Navigating the Globe: Understanding World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating the Globe: Understanding World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Globe: Understanding World Maps with Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Globe: Understanding World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Globe: Understanding World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
- 3.1 Latitude and Longitude: The Grid System of the Earth
- 3.2 The Power of Coordinates: Locating Points on the Globe
- 3.3 Applications of World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
- 3.4 Importance and Benefits of World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
- 3.5 FAQs about World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
- 3.6 Tips for Using World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
- 3.7 Conclusion: Navigating a World Connected by Latitude and Longitude
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Globe: Understanding World Maps with Latitude and Longitude

The world map, a ubiquitous tool in our understanding of the planet, holds a remarkable power to convey vast amounts of information in a single, concise image. Its grid system, composed of latitude and longitude lines, provides a framework for precise location and spatial relationships, serving as a foundation for navigation, cartography, and a multitude of scientific and technological applications. This article delves into the intricacies of world maps with latitude and longitude, exploring their fundamental principles, applications, and importance in our interconnected world.
Latitude and Longitude: The Grid System of the Earth
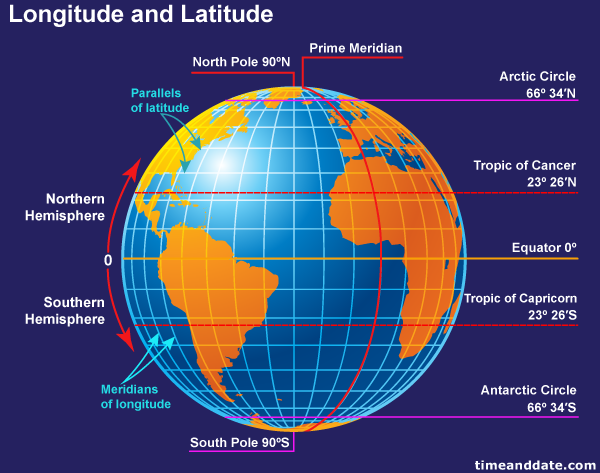
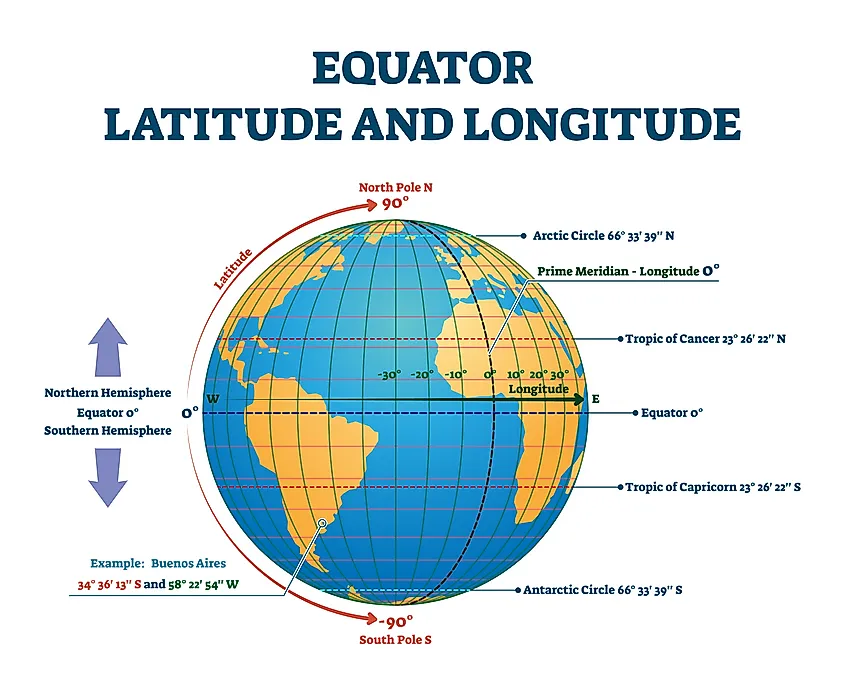
Imagine the Earth as a giant sphere, divided into two key sets of imaginary lines: latitude and longitude. These lines, invisible but essential, form a grid system that allows us to pinpoint any location on the globe with remarkable accuracy.
