Navigating the United States: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
Related Articles: Navigating the United States: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the United States: Understanding Longitude and Latitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the United States: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the United States: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
- 3.1 The Grid System of the Earth: Longitude and Latitude
- 3.2 The United States Within the Global Grid
- 3.3 Applications of Longitude and Latitude in the United States
- 3.4 Understanding the US Map with Longitude and Latitude
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Longitude and Latitude in the US
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding and Using Longitude and Latitude
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the United States: Understanding Longitude and Latitude

The United States, a vast and diverse nation, stretches across a significant portion of the North American continent. Navigating its sprawling landscape, from the bustling metropolises of the East Coast to the rugged mountains of the West, requires a robust system of spatial reference. This system, based on the principles of longitude and latitude, provides a precise and universal method for locating any point on Earth, including every corner of the United States.
The Grid System of the Earth: Longitude and Latitude
Imagine the Earth as a giant sphere, divided by an intricate grid of lines. These lines, known as longitude and latitude, form the foundation of our global positioning system.
-
Longitude: These lines run vertically, from the North Pole to the South Pole, resembling slices of an orange. Each line of longitude represents a specific angular distance east or west of the prime meridian, a designated line of longitude passing through Greenwich, England. The prime meridian serves as the zero-degree reference point for longitude, with values increasing eastward to 180 degrees and westward to 180 degrees.
-
Latitude: These lines run horizontally, parallel to the equator, which is the imaginary line circling the Earth at zero degrees latitude. Each line of latitude represents a specific angular distance north or south of the equator. Latitude values increase northward to 90 degrees at the North Pole and southward to 90 degrees at the South Pole.
This grid system, with its precise measurements of longitude and latitude, allows us to pinpoint any location on Earth with remarkable accuracy.
The United States Within the Global Grid
The United States, situated primarily in the Northern Hemisphere, occupies a specific band of longitude and latitude. Its westernmost point, located in the Aleutian Islands of Alaska, extends to approximately 172 degrees west longitude, while its easternmost point, in Maine, reaches roughly 67 degrees west longitude. The northernmost point, in Alaska, reaches about 71 degrees north latitude, while the southernmost point, in Hawaii, extends to approximately 19 degrees north latitude.
This geographic positioning within the global grid allows for a precise understanding of the United States’ location relative to other countries and regions. It also provides valuable insights into the country’s diverse climate, terrain, and natural resources, which are often influenced by latitude and longitude.
Applications of Longitude and Latitude in the United States
Understanding the longitude and latitude of locations within the United States has numerous practical applications, including:
-
Navigation: GPS systems rely heavily on longitude and latitude coordinates to guide vehicles, ships, and aircraft. These coordinates are essential for accurate navigation, particularly in unfamiliar areas or challenging terrains.
-
Mapping and Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Maps, whether printed or digital, are constructed using longitude and latitude coordinates. GIS systems, which integrate spatial data with other information, rely heavily on this coordinate system for analyzing and visualizing geographic patterns and trends.
-
Weather Forecasting and Climate Monitoring: Latitude plays a crucial role in determining climate zones and weather patterns. Understanding the latitude of a particular location allows meteorologists to predict weather conditions and monitor climate change impacts.
-
Resource Management and Environmental Monitoring: Longitude and latitude are used to track and manage natural resources, such as forests, water bodies, and wildlife populations. These coordinates are also essential for monitoring environmental changes and pollution levels.
-
Emergency Response and Disaster Relief: Precise location data, derived from longitude and latitude, is crucial for coordinating emergency response efforts during natural disasters or other emergencies.
