Navigating the Globe: Understanding the Equator and Tropics on a Blank World Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Globe: Understanding the Equator and Tropics on a Blank World Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Globe: Understanding the Equator and Tropics on a Blank World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Globe: Understanding the Equator and Tropics on a Blank World Map

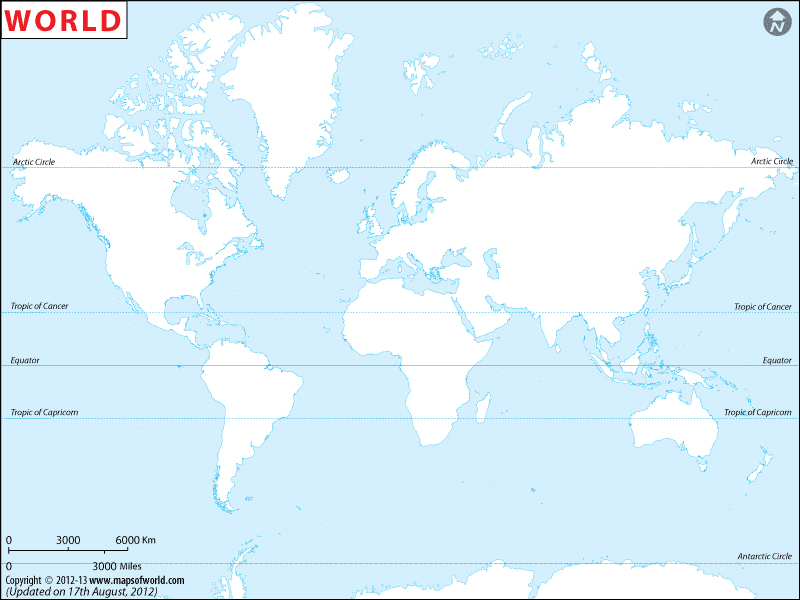
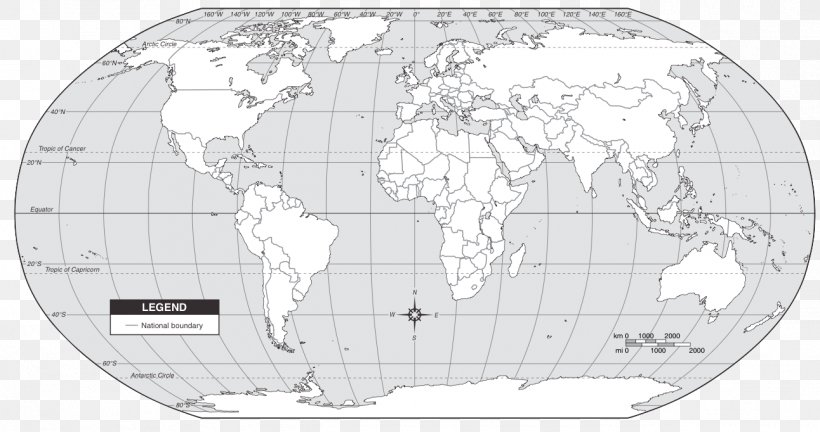
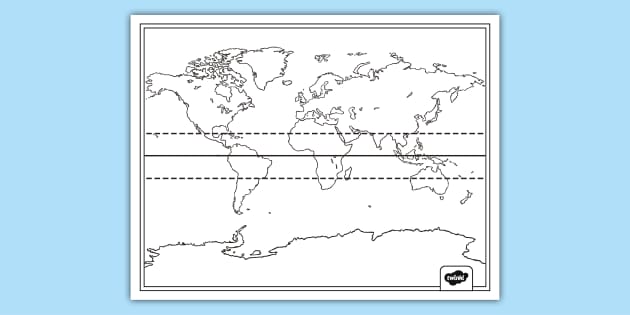
A blank world map, devoid of political boundaries and geographical details, presents a pristine canvas upon which to embark on a journey of discovery. This uncluttered representation of the Earth’s surface allows for a deeper understanding of fundamental geographical concepts, particularly the significance of the equator and tropics.
The Equator: A Line of Symmetry
The equator, an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, is the planet’s most prominent geographical feature. It divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, acting as a line of symmetry for both landmasses and oceans. The equator’s significance stems from its unique position:
- Equal Day and Night: At the equator, the sun’s rays strike the Earth at a near-perpendicular angle throughout the year. This results in equal day and night lengths, a phenomenon absent in other latitudes.
