Navigating the Boston T: A Comprehensive Guide to the City’s Subway Network
Related Articles: Navigating the Boston T: A Comprehensive Guide to the City’s Subway Network
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Boston T: A Comprehensive Guide to the City’s Subway Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Boston T: A Comprehensive Guide to the City’s Subway Network
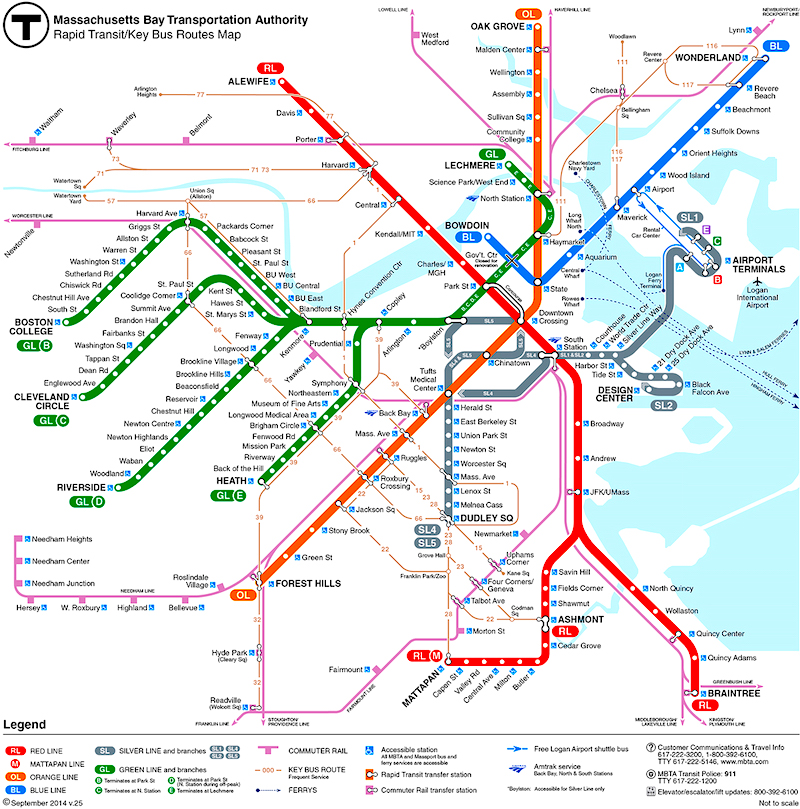
The Boston T, officially known as the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) subway system, is an intricate network of underground and elevated lines that forms the backbone of public transportation in Boston and its surrounding communities. Its complex route map, while initially daunting, unveils a fascinating system designed to connect diverse neighborhoods and facilitate seamless travel throughout the city. This article delves into the intricacies of the Boston T map, providing a comprehensive understanding of its structure, routes, and operational nuances.
Understanding the Map’s Structure
The Boston T map, unlike many other subway systems, utilizes a color-coded system to distinguish its various lines. Each line is represented by a specific color, with corresponding stations marked along the route. This color-coding makes it relatively easy to identify lines and plan routes. However, the map’s complexity stems from the interconnected nature of the lines, with frequent transfers between different routes.
Exploring the Lines
The Boston T boasts a network of eight distinct lines:
- Red Line: This line, marked in red, is the longest and most heavily traveled line in the system. It runs from Alewife in the north to Braintree in the south, traversing through the heart of Boston, including Downtown Crossing, Park Street, and Harvard Square.
- Orange Line: The Orange Line, represented in orange, connects Oak Grove in the north to Forest Hills in the southwest. It serves important areas like Tufts University, Sullivan Square, and Back Bay.
- Blue Line: The Blue Line, distinguished by its blue color, runs from Wonderland in the north to Bowdoin in the south. It serves the Boston Harbor area, including Logan International Airport and the historic Charlestown Navy Yard.
- Green Line: The Green Line, marked in green, is a unique line with three branches: the B, C, and D branches. The B branch runs from Boston College in the west to Park Street in the downtown area. The C branch connects Cleveland Circle in the west to Kenmore Square in the east. The D branch operates between Riverside in the west and Park Street in the downtown area.
- Yellow Line: The Yellow Line, represented in yellow, is a short line connecting the Green Line’s B branch at Kenmore Square to the Orange Line at Ruggles.
