Navigating the Grid: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Grid: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Grid: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Grid: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps

The Earth, a vast sphere, is meticulously mapped to provide a framework for understanding its diverse locations. At the heart of this framework lies the concept of latitude and longitude, a system of invisible lines that crisscross the globe, enabling precise identification of any point on its surface.
Understanding the Grid: Lines of Latitude and Longitude
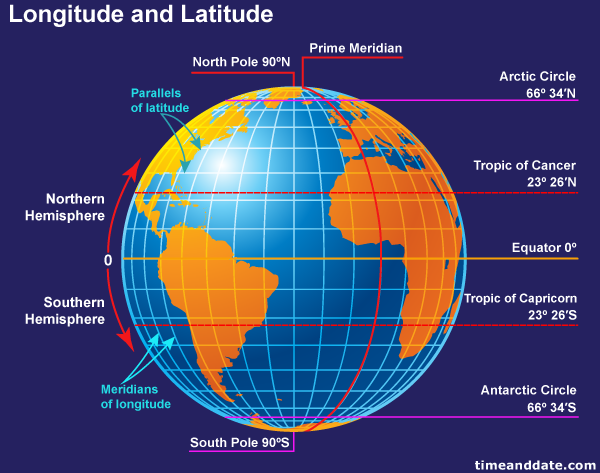
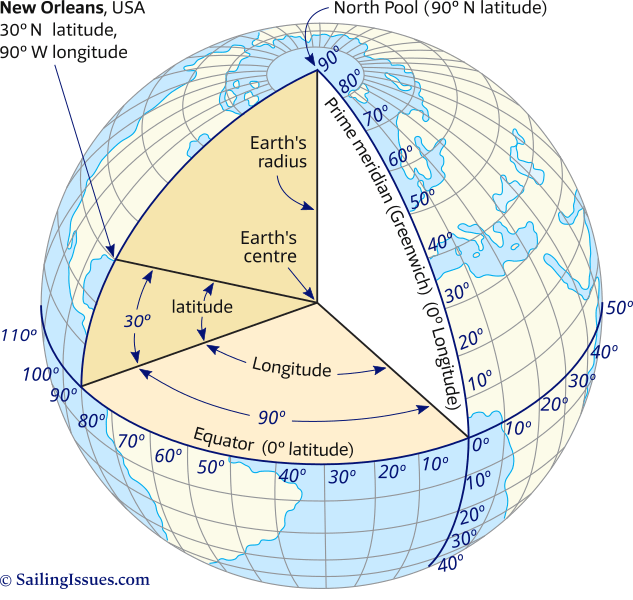
Latitude, often referred to as parallels, are imaginary lines that run east to west, parallel to the equator. The equator, the largest circle of latitude, divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Each degree of latitude is approximately 69 miles (111 kilometers) apart, with values ranging from 0° at the equator to 90° at the North and South poles.
Longitude, also known as meridians, are imaginary lines that run north to south, converging at the poles. The Prime Meridian, passing through Greenwich, England, serves as the zero-degree reference point. Longitude values range from 0° at the Prime Meridian to 180° east or west.
Deciphering the Coordinates: Finding Latitude and Longitude on a Map
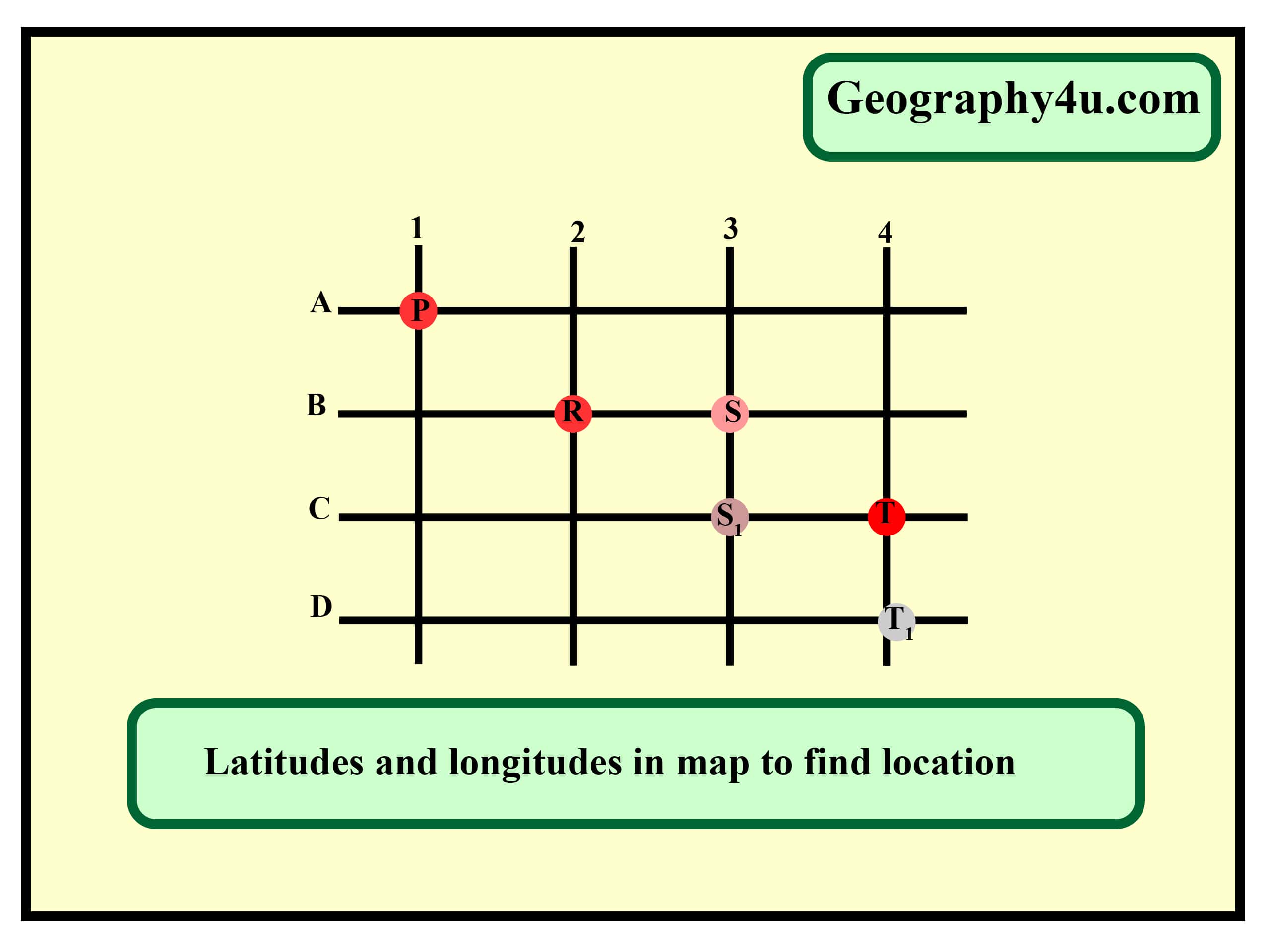
To determine the latitude and longitude of a specific location on a map, follow these steps:
-
Identify the Latitude Lines: Locate the horizontal lines representing degrees of latitude on the map. These lines are typically marked with numbers, indicating the degree of latitude.