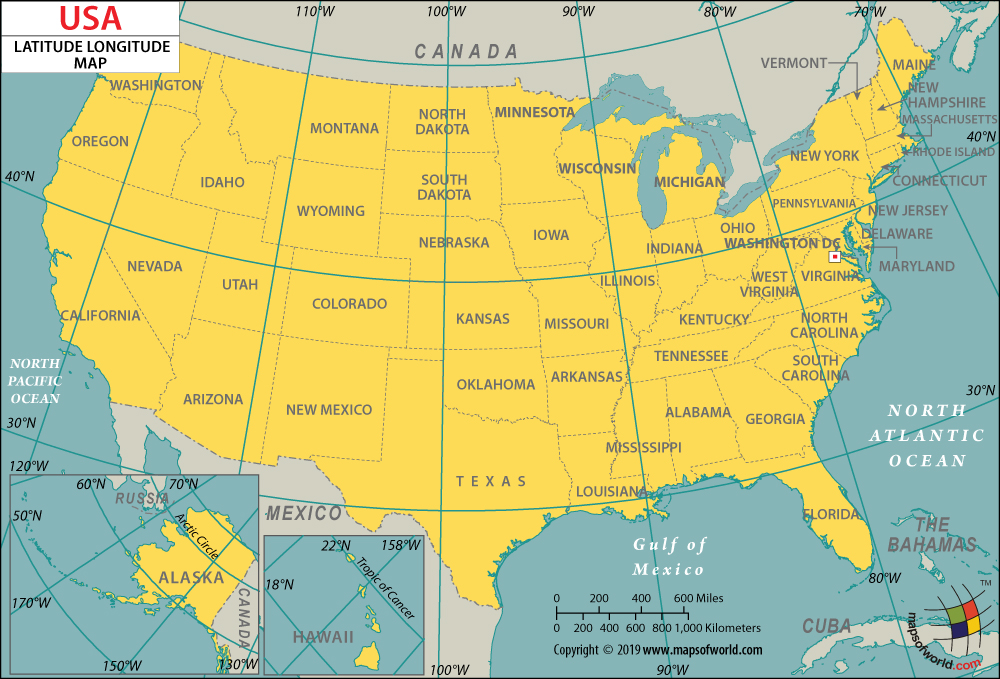
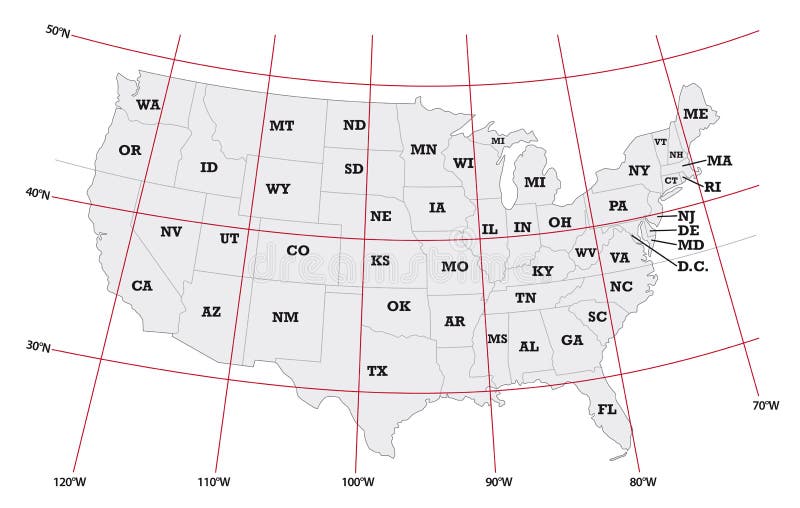
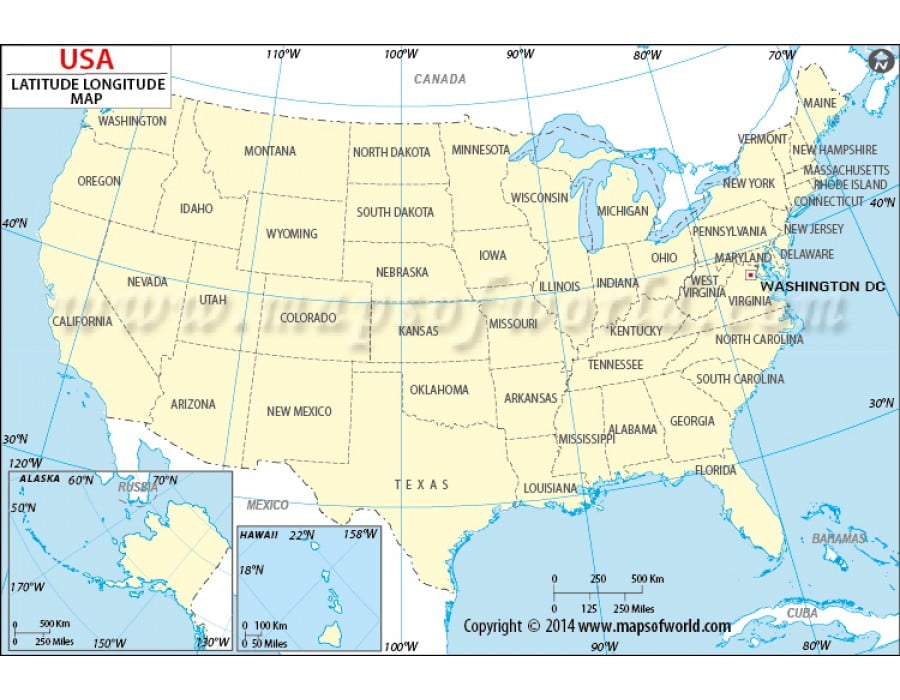
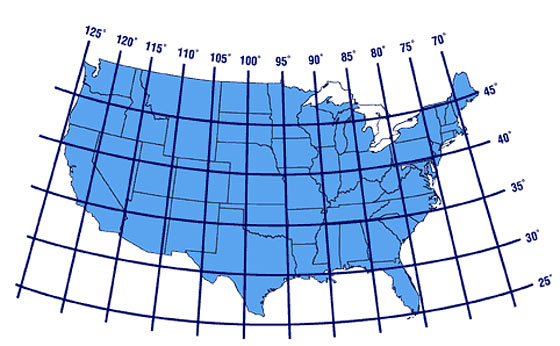
Understanding the US Map with Longitude and Latitude
When studying a US map with longitude and latitude lines, it’s crucial to recognize their significance:
-
Longitude lines: These lines help visualize the east-west extent of the country, highlighting the vast distances between coastal regions and the interior. They also illustrate the difference in time zones across the United States, as each 15-degree shift in longitude corresponds to a one-hour time difference.
-
Latitude lines: These lines provide insights into the north-south extent of the country, revealing its diverse climates and ecosystems. For example, the southernmost point of the United States, located in Hawaii, experiences a tropical climate, while the northernmost point, in Alaska, is characterized by a frigid Arctic climate.
Frequently Asked Questions about Longitude and Latitude in the US
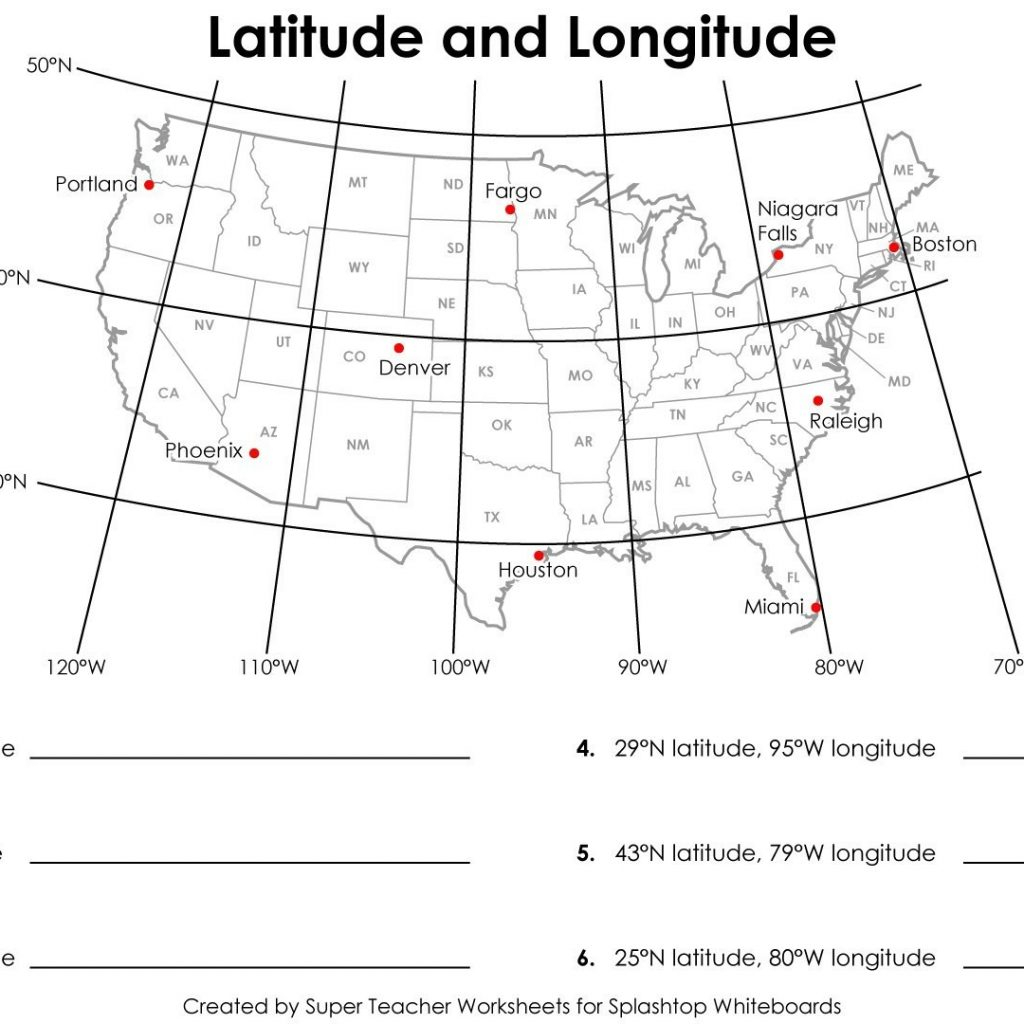
Q: How do I find the longitude and latitude of a specific location in the United States?
A: There are several ways to determine the longitude and latitude of a location. You can use online mapping services like Google Maps or Bing Maps, which provide coordinates for any address or point of interest. Alternatively, you can use a GPS device, which automatically determines your location and displays its longitude and latitude.
