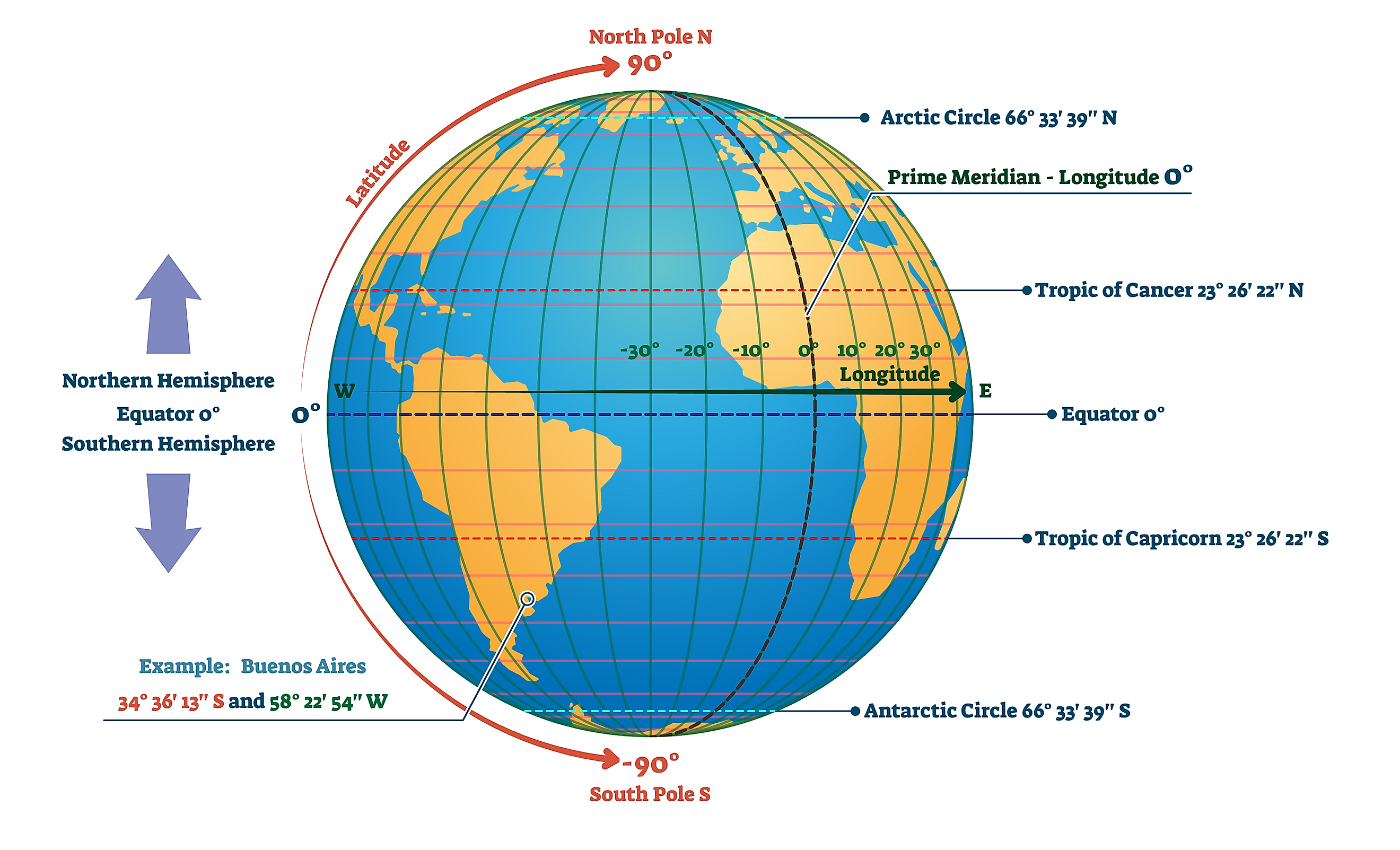
The Earth, a vast and intricate sphere, presents a challenge for accurately pinpointing locations. To overcome this, a system of imaginary lines, known as latitude and longitude, was devised. This grid system, woven across the globe, provides a unique address for every point on Earth, enabling precise navigation and understanding of spatial relationships.
Latitude: Lines of Parallel
Latitude lines, often referred to as parallels, are imaginary circles that run parallel to the equator, which is an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude. They measure the angular distance north or south of the equator, with values ranging from 0 degrees at the equator to 90 degrees at the North and South Poles.
- Equator: This line divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It is the longest latitude line, with a circumference of approximately 40,075 kilometers.