- Silver Line: The Silver Line, marked in silver, operates as a bus rapid transit service. Its Waterfront branch runs from the World Trade Center in the south to South Station in the downtown area. The SL1 branch connects the Silver Line Waterfront branch to Logan International Airport.
- Mattapan High Speed Line: This line, often referred to as the "Mattapan Trolley," operates as an independent branch of the Red Line. It runs from Mattapan Square in the south to the Red Line at Ashmont.
- Framingham/Worcester Line: This commuter rail line connects Framingham and Worcester to Boston’s South Station.
Understanding Transfers and Interchanges
The Boston T map is characterized by numerous transfer points where passengers can seamlessly switch between lines. These interchanges are crucial for navigating the system efficiently. Notable transfer points include:
- Park Street: This station is a major hub where the Red, Green, and Orange Lines intersect.
- Downtown Crossing: This station serves as a transfer point between the Red, Green, and Orange Lines.
- South Station: This station is a major hub for the Red, Silver, and Commuter Rail Lines.
- Haymarket: This station connects the Green and Orange Lines.
- Kenmore: This station connects the Green Line’s B, C, and D branches with the Orange Line and the Yellow Line.
Navigating the System
To navigate the Boston T effectively, it is essential to:
- Consult the map: Familiarize yourself with the lines, stations, and transfer points.
- Plan your route: Utilize online tools, apps, or the MBTA’s website to plan your trip and determine the optimal route.
- Purchase a CharlieCard: This contactless fare card offers discounted fares and provides convenient access to the entire MBTA system.
- Be mindful of peak hours: During rush hour, trains can be crowded, and travel times may be longer.
- Stay informed: Check the MBTA’s website or app for service updates, delays, or closures.
Benefits of the Boston T
The Boston T offers numerous benefits:
- Accessibility: It provides convenient access to various parts of the city, connecting neighborhoods and attractions.
- Efficiency: The system offers a relatively quick and efficient mode of transportation, reducing travel time compared to driving.
- Cost-effectiveness: The T offers affordable fares, making it a budget-friendly option for commuters and visitors.
- Sustainability: The T promotes sustainable transportation, reducing traffic congestion and air pollution.
- Cultural Significance: The T is an integral part of Boston’s history and culture, contributing to the city’s vibrant character.
FAQs
Q: What are the operating hours of the Boston T?
A: The Boston T operates daily, with service hours varying depending on the line and day of the week. Generally, service begins around 5:00 AM and ends around 12:30 AM.
Q: What is the fare for using the Boston T?
A: The fare for the Boston T is based on a zone system, with prices varying depending on the distance traveled. A single ride on the T costs $2.40 with a CharlieCard and $2.60 with cash.
Q: How do I get a CharlieCard?
A: CharlieCards can be purchased at MBTA stations, online, or at select retailers.
Q: Are there any accessibility features on the Boston T?
A: The Boston T is committed to providing accessible transportation for all riders. Most stations have elevators, ramps, and Braille signage.
Q: What are some tips for navigating the Boston T?
A:
- Plan your route in advance: Use the MBTA’s website or app to plan your journey and determine the best route.
- Allow extra time for travel: Especially during peak hours, it is essential to account for potential delays.
- Be aware of your surroundings: Be mindful of your belongings and surroundings, especially in crowded areas.
- Check for service updates: Before your trip, check the MBTA’s website or app for any service disruptions or delays.
Conclusion
The Boston T is a complex yet efficient public transportation system that plays a vital role in the city’s daily life. Understanding the intricate network of lines, transfers, and operational nuances is crucial for navigating the system effectively. By familiarizing oneself with the map, planning routes, and utilizing the available resources, passengers can seamlessly traverse the city and experience its diverse attractions with ease. The Boston T serves as a testament to the city’s commitment to providing accessible, affordable, and sustainable transportation, fostering a vibrant and connected urban environment.

