Navigating Kentucky: A Geographical Exploration through Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating Kentucky: A Geographical Exploration through Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Kentucky: A Geographical Exploration through Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Kentucky: A Geographical Exploration through Latitude and Longitude
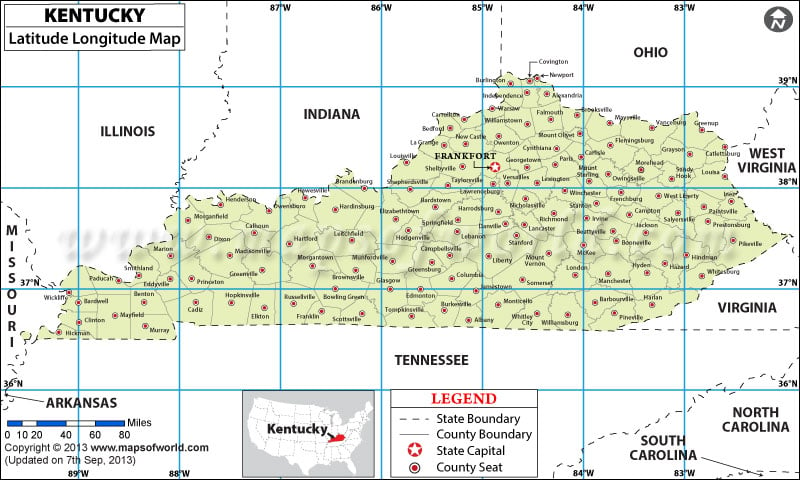
Kentucky, the "Bluegrass State," boasts a captivating landscape sculpted by rolling hills, meandering rivers, and a rich cultural heritage. Understanding its geographical layout, particularly through the lens of latitude and longitude, provides a deeper appreciation for its unique characteristics and the forces that have shaped its identity.
Kentucky’s Geographic Coordinates:
Kentucky’s position on the globe is defined by its latitude and longitude. The state lies between 36°30′ and 39°05′ North latitude and 82°20′ and 89°30′ West longitude. This geographical location places Kentucky squarely within the eastern United States, bordering the Ohio River to the north and the Mississippi River to the west.
Latitude and Longitude: The Foundation of Geographical Understanding:
Latitude and longitude form the foundation of geographical mapping, providing a precise system for pinpointing locations on Earth.
- Latitude: Imaginary lines running parallel to the equator, measuring distance north or south of the equator.
- Longitude: Imaginary lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole, measuring distance east or west of the prime meridian.
Kentucky’s Latitude and its Impact:
Kentucky’s latitude, ranging from 36°30′ to 39°05′ North, places it within the temperate zone. This latitude contributes to the state’s distinct climate, characterized by four distinct seasons. The temperate climate supports a diverse range of plant and animal life, making Kentucky a haven for nature enthusiasts.
Kentucky’s Longitude and its Influence:
Kentucky’s longitude, spanning from 82°20′ to 89°30′ West, positions it within the eastern time zone. This longitudinal position affects daily life, aligning schedules and communication with neighboring states. It also influences the state’s proximity to major metropolitan areas, impacting trade and transportation networks.
The Importance of Latitude and Longitude in Understanding Kentucky:
Latitude and longitude are not just abstract coordinates; they hold significant implications for understanding Kentucky’s geography, climate, and cultural development.
- Climate and Agriculture: Kentucky’s latitude influences its temperate climate, supporting a variety of agricultural activities, including the cultivation of tobacco, corn, and soybeans.
- Natural Resources: The state’s geographical location contributes to its abundance of natural resources, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, shaping its industrial landscape.
- Transportation and Trade: Kentucky’s longitude, placing it within the eastern time zone, facilitates communication and trade with major East Coast cities.
- Cultural Diversity: The state’s geographical position at the crossroads of various regions has contributed to a rich cultural tapestry, blending Appalachian traditions with Southern influences.
