Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical Perspective
Related Articles: Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical Perspective
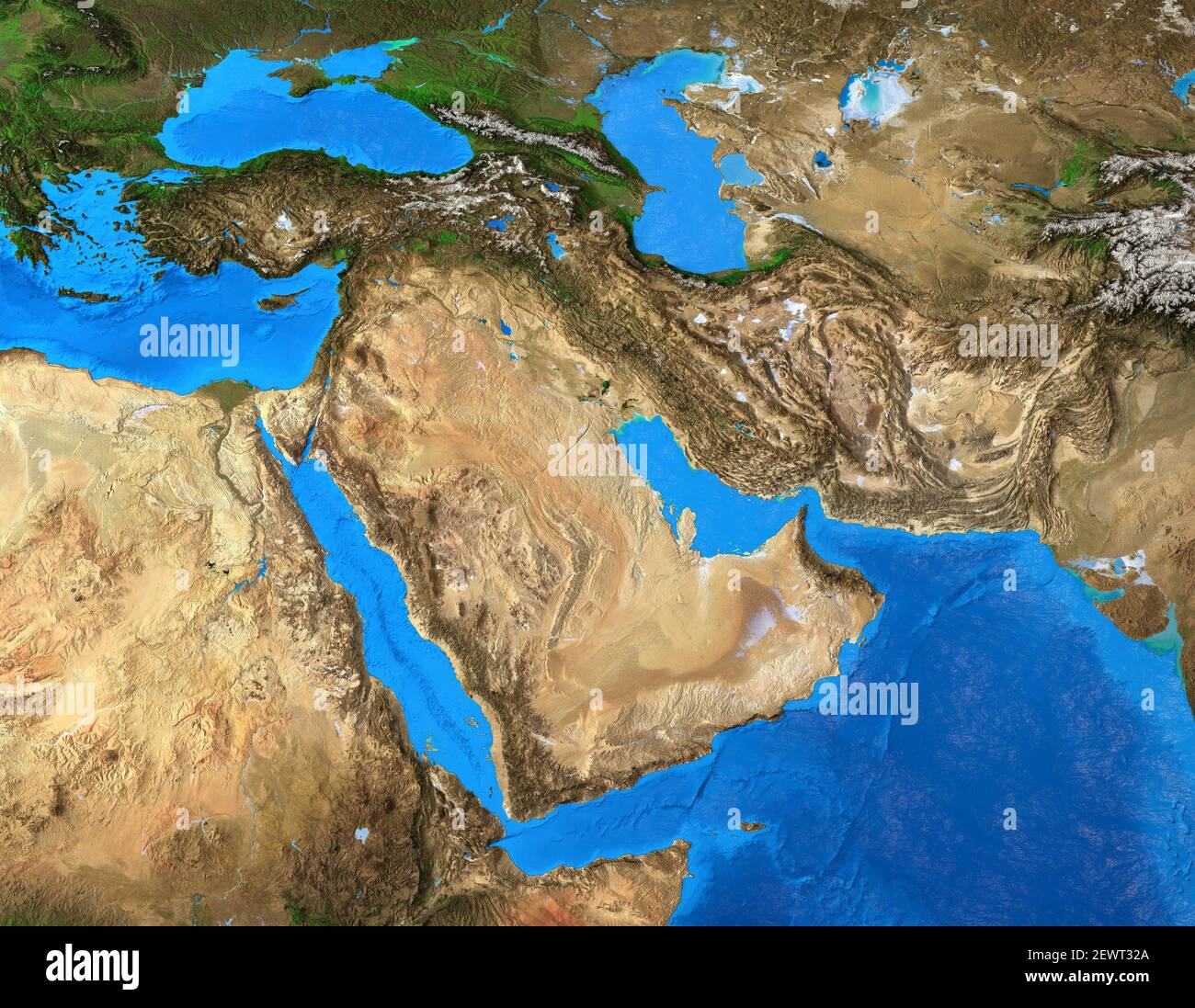
The Middle East, a region steeped in history, culture, and geopolitical significance, occupies a critical geographical space within the Eurasian landmass. Understanding its intricate geography, particularly through the lens of longitude and latitude, provides valuable insights into its diverse landscapes, climates, and cultural tapestry.
