Navigating the Heart of America: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Kansas with Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating the Heart of America: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Kansas with Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Heart of America: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Kansas with Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Heart of America: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Kansas with Latitude and Longitude
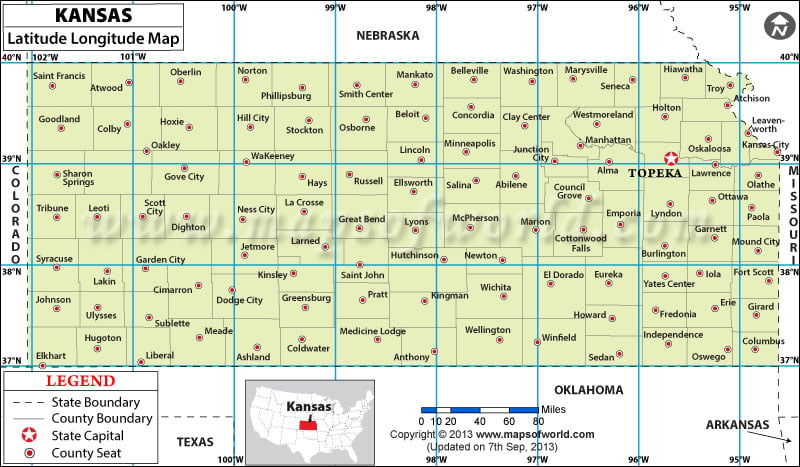
The state of Kansas, often referred to as the "Heart of America," holds a unique position on the map of the United States. Its geographic location, defined by its latitude and longitude coordinates, plays a crucial role in shaping its climate, landscape, and overall character. This article delves into the significance of understanding the map of Kansas with latitude and longitude, highlighting its importance in various fields and offering insights into the state’s diverse geographical features.
The Geographic Framework: Latitude and Longitude in Context
Latitude and longitude form the foundation of geographical mapping, providing a precise system for locating any point on Earth. Latitude lines, running parallel to the equator, measure distance north or south of the equator, expressed in degrees ranging from 0° at the equator to 90° at the poles. Longitude lines, running from pole to pole, measure distance east or west of the prime meridian, also expressed in degrees from 0° to 180°.
Kansas, situated in the central United States, falls within a specific range of latitude and longitude coordinates. Its northernmost point reaches approximately 40° North latitude, while its southernmost point lies around 36° North latitude. The westernmost boundary sits around 102° West longitude, and the easternmost reaches about 94° West longitude. These coordinates define the geographical boundaries of the state, influencing its climate, vegetation, and topography.
The Influence of Latitude: Shaping Climate and Vegetation
Kansas’s latitude plays a significant role in determining its climate. Situated within the mid-latitude zone, the state experiences a continental climate characterized by hot summers and cold winters. The absence of major mountain ranges or significant bodies of water allows for wide temperature fluctuations throughout the year. The average annual temperature in Kansas is approximately 55° Fahrenheit (13° Celsius), with temperatures exceeding 100° Fahrenheit (38° Celsius) during summer and dipping below 0° Fahrenheit (-18° Celsius) during winter.
This mid-latitude location also influences the state’s vegetation. Kansas falls within the transition zone between the Great Plains grasslands to the west and the deciduous forests to the east. The western portion of the state is dominated by tallgrass prairies, while the eastern region features a mix of grasslands and forests. This diverse vegetation pattern is directly linked to the state’s latitude and its associated climate.
The Significance of Longitude: Connecting East and West
Kansas’s longitude position places it squarely in the heart of the North American continent, connecting the eastern and western regions of the United States. This central location has historically been crucial for transportation and trade, with Kansas serving as a vital link between the Atlantic and Pacific coasts. The state’s central location also makes it a hub for agriculture, with its fertile soils and access to major transportation routes contributing to its status as a leading agricultural producer.
Moreover, Kansas’s longitude position influences its relationship with the jet stream, a powerful air current that circles the globe. The state experiences a variety of weather patterns due to the jet stream’s influence, leading to fluctuations in temperature and precipitation throughout the year. This variability in weather patterns further contributes to the state’s diverse agricultural landscape and its adaptation to different climatic conditions.