- Climate and Weather Patterns: The equator experiences consistent, high temperatures due to the direct solar radiation. This contributes to the formation of tropical rainforests, characterized by high humidity and abundant rainfall.
- Global Circulation Patterns: The equator plays a crucial role in the Earth’s atmospheric circulation. The intense heating at the equator leads to the rising of warm, moist air, which then cools and releases precipitation. This process drives global wind patterns and ocean currents.
The Tropics: Zones of Abundant Sunlight
The tropics, encompassing the regions between the Tropic of Cancer (23.5 degrees North) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5 degrees South), are defined by their proximity to the equator. These zones receive a high amount of solar radiation throughout the year, resulting in warm temperatures and distinctive climate patterns:
- Tropical Climates: The tropics are characterized by a variety of tropical climates, including tropical rainforests, savannas, and deserts. These climates are defined by their high temperatures, distinct wet and dry seasons, and often abundant rainfall.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: The tropics are home to a staggering diversity of flora and fauna, making them crucial for global biodiversity conservation. The abundance of sunlight and consistent rainfall support a wide range of ecosystems and species.
- Economic Importance: The tropics are rich in natural resources, including agricultural products, minerals, and timber. These resources contribute significantly to the global economy and support the livelihoods of millions.
Using a Blank World Map with Equator and Tropics:
A blank world map featuring the equator and tropics serves as a valuable tool for understanding the Earth’s geography and its influence on climate, weather, and ecosystems. It provides a visual representation of:
- Latitude and Longitude: The equator serves as the baseline for latitude measurements, while the tropics highlight the zones between 23.5 degrees North and 23.5 degrees South.
- Global Distribution of Land and Water: The map reveals the distribution of continents and oceans, emphasizing the concentration of landmasses in the Northern Hemisphere and the dominance of water in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Climate Zones: The equator and tropics act as visual indicators of the Earth’s major climate zones, allowing for a comparative study of tropical, temperate, and polar regions.
- Geographic Relationships: The map facilitates understanding the interconnectedness of different regions, highlighting the impact of the equator and tropics on global weather patterns and ocean currents.
Benefits of Using a Blank World Map with Equator and Tropics:
- Enhanced Learning: The blank map encourages active engagement and fosters a deeper understanding of geographical concepts.
- Visual Representation: The map provides a clear and concise visual representation of the Earth’s fundamental geographical features.
- Focus on Key Concepts: By omitting unnecessary details, the map emphasizes the importance of the equator and tropics.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: The blank map can be customized with additional information, such as political boundaries, elevation contours, or climate data.
FAQs about Blank World Maps with Equator and Tropics:
Q: What are some examples of how a blank world map with equator and tropics can be used in education?
A: This map can be used for a variety of educational purposes, including:
- Geography lessons: To illustrate the concepts of latitude, longitude, and climate zones.
- Social studies lessons: To explore the distribution of population, cultural regions, and economic activities.
- Science lessons: To understand the Earth’s climate patterns, ocean currents, and biodiversity hotspots.
Q: What are some of the challenges associated with using a blank world map with equator and tropics?
A: One challenge is the potential for oversimplification. While the blank map is useful for focusing on key concepts, it may not adequately represent the complexity of the Earth’s geography.
Q: How can a blank world map with equator and tropics be used in professional settings?
A: This map can be used by professionals in various fields, such as:
- Environmental science: To analyze the impact of climate change on different regions.
- International business: To understand the global distribution of resources and markets.
- Geopolitics: To study the strategic importance of different geographic locations.
Tips for Using a Blank World Map with Equator and Tropics:
- Choose the right scale: Select a map that is appropriate for the intended purpose, considering the level of detail needed.
- Use different colors: Employ different colors to highlight specific features, such as landmasses, oceans, climate zones, or elevation contours.
- Add labels and annotations: Include labels for key geographical features, such as continents, oceans, and major cities.
- Encourage active learning: Engage students or colleagues in discussions and activities that promote understanding and critical thinking.
Conclusion:
A blank world map with the equator and tropics serves as a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding the Earth’s fundamental geographical features. It provides a foundation for exploring the interconnectedness of different regions, the influence of climate on human societies, and the importance of sustainable management of the planet’s resources. By using this map effectively, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and interconnected nature of our world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Globe: Understanding the Equator and Tropics on a Blank World Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!