Navigating the Grid: Understanding and Measuring Latitude and Longitude on Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Grid: Understanding and Measuring Latitude and Longitude on Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Grid: Understanding and Measuring Latitude and Longitude on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Grid: Understanding and Measuring Latitude and Longitude on Maps

Latitude and longitude, the fundamental building blocks of geographic coordinates, form an invisible grid that encompasses the Earth. This grid system, crucial for pinpointing locations with precision, allows for efficient navigation, accurate mapping, and effective communication across various disciplines.
Understanding the Grid: Latitude and Longitude
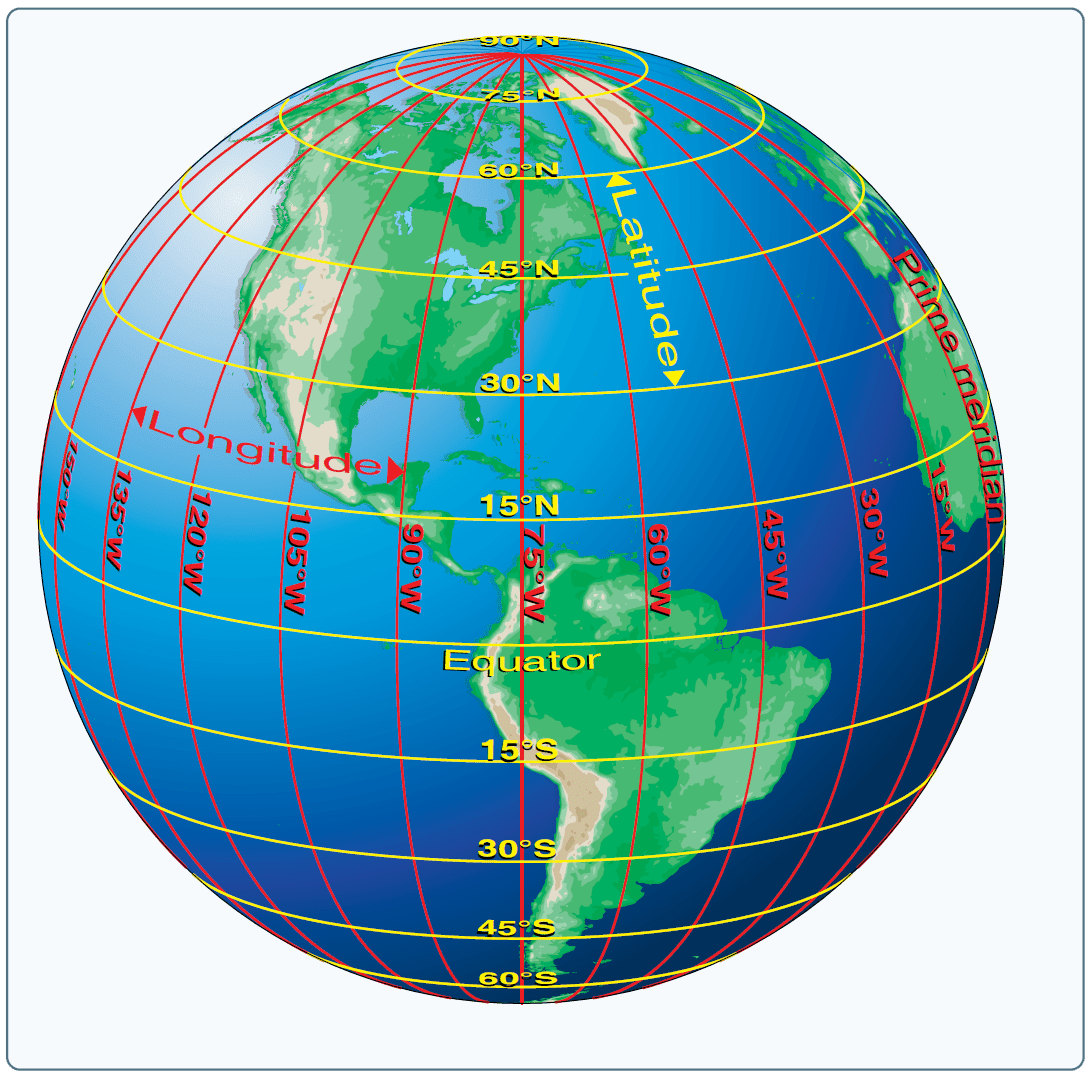
Imagine the Earth as a giant sphere, sliced horizontally and vertically by imaginary lines. These lines, representing latitude and longitude, are essential for defining a location’s position on the globe.