Delving Deeper: Geographical Features and Regional Variations
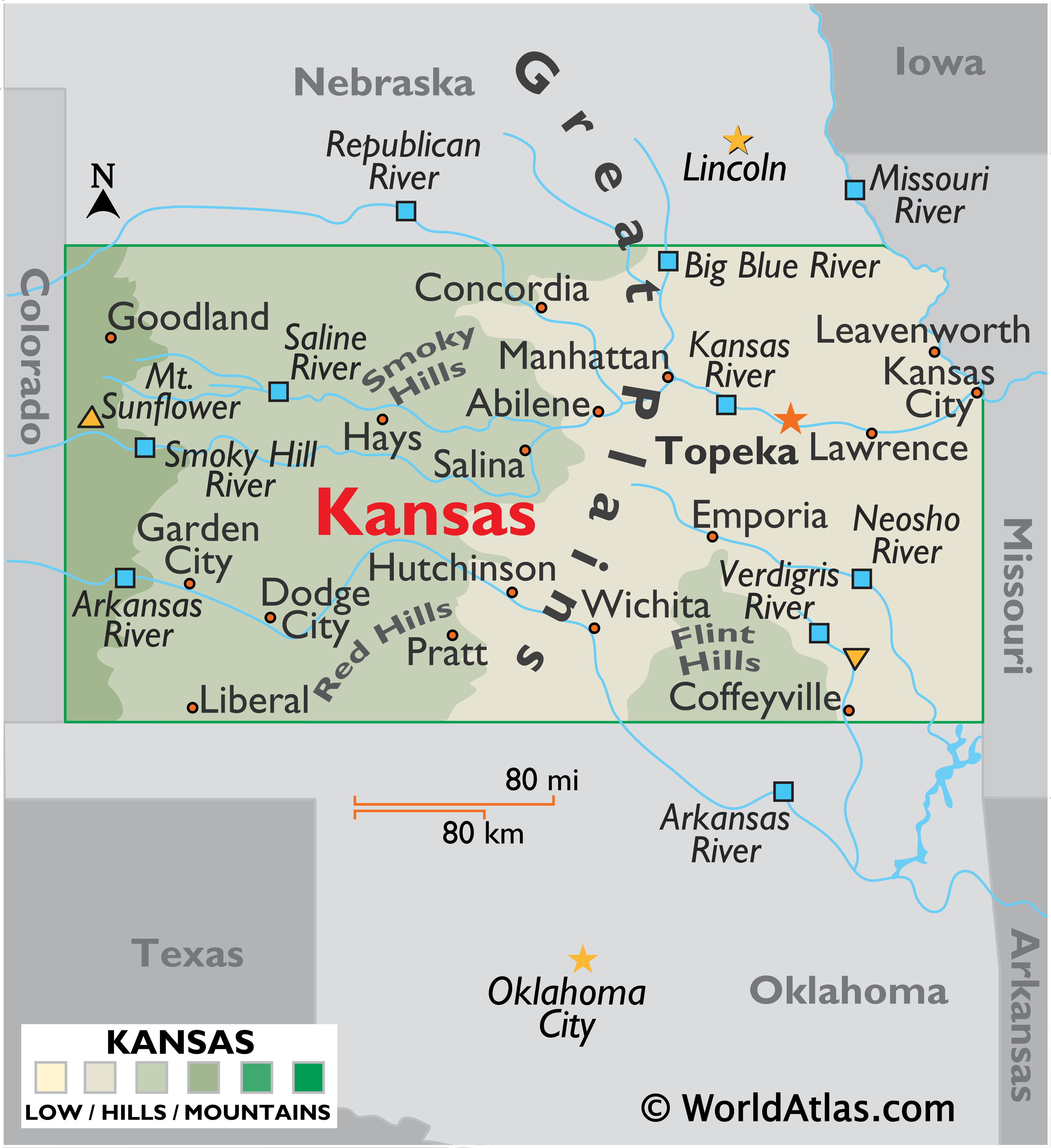
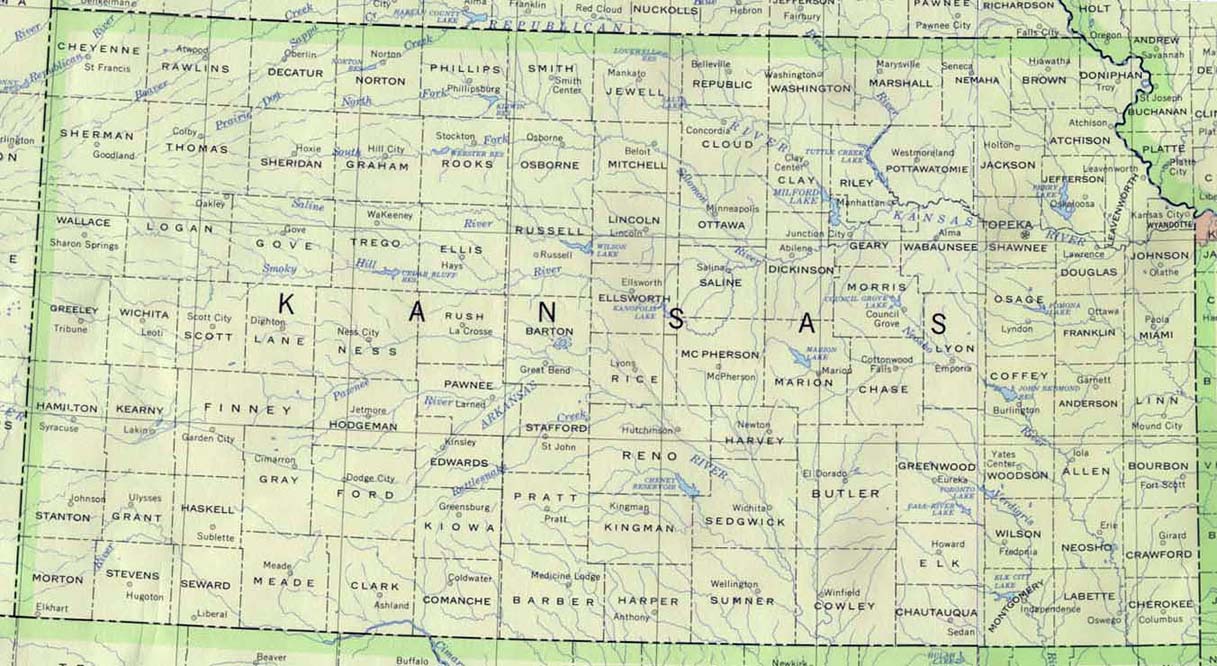
The map of Kansas with latitude and longitude reveals more than just the state’s boundaries. It provides a framework for understanding the state’s diverse geographical features, including its major rivers, plains, and hills.