Latitude: These lines, also known as parallels, run horizontally around the Earth, parallel to the equator. The equator, situated at 0 degrees latitude, divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Each degree of latitude is approximately 111 kilometers (69 miles) apart. As one moves further away from the equator, the lines of latitude become smaller, converging at the poles.
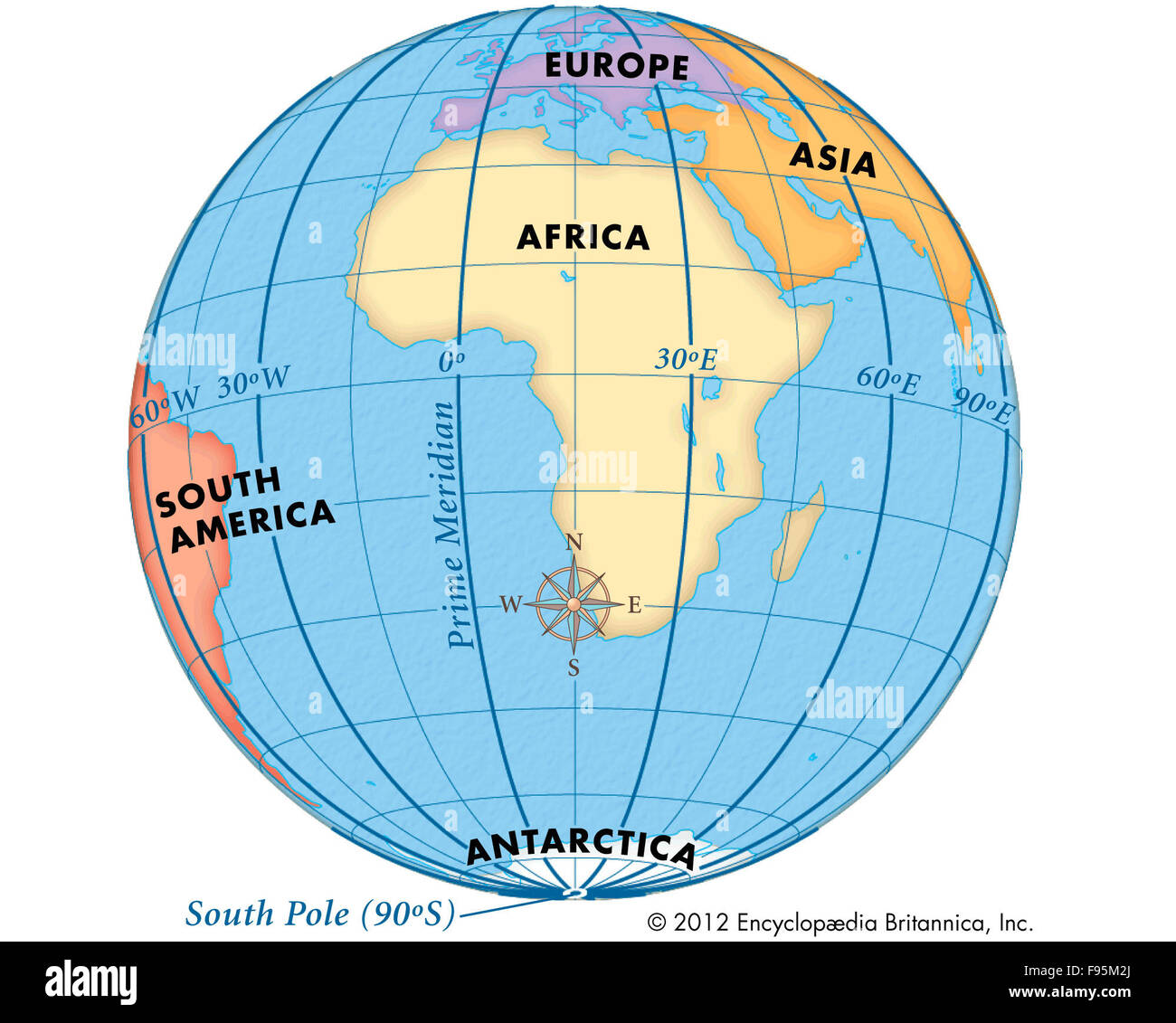
Longitude: These lines, also known as meridians, run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, intersecting with the equator at right angles. The prime meridian, located at 0 degrees longitude, passes through Greenwich, England, and serves as the reference point for measuring longitude. Each degree of longitude is also approximately 111 kilometers (69 miles) apart at the equator. However, unlike latitude, these lines converge at the poles, becoming closer together as they approach.
