Mapping Zip Codes: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Geographic Data
Related Articles: Mapping Zip Codes: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Geographic Data
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping Zip Codes: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Geographic Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Zip Codes: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Geographic Data

The ability to map zip codes is a powerful tool for businesses, researchers, and individuals alike. It allows for the visualization of geographic data, providing insights into population demographics, market trends, and spatial relationships. This article will delve into the various methods of mapping zip codes, exploring the necessary tools, data sources, and best practices for creating effective and informative maps.
Understanding the Significance of Zip Code Mapping
Zip codes, originally designed for efficient mail delivery, have evolved into valuable identifiers of geographic regions. They offer a granular level of spatial information, enabling the analysis of data within specific areas. Mapping zip codes unlocks a plethora of applications, including:
- Market Research and Analysis: Identifying potential customer bases, analyzing market penetration, and understanding consumer behavior within specific regions.
- Real Estate and Property Management: Determining property values, identifying desirable neighborhoods, and understanding market trends.
- Public Health and Social Services: Mapping disease outbreaks, identifying vulnerable populations, and understanding healthcare access disparities.
- Urban Planning and Development: Assessing population density, identifying areas for infrastructure development, and understanding community needs.
- Environmental Studies: Analyzing pollution patterns, identifying areas of ecological vulnerability, and understanding the impact of environmental changes.
Methods for Mapping Zip Codes
Several approaches can be employed to map zip codes, each offering unique advantages and limitations.
1. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Software
GIS software, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo, provides robust tools for creating, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data. These platforms offer:
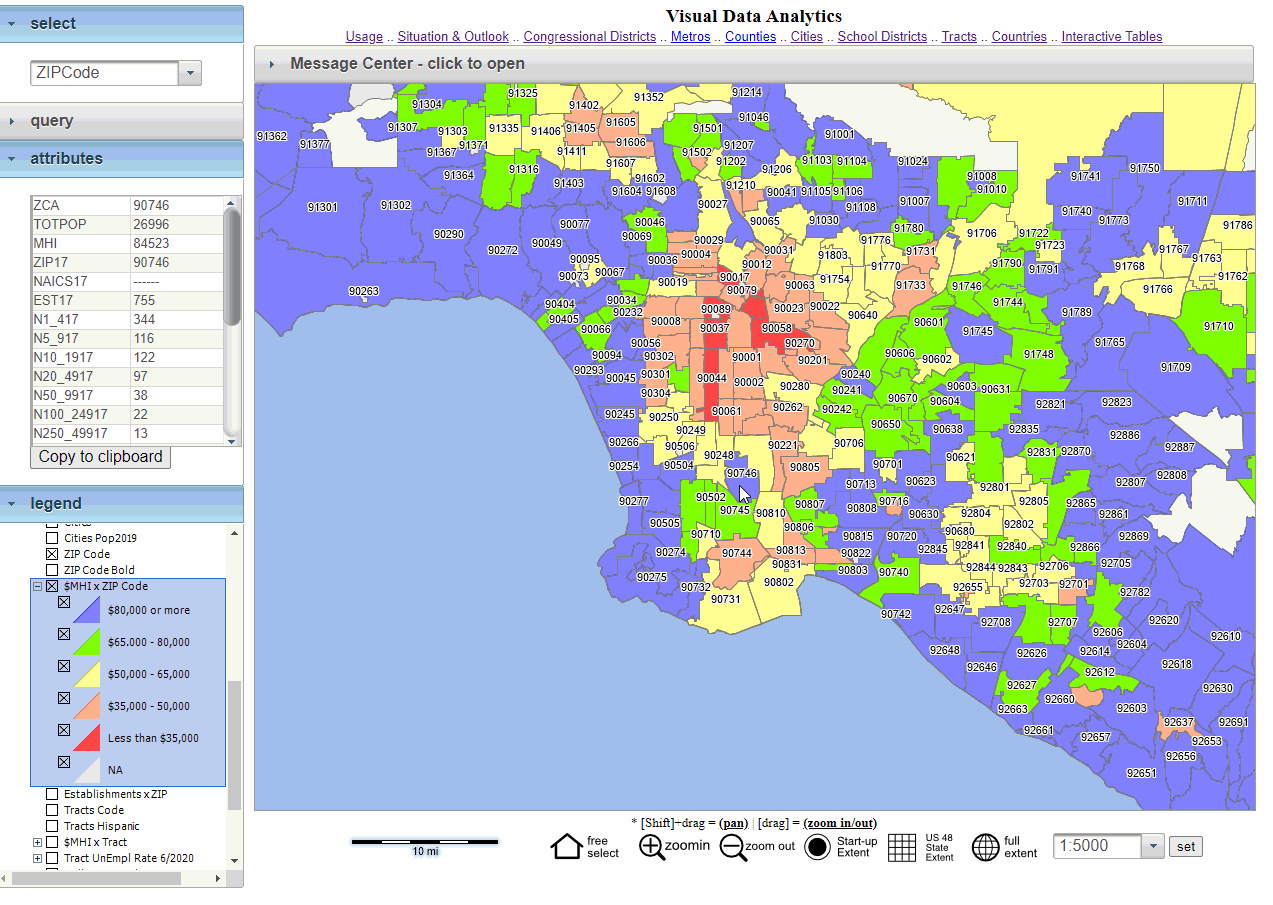
- Pre-built Zip Code Shapefiles: Many GIS platforms include pre-built shapefiles containing the geographic boundaries of zip codes. These files can be directly imported into the software, enabling the visualization of zip code areas on a map.