-
The Great Plains: The western portion of Kansas is characterized by the vast expanse of the Great Plains, a region of gently rolling hills and grasslands. This region is known for its fertile soils, which support a wide range of agricultural activities.
-
The Flint Hills: The central region of Kansas features the Flint Hills, a unique ecological region known for its tallgrass prairie and limestone outcroppings. The Flint Hills are home to a diverse array of wildlife, including bison, elk, and prairie chickens.
-
The Smoky Hills: The Smoky Hills region, located in the central part of the state, is characterized by its rolling hills and rugged terrain. This region is known for its rich history, including its role in the Santa Fe Trail, a historic trade route that connected Missouri to New Mexico.
-
The Ozark Plateau: The southeastern corner of Kansas extends into the Ozark Plateau, a region known for its rugged hills and forests. This region is home to a variety of recreational opportunities, including hiking, fishing, and camping.
The Map’s Practical Applications: Navigation, Planning, and Research
The map of Kansas with latitude and longitude holds immense practical value across various fields.
-
Navigation: The coordinates provide a precise system for navigation, enabling accurate location tracking and efficient route planning. This is particularly relevant for emergency services, transportation, and logistics.
-
Planning: Understanding the state’s geographical features and climate patterns is crucial for urban planning, resource management, and infrastructure development. By analyzing the map, planners can identify areas suitable for different land uses, optimize resource allocation, and minimize environmental impact.
-
Research: The map serves as a fundamental tool for researchers studying various aspects of Kansas, including its geology, ecology, and history. By analyzing the spatial distribution of different features, researchers can gain valuable insights into the state’s natural resources, environmental challenges, and historical development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1: What is the most northern point in Kansas?
A1: The most northern point in Kansas is located at approximately 40° North latitude, near the town of White Cloud in Doniphan County.
Q2: What is the most southern point in Kansas?
A2: The most southern point in Kansas is located at approximately 36° North latitude, near the town of Riverton in Seward County.
Q3: What is the most eastern point in Kansas?
A3: The most eastern point in Kansas is located at approximately 94° West longitude, near the town of Weir in Cherokee County.
Q4: What is the most western point in Kansas?
A4: The most western point in Kansas is located at approximately 102° West longitude, near the town of Ulysses in Grant County.
Q5: What is the significance of the Kansas-Oklahoma state line?
A5: The Kansas-Oklahoma state line is marked by the 37th parallel north, a line of latitude that divides the two states. This line has historical significance, as it served as a boundary between the Louisiana Purchase and the Spanish territories.
Tips for Using the Map of Kansas with Latitude and Longitude:
-
Utilize online mapping tools: Numerous online mapping platforms provide interactive maps of Kansas, allowing users to zoom in, explore different regions, and identify specific locations.
-
Consider scale and resolution: The scale of the map determines the level of detail shown. For detailed information, use maps with a larger scale.
-
Combine with other data sources: Integrating the map with other data sources, such as climate data, population density, or agricultural production, can provide a comprehensive understanding of the state’s geographical features and their influence on various aspects of life.
Conclusion:
The map of Kansas with latitude and longitude serves as a powerful tool for understanding the state’s geography, climate, and history. Its coordinates provide a precise system for navigation, planning, and research, while its geographical features influence the state’s diverse landscape, agricultural practices, and overall character. By utilizing this map and understanding the significance of latitude and longitude, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the unique position of Kansas within the United States and its role in shaping the nation’s history and development.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Heart of America: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Kansas with Latitude and Longitude. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!