A Tapestry of Latitude and Longitude:
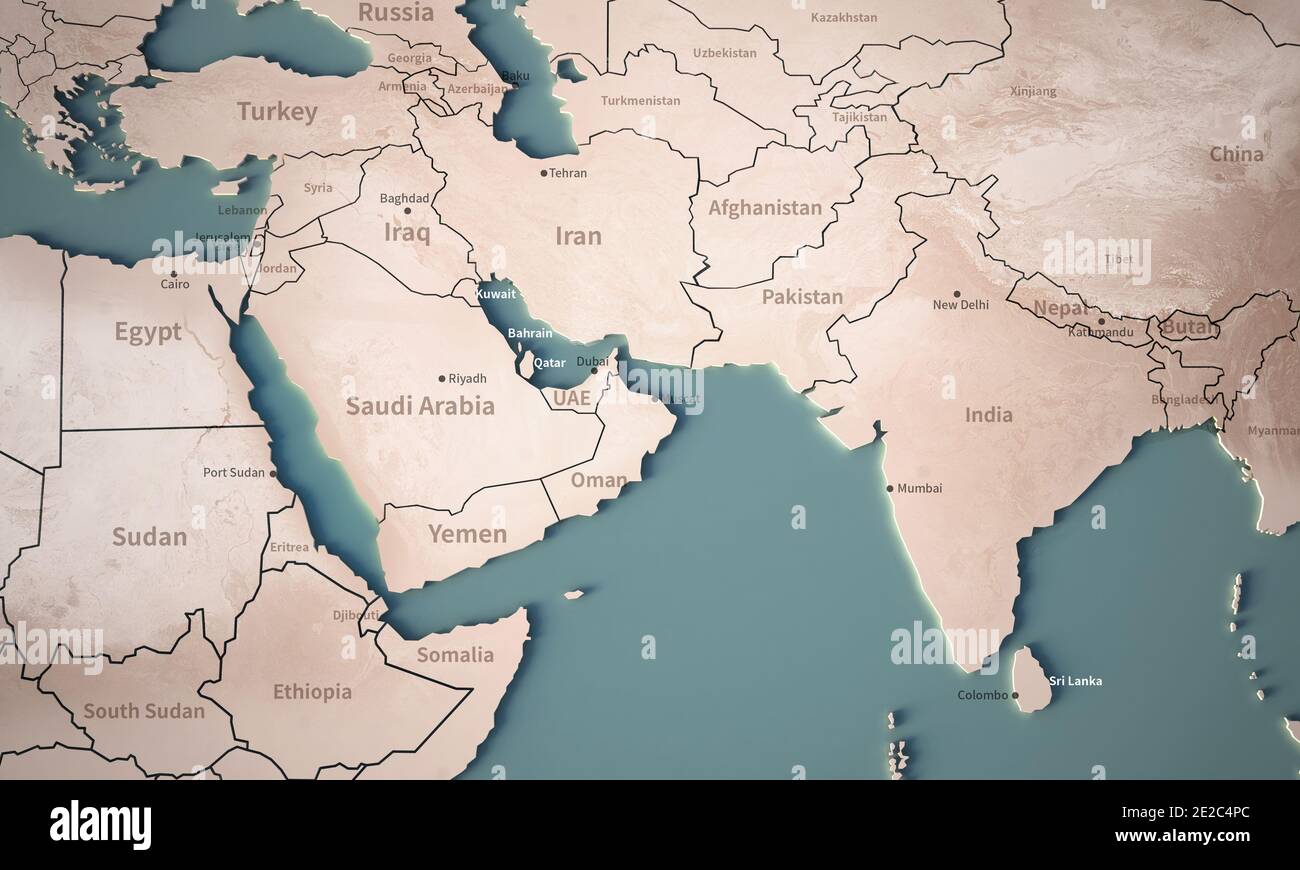
The Middle East, encompassing a vast area stretching from the Mediterranean Sea in the west to the Arabian Sea in the east, is characterized by its diverse geographical features. The region’s latitude and longitude play a crucial role in shaping its climate, vegetation, and human settlements.
Latitude:
- Northern Latitude: Countries like Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, and Israel fall within the 30° to 40° North latitude range. This area experiences Mediterranean-type climates with warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The fertile coastal plains and mountainous regions support a diverse range of flora and fauna.
- Tropical Latitude: Regions like Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates fall within the 15° to 30° North latitude range. These areas experience arid desert climates with scorching temperatures and minimal rainfall. The landscape is dominated by vast sand deserts and rocky plateaus, where life has adapted to extreme conditions.
Longitude:
- Eastern Longitude: The majority of the Middle East lies within the 30° to 70° East longitude range. This longitudinal spread highlights the region’s vastness and its diverse geographical features.
- The Importance of Longitude: Longitude lines help us understand the time zones within the region. The Middle East spans multiple time zones, with the easternmost countries experiencing daylight hours earlier than those in the west.
Geographical Features and Their Significance:
The Middle East’s geographical features are intertwined with its history, culture, and economy.