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude lines run horizontally, parallel to the equator, and measure distance north or south of the equator. Longitude lines run vertically, from the North Pole to the South Pole, and measure distance east or west of the prime meridian.
Q: Why is the prime meridian located at Greenwich, England?
A: The prime meridian was chosen as the zero-degree reference point for longitude because Greenwich, England, housed the Royal Observatory, a prominent astronomical institution. At the time of its establishment, England was a global maritime power, and the prime meridian’s location at Greenwich facilitated international navigation and communication.
Q: How does longitude affect time zones?
A: As the Earth rotates on its axis, different parts of the planet experience daylight at different times. Longitude plays a crucial role in determining time zones because each 15-degree shift in longitude corresponds to a one-hour time difference. This is why the United States has multiple time zones, with each zone encompassing a specific range of longitudes.
Tips for Understanding and Using Longitude and Latitude
-
Visualize the grid: Imagine the Earth as a sphere divided by a grid of longitude and latitude lines. This mental model will help you grasp the spatial relationships between locations.
-
Use online mapping tools: Explore online mapping services like Google Maps or Bing Maps, which allow you to zoom in on specific locations and view their longitude and latitude coordinates.
-
Study maps with longitude and latitude lines: Pay attention to the location of these lines on US maps and how they correspond to different regions and features.
-
Relate longitude and latitude to real-world applications: Connect these concepts to navigation, weather forecasting, resource management, and other practical applications.
Conclusion
Understanding the principles of longitude and latitude is essential for navigating and comprehending the vast expanse of the United States. This system provides a precise and universal method for locating any point within the country, enabling accurate navigation, mapping, and resource management. By appreciating the significance of these coordinates, we gain a deeper understanding of the United States’ geographic diversity, its relationship to the global grid, and the various applications of this fundamental spatial reference system.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the United States: Understanding Longitude and Latitude. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!