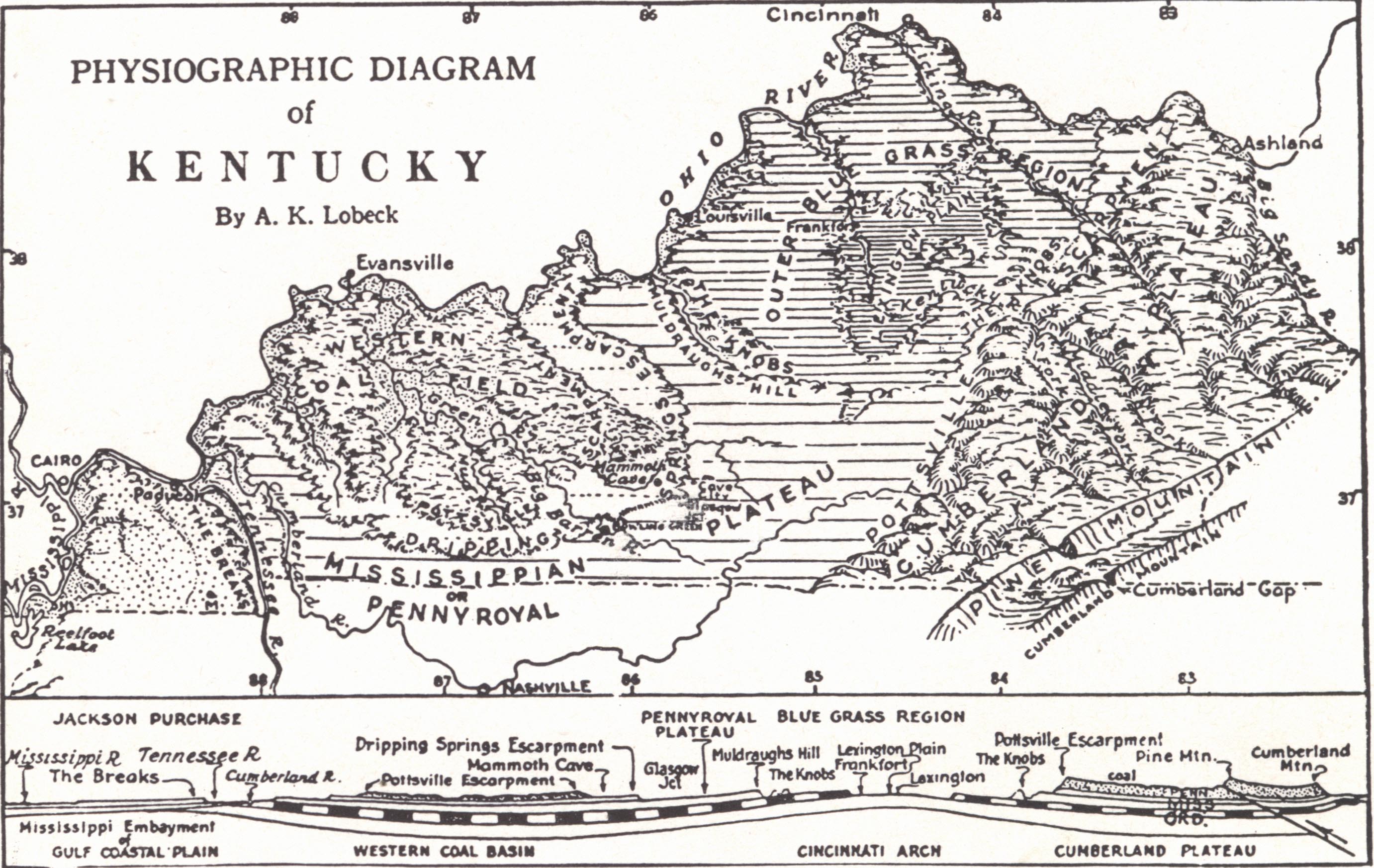
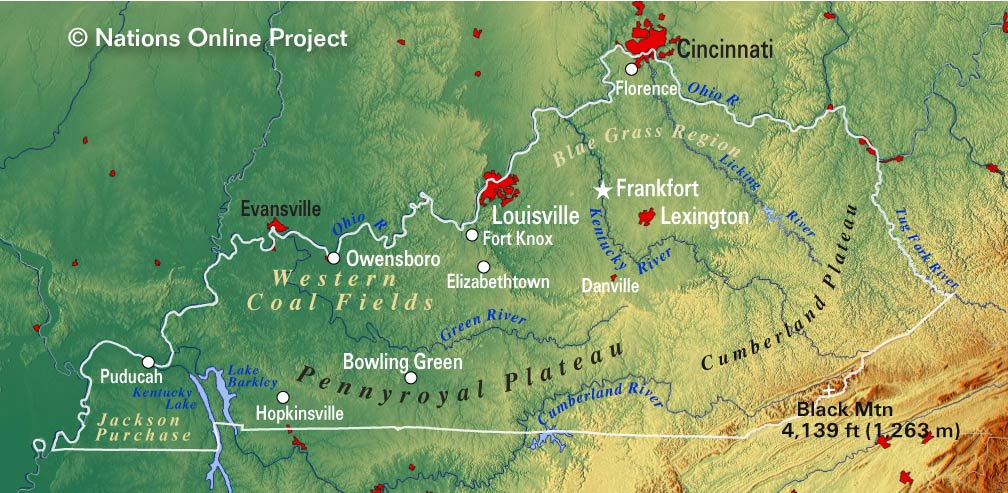
Kentucky’s Geographic Features: A Closer Look:
Kentucky’s geography is marked by a diverse landscape, shaped by geological forces and human intervention.