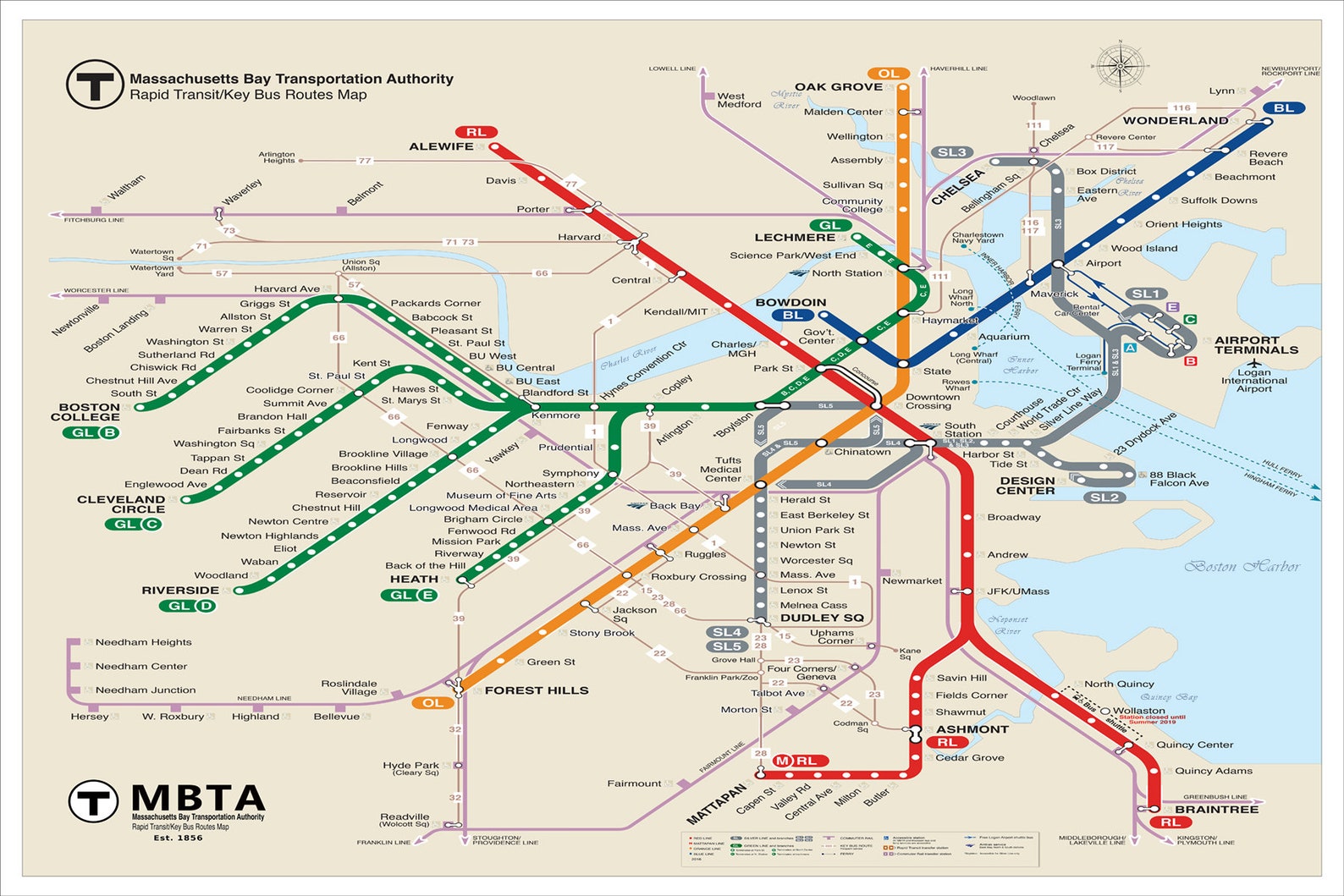



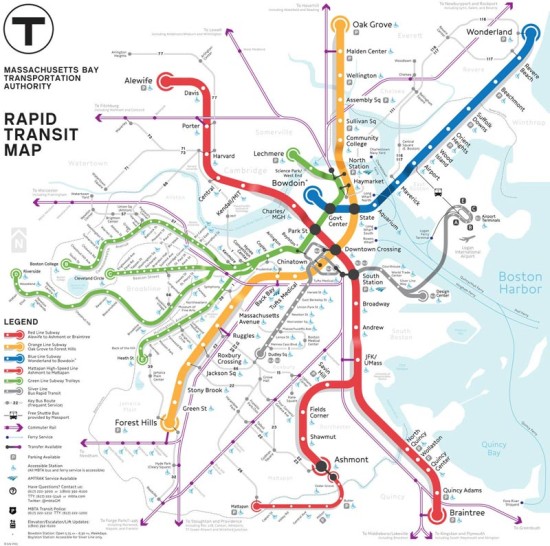


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Boston T: A Comprehensive Guide to the City’s Subway Network. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!