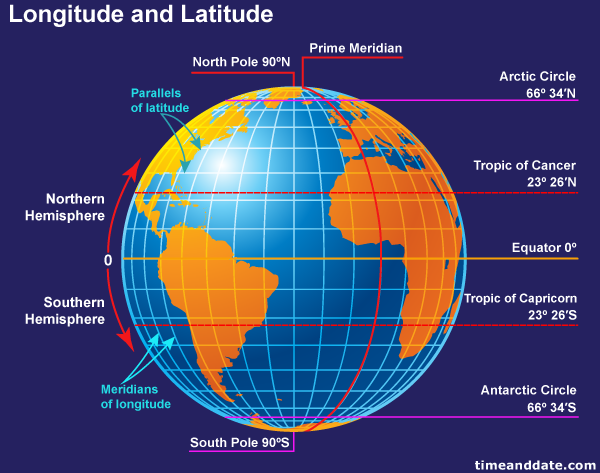
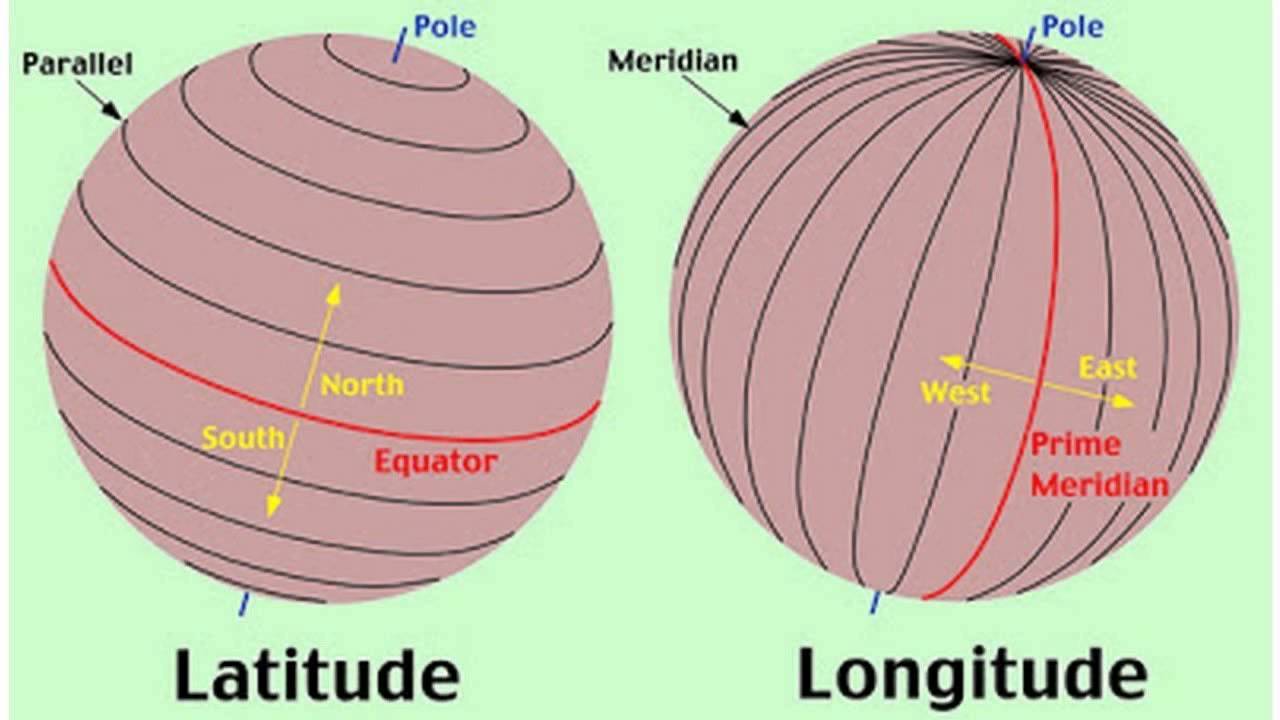
- Latitude: These lines run parallel to the equator, a horizontal circle that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Latitude is measured in degrees, ranging from 0° at the equator to 90° at the North and South poles. Locations north of the equator have positive latitude values, while those south have negative values.
- Longitude: These lines, known as meridians, run from the North Pole to the South Pole, perpendicular to the equator. Longitude is measured in degrees, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian, passing through Greenwich, England, to 180° east and west. Locations east of the Prime Meridian have positive longitude values, while those west have negative values.
