Navigating the Land of the Long White Cloud: A Comprehensive Look at New Zealand’s Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating the Land of the Long White Cloud: A Comprehensive Look at New Zealand’s Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Land of the Long White Cloud: A Comprehensive Look at New Zealand’s Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Land of the Long White Cloud: A Comprehensive Look at New Zealand’s Latitude and Longitude

New Zealand, a nation nestled in the southwest Pacific Ocean, is often referred to as the "Land of the Long White Cloud." This picturesque archipelago, with its diverse landscapes and rich cultural heritage, is also a fascinating study in geography. Understanding its latitude and longitude provides a fundamental framework for comprehending its location, climate, and even its history.
A Geographic Overview: Latitude and Longitude in Context
Latitude and longitude are the two primary coordinates used to define a location on Earth. Latitude, measured in degrees north or south of the equator, determines a location’s distance from the equator. Longitude, measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian, determines a location’s distance from the prime meridian.
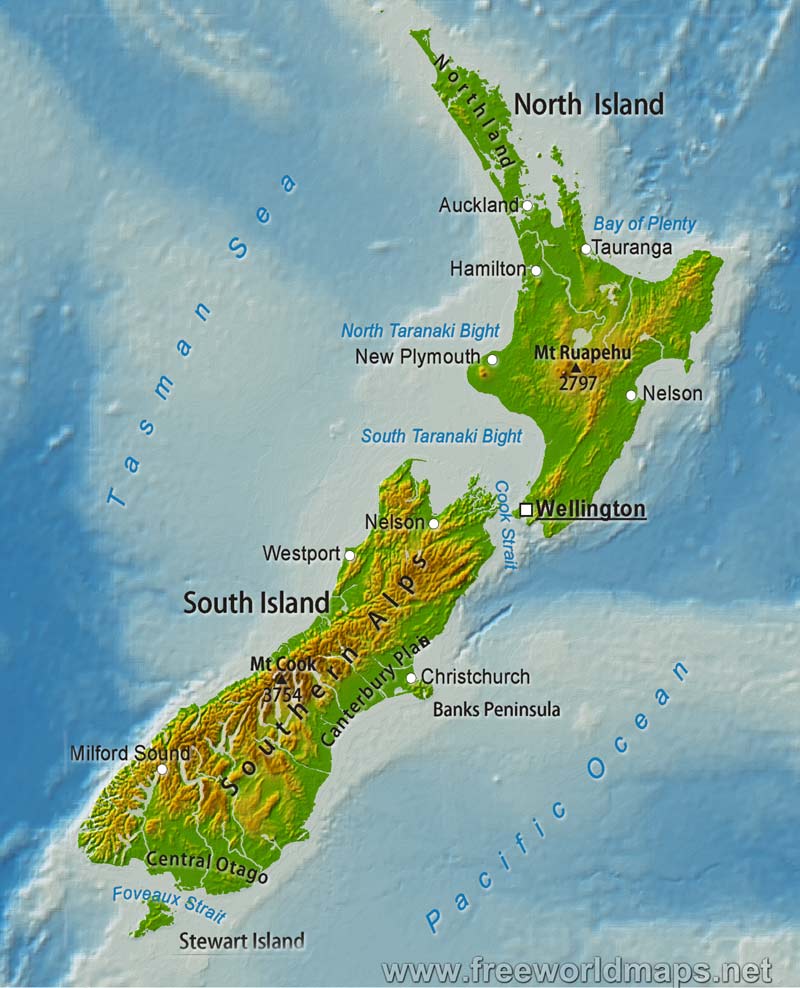
New Zealand’s geographic position is characterized by its unique location in the Southern Hemisphere. The country is situated between approximately 34° and 47° South latitude and 166° and 179° East longitude. This placement contributes significantly to its distinctive climate, biodiversity, and cultural identity.
Understanding New Zealand’s Latitude: A Look at Climate and Seasons
New Zealand’s latitude, ranging from the mid-latitudes to the sub-antarctic zone, plays a crucial role in shaping its climate. The country experiences a temperate climate, characterized by four distinct seasons. The southern location means that the seasons are reversed compared to the Northern Hemisphere, with summer occurring from December to February and winter from June to August.
The influence of latitude on climate is evident in the diverse microclimates found across New Zealand. The North Island, situated closer to the equator, enjoys warmer temperatures and longer summers compared to the South Island, which experiences colder winters and shorter summers. The mountainous terrain and proximity to the ocean also contribute to the variations in climate across different regions.
Exploring New Zealand’s Longitude: Unveiling Time Zones and Daylight
New Zealand’s longitude, spanning across several time zones, impacts its daylight hours and timekeeping. The country is divided into three main time zones: New Zealand Standard Time (NZST), New Zealand Daylight Saving Time (NZDT), and Chatham Standard Time (CST).
The majority of New Zealand observes NZST, which is 12 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). During daylight saving time, which typically runs from late September to late April, clocks are advanced by one hour, resulting in NZDT. The Chatham Islands, located east of the main islands, have their own time zone, CST, which is 12 hours and 45 minutes ahead of UTC.
The longitudinal location also influences the length of daylight hours throughout the year. During summer, New Zealand experiences long daylight hours, with the sun setting late in the evening. Conversely, during winter, the daylight hours are shorter, with the sun setting earlier in the afternoon.