- Data Integration and Analysis: GIS software allows users to integrate zip code data with other datasets, such as population demographics, income levels, or business locations. This integration enables complex spatial analyses and the creation of thematic maps highlighting specific patterns or trends.
- Customization and Visualization: GIS platforms offer advanced tools for map customization, including the ability to change colors, symbols, and labels. This allows for the creation of visually appealing and informative maps tailored to specific needs.
2. Online Mapping Tools
Several online platforms provide user-friendly interfaces for mapping zip codes, often without requiring specialized software. Some popular options include:
- Google Maps: Google Maps offers basic functionality for plotting zip codes, allowing users to visualize their location and surrounding areas. While limited in terms of advanced analysis, Google Maps is accessible and easy to use.
- Mapbox: Mapbox is a cloud-based mapping platform that provides developers with tools for creating custom maps. It offers APIs and libraries for integrating zip code data into web applications, allowing for interactive and dynamic map visualizations.
- CartoDB: CartoDB is a cloud-based platform that combines mapping and data analysis features. It allows users to upload and visualize data, including zip codes, and create interactive maps with customizable styles.
3. Spreadsheet Software and Data Visualization Tools
Mapping zip codes can be achieved using spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets in conjunction with data visualization tools. This approach involves:
- Data Preparation: Obtaining a dataset containing zip codes and corresponding geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude). This data can be sourced from public databases or purchased from data providers.
- Visualization Tools: Spreadsheet software can be used to create basic scatter plots or heatmaps using the latitude and longitude data associated with zip codes. Alternatively, data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI offer more advanced features for creating interactive and dynamic maps.
Data Sources for Zip Code Mapping
Acquiring accurate and up-to-date zip code data is crucial for effective mapping. Several sources can provide the necessary information:
- United States Postal Service (USPS): The USPS maintains a database of zip codes and their corresponding geographic boundaries. This data is publicly available and can be downloaded in various formats.
- United States Census Bureau: The Census Bureau provides detailed demographic and geographic data, including zip code boundaries and population statistics.
- Commercial Data Providers: Companies like Esri, MapInfo, and Geocoding Solutions offer comprehensive zip code databases with additional data points, such as income levels, household size, and business locations.
Best Practices for Effective Zip Code Mapping
Creating informative and impactful zip code maps requires careful planning and execution. Following these best practices can enhance the quality and clarity of your maps:
- Define Objectives: Clearly define the purpose of the map and the specific insights you aim to convey. This will guide your data selection, map design, and analysis.
- Choose Appropriate Data: Select relevant data sources and ensure the data is accurate, up-to-date, and consistent with your objectives.