The Power of Coordinates: Locating Points on the Globe
The intersection of a latitude line and a longitude line forms a unique coordinate point, allowing for the precise identification of any location on the Earth’s surface. This coordinate system, expressed as latitude and longitude, is fundamental to navigation, mapping, and various technological applications.
Navigation: Sailors, pilots, and explorers have relied on latitude and longitude for centuries to navigate across oceans and continents. By referencing celestial bodies and using navigational instruments, they could determine their position relative to the grid system and plot their course.
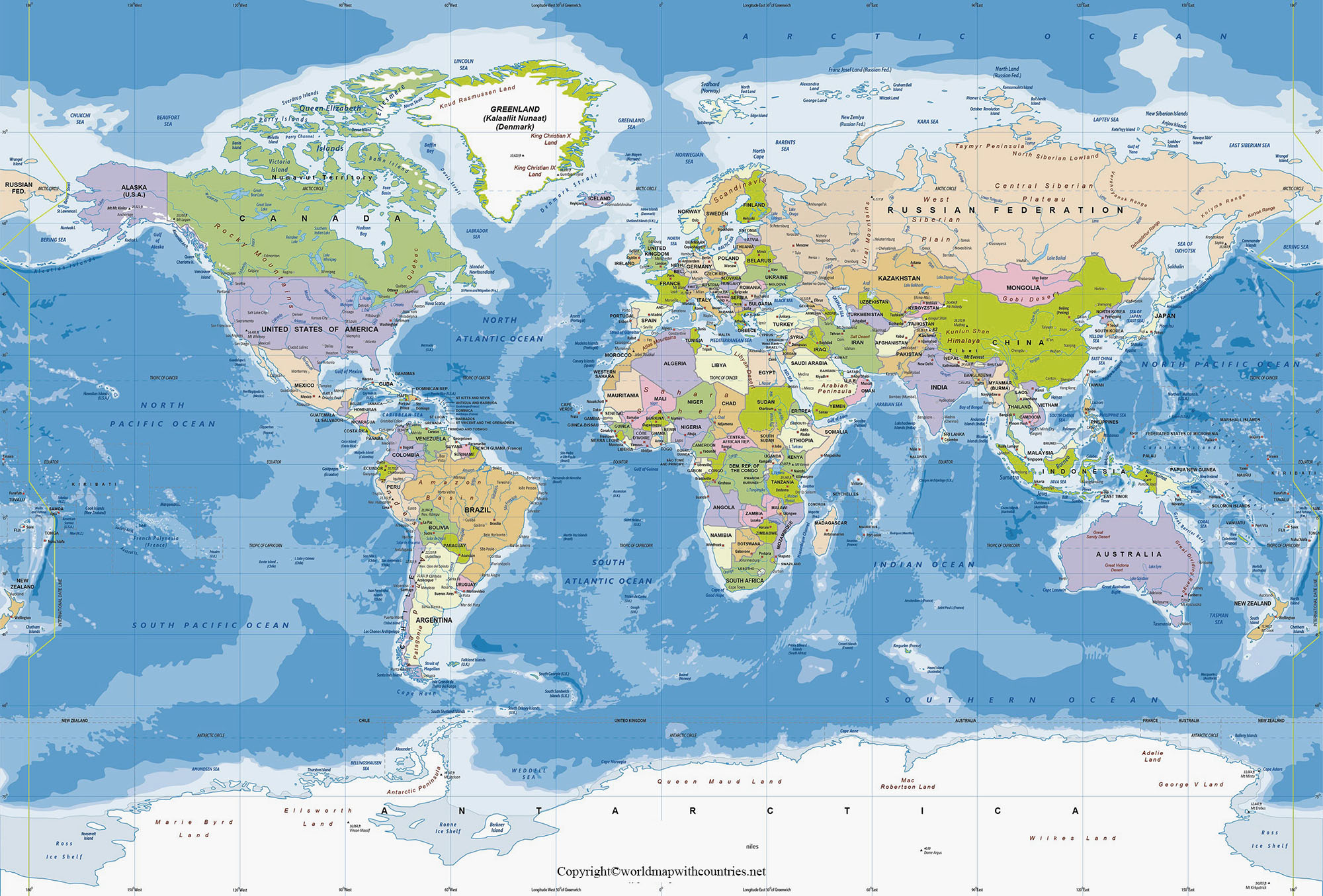
Mapping: Cartographers use latitude and longitude to create accurate representations of the Earth’s surface. By plotting points on a map based on their coordinates, they can depict continents, countries, cities, and even individual buildings with remarkable detail.