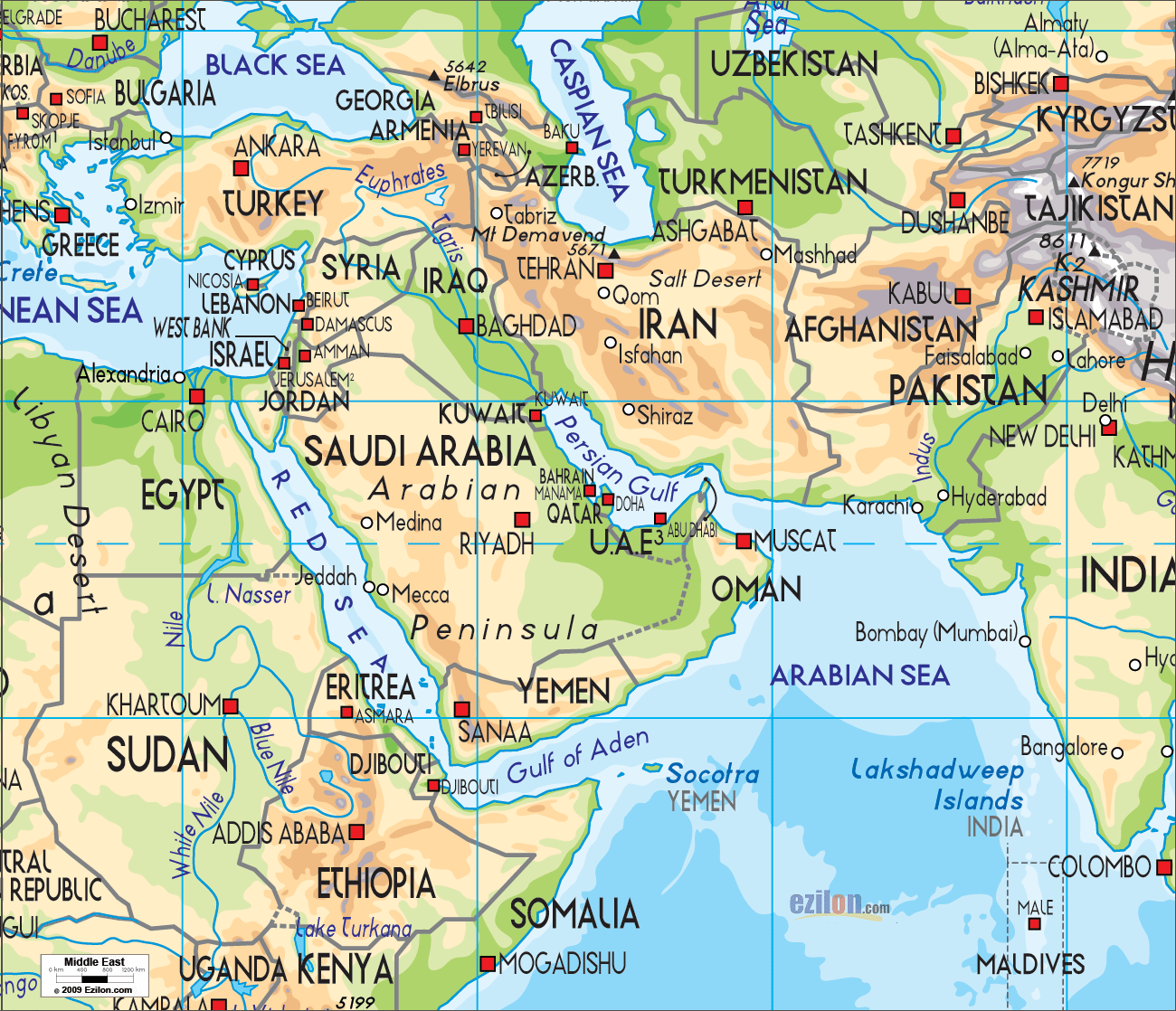
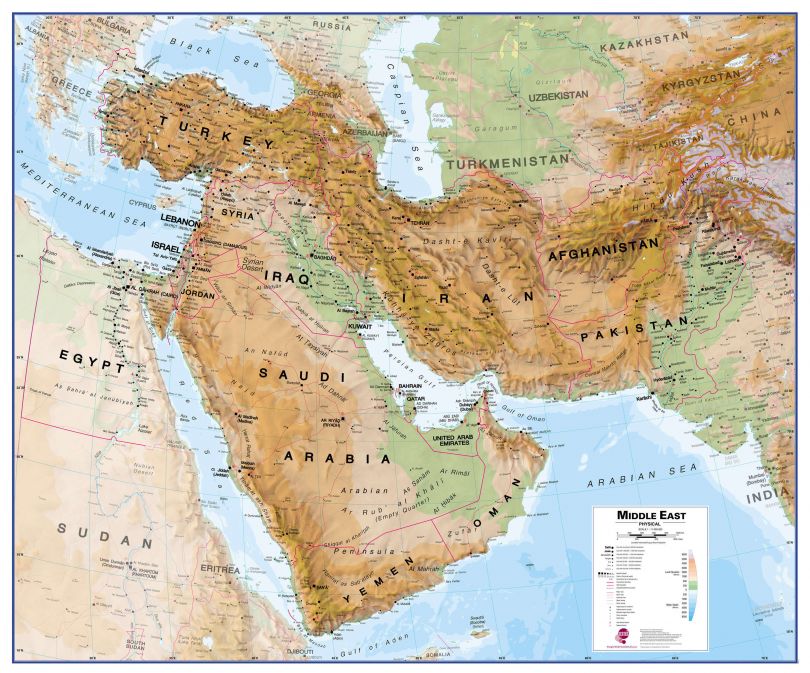
- The Nile River: This lifeblood of Egypt flows from south to north, providing a vital source of irrigation and transportation. The fertile Nile Valley has been a cradle of civilization for millennia, supporting dense populations and flourishing agriculture.