Measuring Latitude and Longitude on a Map
Several methods allow for the measurement of latitude and longitude on maps, each with its own advantages and limitations:
1. Using a Protractor and Ruler:
This traditional method involves using a protractor and a ruler to measure angles and distances on the map.
- For Latitude: Identify the latitude lines printed on the map, representing degrees north or south of the equator. Align the protractor with the latitude line corresponding to the desired location and measure the angle from the horizontal axis.
- For Longitude: Identify the longitude lines printed on the map, representing degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian. Align the protractor with the longitude line corresponding to the desired location and measure the angle from the vertical axis.
- Distance Measurement: Use a ruler to measure the distance between two points on the map. Remember to consider the map’s scale to convert the measured distance to real-world units.
2. Using a Map Scale:
A map scale provides a ratio between distances on the map and corresponding distances in the real world. This method is particularly useful for measuring distances between two locations.
- Determining the Scale: Identify the map scale, often presented as a ratio (e.g., 1:100,000) or a verbal statement (e.g., "1 inch equals 1 mile").
- Measuring Distance: Use a ruler to measure the distance between the two points on the map. Apply the map scale to convert the measured distance into real-world units.
3. Using Online Tools and Mapping Software:
Modern technology offers numerous online tools and mapping software that simplify the process of measuring latitude and longitude.
- Online Mapping Tools: Websites like Google Maps and Bing Maps allow users to locate points on the map and display their corresponding latitude and longitude coordinates.
- Mapping Software: Dedicated mapping software like ArcGIS and QGIS offer advanced functionalities for precise coordinate measurement and analysis.
4. Using GPS Devices:
Global Positioning System (GPS) devices utilize satellite signals to determine a user’s precise location, providing real-time latitude and longitude coordinates. These devices are widely used for navigation, mapping, and geospatial applications.
Importance of Measuring Latitude and Longitude
The ability to accurately measure latitude and longitude is paramount in various fields:
- Navigation: Accurate coordinates are essential for pilots, sailors, and drivers to navigate safely and efficiently.
- Mapping and Surveying: Cartographers and surveyors rely on precise latitude and longitude measurements to create detailed maps and accurate representations of the Earth’s surface.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS systems utilize latitude and longitude data to analyze spatial relationships, manage resources, and solve complex problems.
- Environmental Monitoring: Measuring latitude and longitude helps track environmental changes, monitor wildlife populations, and manage natural resources.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use latitude and longitude to define the position of celestial objects in the sky.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
Latitude refers to the angular distance north or south of the equator, while longitude refers to the angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
2. How do I convert decimal degrees to degrees, minutes, and seconds (DMS)?
To convert decimal degrees to DMS, follow these steps:
- Degrees: The whole number before the decimal point represents the degrees.
- Minutes: Multiply the decimal part by 60. The whole number represents the minutes.
- Seconds: Multiply the decimal part of the minutes by 60. The resulting number represents the seconds.
3. How can I use latitude and longitude for navigation?
Latitude and longitude coordinates can be used in conjunction with GPS devices or navigation apps to pinpoint your location and find your way to a desired destination.
4. What are some common applications of latitude and longitude in everyday life?
Latitude and longitude are used in various everyday applications, including:
- Weather forecasting: Weather maps use latitude and longitude to display weather patterns and forecasts.
- Social media: Many social media platforms use latitude and longitude to display location information in posts and check-ins.
- Mobile apps: Many apps use location services, relying on latitude and longitude data to provide location-based services.
Tips for Measuring Latitude and Longitude on Maps
- Use a high-quality map: Ensure the map you are using has clear and accurate latitude and longitude lines.
- Check the map scale: Understand the map scale to accurately convert measurements from the map to real-world distances.
- Practice your technique: Regularly practice measuring latitude and longitude on maps to improve your accuracy.
- Use online tools and software: Explore online mapping tools and software for efficient and precise coordinate measurement.
Conclusion
Understanding and measuring latitude and longitude are fundamental skills for navigating the world, analyzing geographic data, and solving complex problems. By mastering these techniques, individuals can unlock a deeper understanding of our planet and its intricate spatial relationships. Whether using traditional methods or modern tools, the ability to accurately measure latitude and longitude remains a cornerstone of geographic exploration and analysis.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Grid: Understanding and Measuring Latitude and Longitude on Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!