The Importance of Latitude and Longitude: Navigation, Mapping, and Beyond
The latitude and longitude coordinates of New Zealand are not just geographical markers; they are fundamental to a wide range of applications.
- Navigation and Mapping: Latitude and longitude are essential for navigation and mapping, allowing for precise location identification and accurate representation on maps and charts. This is crucial for industries such as shipping, aviation, and tourism.
- Climate Modeling and Weather Forecasting: Understanding the latitude and longitude of New Zealand helps scientists model climate patterns, forecast weather conditions, and assess the impact of climate change on the country.
- Resource Management and Environmental Protection: Latitude and longitude are used to monitor and manage natural resources, such as forests, fisheries, and water resources. This information is crucial for environmental protection and sustainable development.
- Cultural Identity and Heritage: New Zealand’s unique location in the Southern Hemisphere has shaped its cultural identity and heritage. The country’s isolation and connection to the ocean have influenced its indigenous Maori culture, its art, and its literature.
Frequently Asked Questions about New Zealand’s Latitude and Longitude
Q: What are the extreme latitude and longitude coordinates of New Zealand?
A: The northernmost point of New Zealand is at 34°09′ South latitude, while the southernmost point is at 47°17′ South latitude. The easternmost point is at 179°00′ East longitude, and the westernmost point is at 166°32′ East longitude.
Q: How does New Zealand’s latitude affect its climate?
A: New Zealand’s latitude, ranging from the mid-latitudes to the sub-antarctic zone, results in a temperate climate with four distinct seasons. The southern location also means that the seasons are reversed compared to the Northern Hemisphere.
Q: Why does New Zealand have three different time zones?
A: New Zealand’s longitude spans across several time zones. The country is divided into three main time zones: NZST, NZDT, and CST. This ensures that the time in different parts of the country aligns with the sun’s position and daylight hours.
Q: What is the significance of New Zealand’s location in the Southern Hemisphere?
A: New Zealand’s location in the Southern Hemisphere has shaped its climate, biodiversity, and cultural identity. It has also influenced its relationship with other countries in the region and its role in global affairs.
Tips for Understanding New Zealand’s Latitude and Longitude
- Use online mapping tools: Interactive maps and globes can help visualize New Zealand’s location and its relationship to other countries.
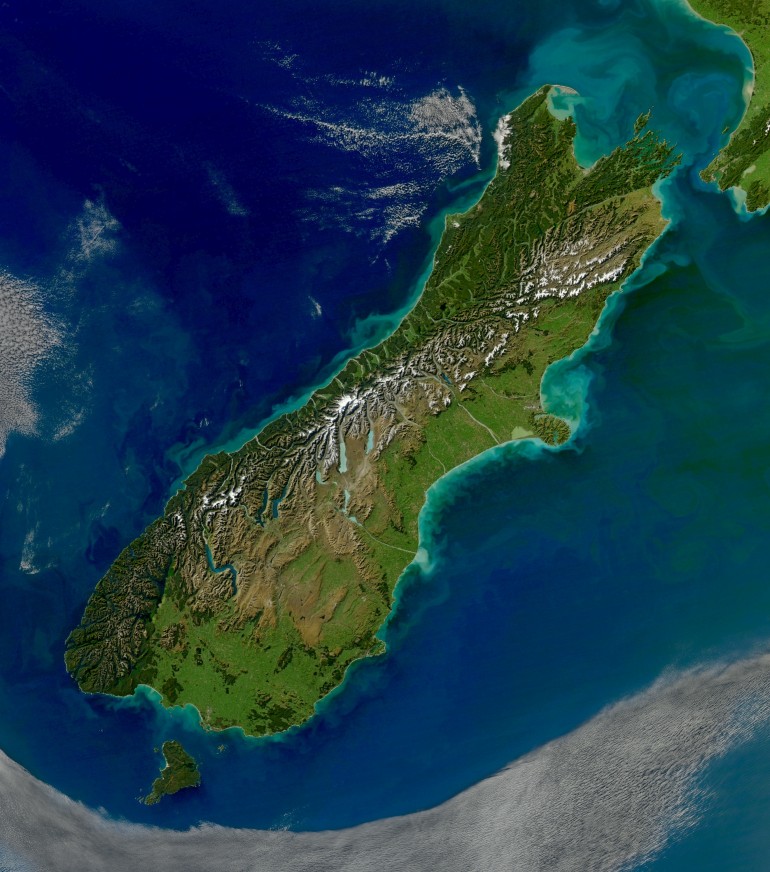
- Explore satellite imagery: Satellite images provide a comprehensive view of New Zealand’s geography and its diverse landscapes.
- Read about the history and culture of New Zealand: Understanding the country’s history and culture can provide insights into how its location has shaped its development.
- Engage with local communities: Talking to people who live in New Zealand can provide firsthand perspectives on the country’s geography and its impact on daily life.
Conclusion: A Framework for Understanding New Zealand’s Identity
New Zealand’s latitude and longitude are not just numbers on a map; they are fundamental to understanding the country’s identity. These coordinates define its location, shape its climate, influence its timekeeping, and contribute to its rich cultural heritage. By understanding the significance of latitude and longitude, we gain a deeper appreciation for the unique character of this island nation, its diverse landscapes, and its vibrant culture.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Land of the Long White Cloud: A Comprehensive Look at New Zealand’s Latitude and Longitude. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!