- The Arabian Peninsula: The world’s largest peninsula, it is dominated by vast deserts and oil reserves. This region has played a pivotal role in global energy markets and has shaped the economic and political landscape of the Middle East.
- The Zagros Mountains: Stretching across Iran and Iraq, these mountains form a natural barrier, influencing climate patterns and providing strategic defense positions.
- The Mediterranean Sea: This historic waterway has served as a vital trade route for centuries, connecting the Middle East with Europe and Africa. Its coastline has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous empires, leaving behind a rich cultural heritage.
The Importance of Understanding the Middle East’s Geography:
Understanding the Middle East’s geography is crucial for several reasons:
- Geopolitical Stability: The region’s strategic location and its abundant natural resources have made it a focal point of international relations. Understanding its geography helps in navigating complex geopolitical dynamics.
- Climate Change: The Middle East is particularly vulnerable to climate change, with rising temperatures and water scarcity posing significant challenges. Comprehending the region’s geography is essential for developing sustainable solutions to these challenges.
- Resource Management: The Middle East possesses vast reserves of oil and natural gas, which are vital for global energy security. Understanding the distribution and extraction of these resources is crucial for effective resource management and sustainable development.
- Cultural Understanding: The Middle East’s diverse landscapes and climates have shaped its cultural traditions and societal structures. Understanding its geography provides insights into the region’s rich cultural heritage.
FAQs about the Middle East Map with Longitude and Latitude:
Q: What are the major geographical features of the Middle East?
A: The Middle East encompasses a diverse range of geographical features, including the Nile River, the Arabian Peninsula, the Zagros Mountains, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Dead Sea.
Q: How does latitude influence the climate of the Middle East?
A: Latitude plays a significant role in determining the climate of the Middle East. Northern latitudes experience Mediterranean climates, while tropical latitudes are characterized by arid desert conditions.
Q: What is the importance of longitude in the Middle East?
A: Longitude helps us understand the time zones within the region, as the Middle East spans multiple time zones due to its vast longitudinal spread.
Q: How does geography influence the cultural diversity of the Middle East?
A: The diverse landscapes and climates of the Middle East have shaped its cultural traditions, languages, and societal structures, contributing to its rich cultural tapestry.
Q: What are the challenges posed by climate change to the Middle East?
A: The Middle East is particularly vulnerable to climate change, with rising temperatures, water scarcity, and desertification posing significant challenges to its environment and economy.
Tips for Studying the Middle East Map with Longitude and Latitude:
- Use Interactive Maps: Explore online interactive maps that allow you to zoom in on specific areas, identify geographical features, and understand latitude and longitude coordinates.
- Study Physical Maps: Analyze physical maps that depict landforms, water bodies, and elevation changes. This will provide a visual understanding of the region’s terrain.
- Research Climate Data: Explore climate data for different regions of the Middle East to understand the variations in temperature, rainfall, and other climatic factors.
- Connect Geography to History and Culture: Explore the historical and cultural significance of different geographical features, understanding how they have shaped the region’s development and identity.
Conclusion:
The Middle East map with longitude and latitude serves as a powerful tool for understanding the region’s intricate geography, its diverse landscapes, and its profound influence on history, culture, and global affairs. By utilizing this tool, we gain valuable insights into the region’s complex geopolitical dynamics, its environmental challenges, and its rich cultural heritage. The map becomes more than just a visual representation; it transforms into a key to unlocking the secrets and understanding the complexities of this vital region.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical Perspective. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!