-
Locate the Longitude Lines: Identify the vertical lines representing degrees of longitude. These lines are also marked with numbers, indicating the degree of longitude.
-
Locate the Target Location: Pinpoint the precise location on the map for which you need to determine the coordinates.
-
Determine the Latitude: Find the latitude line that passes through or is closest to the target location. Note the degree of latitude indicated on the line.
-
Determine the Longitude: Find the longitude line that passes through or is closest to the target location. Note the degree of longitude indicated on the line.
-
Refine the Coordinates: Most maps use a grid system to provide a more precise location within the degree of latitude and longitude. These grids are typically marked with smaller increments, often in minutes and seconds. Determine the minute and second values for both latitude and longitude.
Expressing Coordinates: The Standard Format
The standard format for expressing latitude and longitude coordinates is:
- Latitude: Degrees, Minutes, Seconds (DMS) – For example, 40° 45′ 33" N (North)
- Longitude: Degrees, Minutes, Seconds (DMS) – For example, 74° 00′ 21" W (West)
Beyond the Basics: Types of Maps and Coordinate Systems
Maps come in various forms, each employing different coordinate systems. Common map types include:
-
Topographic Maps: These maps depict terrain features, elevation, and contour lines. They often use UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator) or other projected coordinate systems.
-
Nautical Charts: These maps are specifically designed for maritime navigation. They typically use the Geographic Coordinate System (GCS) with latitude and longitude expressed in decimal degrees.
-
Online Mapping Platforms: Digital mapping platforms like Google Maps and Bing Maps utilize various coordinate systems, including WGS84 (World Geodetic System 1984) and UTM.
Importance and Benefits of Latitude and Longitude
The ability to determine latitude and longitude on maps is vital for various applications:
-
Navigation: Latitude and longitude are fundamental for navigation, enabling precise location identification and course plotting.
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software relies heavily on latitude and longitude to analyze spatial data, map patterns, and understand geographical relationships.
-
Mapping and Surveying: Surveyors utilize latitude and longitude to establish precise boundaries, measure distances, and create detailed maps.
-
Scientific Research: Researchers use latitude and longitude to study climate patterns, track wildlife movements, and analyze geological formations.
FAQs about Finding Latitude and Longitude on Maps
1. What are the units used for latitude and longitude?
Latitude and longitude are typically expressed in degrees (°), minutes (‘), and seconds (").
2. How can I convert latitude and longitude from DMS to decimal degrees?
To convert from DMS to decimal degrees, divide the minutes by 60 and the seconds by 3600, then add the results to the degrees. For example, 40° 45′ 33" N becomes 40.75916667° N.
3. Are there any online tools to find latitude and longitude?
Yes, several online tools allow you to enter an address or place name to retrieve its latitude and longitude coordinates. Examples include Google Maps, Bing Maps, and Geocoding APIs.
4. What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
Latitude lines run horizontally, parallel to the equator, and measure the distance north or south of the equator. Longitude lines run vertically, converging at the poles, and measure the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
5. How can I use latitude and longitude to find a location on a map?
Locate the latitude and longitude lines on the map, find the intersection point of those lines, and that point will represent the location with the given coordinates.
Tips for Finding Latitude and Longitude on Maps
-
Use a compass: A compass can help you orient yourself on a map and determine north, which is essential for understanding the direction of latitude and longitude lines.
-
Look for grid lines: Most maps use grid lines to help locate specific points. These grids are typically marked with numbers representing degrees, minutes, and seconds.
-
Use a ruler: A ruler can be helpful for measuring distances on a map, especially when trying to determine the precise location of a point.
-
Practice makes perfect: The more you practice finding latitude and longitude on maps, the more familiar you will become with the process.
Conclusion
Understanding latitude and longitude is crucial for navigating the world, utilizing geographic information, and conducting research. By mastering the ability to locate and interpret these coordinates on maps, individuals gain a deeper understanding of their surroundings and unlock the power of spatial information. From navigating unfamiliar territories to analyzing environmental data, the ability to read and interpret latitude and longitude remains an essential skill in our interconnected world.




/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Grid: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!