- Appalachian Mountains: The eastern part of the state is dominated by the Appalachian Mountains, offering scenic views and opportunities for hiking and outdoor recreation.
- Kentucky River Valley: The Kentucky River carves a path through the state, creating a fertile valley known for its agricultural productivity and charming towns.
- The Ohio River: The Ohio River forms the northern border of Kentucky, serving as a vital waterway for transportation and commerce.
- The Mississippi River: The Mississippi River defines the western border, connecting Kentucky to the vast network of waterways that flow through the heartland of America.
Kentucky’s Geographic Diversity: A Source of Strength:
Kentucky’s diverse landscape, influenced by its latitude and longitude, contributes to its economic and cultural vitality.
- Tourism: The state’s natural beauty, from its rolling hills to its majestic mountains, attracts tourists from around the world, boosting the tourism industry.
- Agriculture: Kentucky’s fertile valleys support a thriving agricultural sector, producing a variety of crops and livestock.
- Energy Production: The state’s abundance of natural resources, particularly coal, fuels its energy production and industrial development.
- Cultural Heritage: The diverse landscape and cultural influences have shaped Kentucky’s unique identity, marked by its rich musical heritage, culinary traditions, and storytelling traditions.
Navigating Kentucky: The Power of Maps:
Maps, particularly those incorporating latitude and longitude, provide invaluable tools for navigating Kentucky’s diverse landscape.
- Road Maps: Road maps, utilizing latitude and longitude, help travelers navigate highways and backroads, exploring the state’s vast network of roads and attractions.
- Topographical Maps: Topographical maps, incorporating elevation data and contour lines, offer detailed insights into the state’s terrain, aiding hikers, campers, and outdoor enthusiasts.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellite imagery, utilizing latitude and longitude, provides a bird’s-eye view of Kentucky’s landscape, showcasing the state’s geographical features and human settlements.
FAQs on Kentucky’s Geography:
Q: What is the highest point in Kentucky?
A: The highest point in Kentucky is Black Mountain, located in the eastern part of the state, with an elevation of 4,145 feet above sea level.
Q: What is the lowest point in Kentucky?
A: The lowest point in Kentucky is at the Mississippi River, where the state’s western border meets the river, with an elevation of 257 feet above sea level.
Q: What is the average elevation of Kentucky?
A: The average elevation of Kentucky is approximately 750 feet above sea level, reflecting its predominantly hilly terrain.
Q: What are the major rivers in Kentucky?
A: The major rivers in Kentucky include the Ohio River, the Mississippi River, the Kentucky River, the Cumberland River, and the Tennessee River.
Q: What are the major cities in Kentucky?
A: The major cities in Kentucky include Louisville, Lexington, Bowling Green, Owensboro, and Covington.
Tips for Exploring Kentucky’s Geography:
- Plan your trip: Utilize maps, including those incorporating latitude and longitude, to plan your itinerary, identifying points of interest and potential routes.
- Embrace the outdoors: Explore Kentucky’s diverse landscape through hiking, camping, fishing, and other outdoor activities.
- Learn about the history: Visit historical sites and museums to gain insights into the state’s rich cultural heritage.
- Savor the local cuisine: Indulge in Kentucky’s culinary delights, from its famous bourbon to its traditional dishes.
Conclusion:
Kentucky’s geography, defined by its latitude and longitude, plays a crucial role in shaping its climate, natural resources, transportation networks, and cultural development. By understanding the state’s geographical coordinates and the forces that have shaped its landscape, we gain a deeper appreciation for the "Bluegrass State," its unique character, and its enduring appeal. From its rolling hills to its majestic mountains, Kentucky offers a captivating tapestry of experiences for visitors and residents alike.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Kentucky: A Geographical Exploration through Latitude and Longitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!