Technology: Modern technologies like GPS (Global Positioning System) and GIS (Geographic Information Systems) heavily rely on latitude and longitude. GPS receivers use satellite signals to pinpoint a user’s location, while GIS systems utilize spatial data to analyze and visualize geographical information.
Applications of World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
World maps with latitude and longitude extend far beyond basic navigation and mapping. They serve as powerful tools for understanding and addressing critical issues in various fields, including:
Environmental Studies: Maps can help visualize and analyze environmental data, such as deforestation rates, pollution levels, and climate change impacts. By overlaying data onto a grid system, researchers can identify patterns, trends, and hotspots, facilitating informed decision-making for environmental protection.
Social Sciences: Socioeconomic indicators, such as population density, poverty rates, and access to healthcare, can be visualized on maps to reveal spatial patterns and inequalities. This data can guide policy development and resource allocation for social development initiatives.
Disaster Management: During natural disasters, maps are crucial for coordinating rescue efforts, distributing aid, and assessing damage. By understanding the geographical context of a disaster, authorities can effectively manage resources and minimize casualties.
Urban Planning: Maps play a vital role in urban planning, enabling the analysis of land use, infrastructure development, and transportation networks. By visualizing these elements, planners can make informed decisions about city growth and development.
Importance and Benefits of World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
The use of latitude and longitude on world maps offers numerous benefits, underscoring their importance in our interconnected world:
Precise Location: The grid system enables precise location identification, eliminating ambiguity and ensuring accurate communication of geographical information.
Spatial Relationships: Maps allow us to visualize the relative positions of different places, understanding distances, directions, and connections between locations.
Data Visualization: Maps provide a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing geographical data, revealing patterns, trends, and insights that might not be apparent otherwise.
Decision-Making: Maps support informed decision-making in various fields by providing a spatial context for data analysis and understanding.
Global Connectivity: Maps facilitate communication and collaboration across the globe, fostering a sense of interconnectedness and shared understanding of our planet.
FAQs about World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
Q: How do I use latitude and longitude to find a location on a map?
A: Each location on Earth has a unique latitude and longitude coordinate. To find a location, locate the latitude line (parallel) and longitude line (meridian) that intersect at that point.
Q: Are there different types of world maps?
A: Yes, there are various types of world maps, including Mercator projections, Robinson projections, and Winkel Tripel projections. Each projection distorts the Earth’s surface in different ways, affecting the accuracy of distances and shapes.
Q: What are the advantages of using digital world maps?
A: Digital maps offer several advantages, including interactivity, data layering, and access to real-time information. They can be easily updated, customized, and integrated with other applications.
Q: How can I create my own world map with latitude and longitude?
A: Several software programs, such as Google Earth, QGIS, and ArcGIS, allow users to create custom maps with latitude and longitude grids.
Tips for Using World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
1. Understand Projections: Be aware of the map projection used, as it can influence the accuracy of distances and shapes.
2. Use Appropriate Tools: Utilize appropriate tools, such as compasses, rulers, and protractors, for accurate measurements and calculations.
3. Interpret Data: Pay attention to the data represented on the map and its units of measurement.
4. Consider Scale: Understand the map’s scale to accurately interpret distances and areas.
5. Stay Updated: Use current and reliable sources for map information, as geographical data can change over time.
Conclusion: Navigating a World Connected by Latitude and Longitude
World maps with latitude and longitude remain indispensable tools for understanding our planet and navigating its complexities. From exploring distant lands to tackling global challenges, these maps serve as a foundation for spatial awareness, data visualization, and informed decision-making. As our world becomes increasingly interconnected, the importance of understanding and utilizing these powerful tools will only continue to grow. By embracing the power of latitude and longitude, we can navigate the complexities of our world with greater clarity and purpose.

/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Globe: Understanding World Maps with Latitude and Longitude. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!