- Tropics: The Tropic of Cancer (23.5 degrees North) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5 degrees South) mark the boundaries of the tropical regions, where the sun’s rays are directly overhead at least once a year.
- Arctic and Antarctic Circles: These circles, located at 66.5 degrees North and South respectively, define the polar regions.
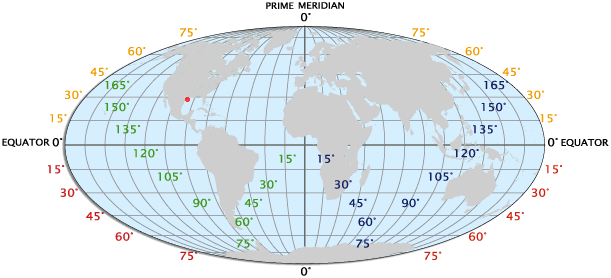
Longitude: Lines of Meridian
Longitude lines, also known as meridians, are imaginary half-circles that extend from the North Pole to the South Pole, passing through a specific point on the Earth’s surface. They measure the angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian, which is a reference meridian passing through Greenwich, England, at 0 degrees longitude.
- Prime Meridian: This line divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. It is the only meridian that is a full circle, with a circumference of approximately 40,008 kilometers.
- International Date Line: This line, generally following the 180th meridian, marks the boundary between two consecutive calendar days.
Coordinates: The Intersection of Latitude and Longitude
The intersection of a specific latitude line and a longitude line defines a unique point on the Earth’s surface. This intersection is known as a coordinate, expressed as a pair of numbers, with latitude listed first followed by longitude. For example, the coordinates of the Eiffel Tower in Paris are 48.8584° N, 2.2945° E.
Benefits of Latitude and Longitude
The system of latitude and longitude offers numerous benefits, making it indispensable for various applications:
- Precise Location Determination: Latitude and longitude provide an accurate and unambiguous way to pinpoint any location on Earth. This is crucial for navigation, mapping, and various scientific applications.
- Spatial Analysis: By understanding the coordinates of different locations, spatial relationships between them can be established, allowing for analysis of distances, directions, and geographic patterns.
- Global Communication and Collaboration: The standardized system of latitude and longitude facilitates global communication and collaboration, enabling people from different parts of the world to share location information and coordinate activities.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Latitude and longitude form the foundation of GIS, a powerful tool used for managing, analyzing, and visualizing geographic data. GIS applications are used in various fields, including urban planning, environmental monitoring, and resource management.
- Navigation and Travel: Latitude and longitude are essential for navigation systems, including GPS (Global Positioning System), which use satellite signals to determine the user’s location based on their latitude and longitude coordinates.
FAQs about Latitude and Longitude
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude measures the angular distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
Q: How are latitude and longitude measured?
A: They are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds, with each degree divided into 60 minutes and each minute divided into 60 seconds.
Q: Why is the equator considered 0 degrees latitude?
A: The equator is considered 0 degrees latitude as it is the starting point for measuring distances north or south.
Q: Why is the Prime Meridian considered 0 degrees longitude?
A: The Prime Meridian is considered 0 degrees longitude as it is the starting point for measuring distances east or west.
Q: What is the difference between the International Date Line and the Prime Meridian?
A: The International Date Line marks the boundary between two consecutive calendar days, while the Prime Meridian is the reference meridian for measuring longitude.
Q: How can I find the latitude and longitude of a specific location?
A: You can use online mapping services like Google Maps or other mapping applications that provide latitude and longitude coordinates.
Tips for Understanding and Using Latitude and Longitude
- Visualize the Grid: Imagine the Earth as a giant grid with latitude lines running horizontally and longitude lines running vertically.
- Practice with Maps: Use maps and globes to familiarize yourself with the location of major latitude and longitude lines.
- Understand the Coordinate System: Remember that latitude is listed first, followed by longitude, and that degrees, minutes, and seconds are used for measurement.
- Explore Online Resources: Utilize online mapping services and educational websites to learn more about latitude and longitude and how they are used in various applications.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude, a seemingly simple system of imaginary lines, have revolutionized our understanding and navigation of the Earth. This fundamental framework provides a precise and standardized way to locate any point on the globe, facilitating communication, collaboration, and spatial analysis. From mapping to navigation and GIS applications, latitude and longitude remain essential tools for exploring, understanding, and managing our planet. As technology advances, the importance of this system will only continue to grow, ensuring a more interconnected and informed world.
/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!