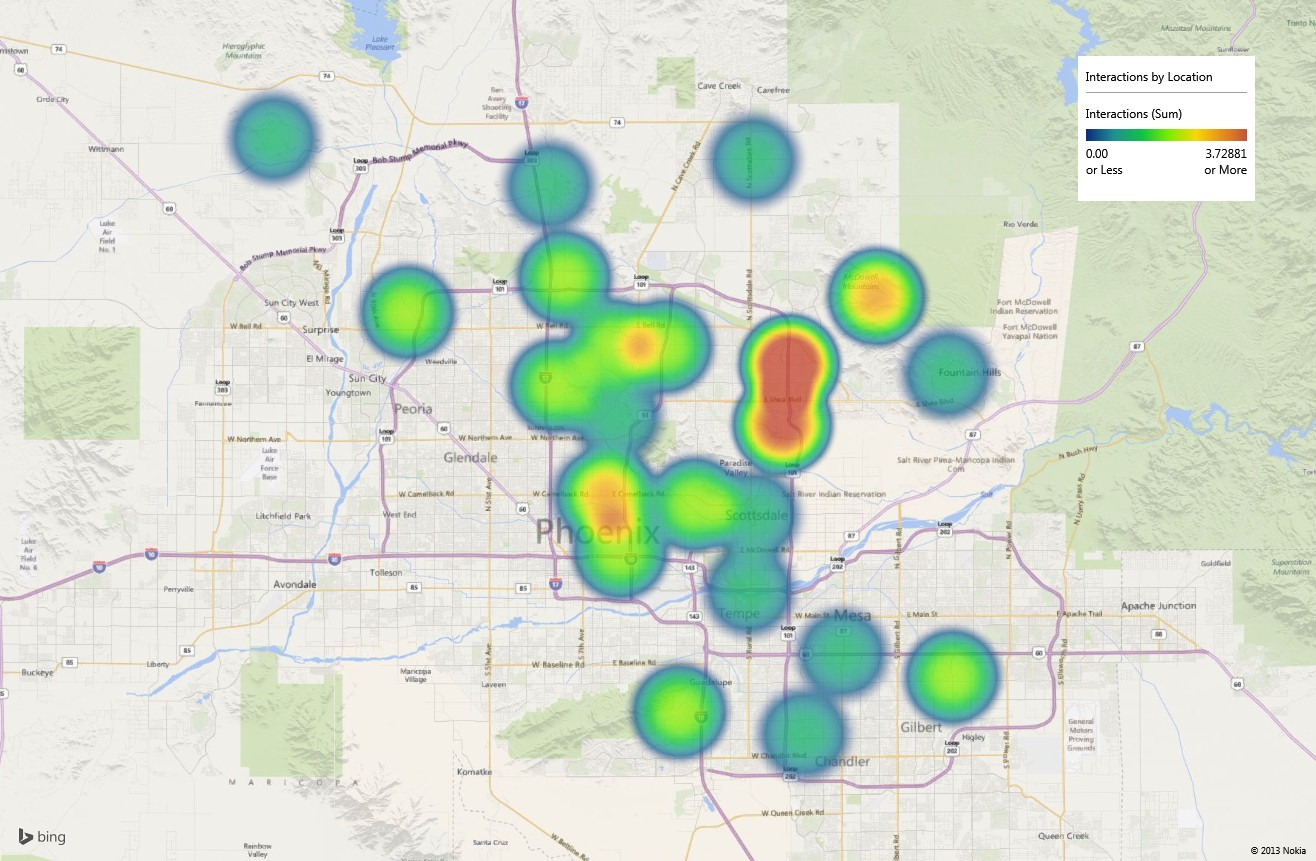
- Data Visualization Techniques: Select visualization techniques that effectively communicate the data patterns and relationships. Consider using different map types (choropleth, dot density, heatmap) depending on the data and message.
- Map Design and Aesthetics: Employ clear and consistent labeling, use appropriate colors and symbols, and maintain a visually appealing and easy-to-understand design.
- Transparency and Accuracy: Clearly indicate data sources, acknowledge limitations, and ensure the map accurately reflects the data being presented.
FAQs on Mapping Zip Codes
Q: What is the difference between a zip code and a ZIP+4 code?
A: A zip code is a five-digit code that identifies a general geographic area, while a ZIP+4 code is a nine-digit code that pinpoints a specific delivery location within a zip code area.
Q: How can I obtain zip code boundaries for mapping?
A: Zip code boundaries can be obtained from the USPS, the Census Bureau, or commercial data providers. These sources offer various formats, including shapefiles, CSV files, and geoJSON.
Q: What are some common challenges in mapping zip codes?
A: Challenges include data accuracy, consistency, and timeliness. Zip code boundaries can change over time, and data sources may not always be up-to-date. Additionally, some zip codes may cover large geographic areas, potentially masking local variations.
Q: What are some advanced techniques for mapping zip codes?
A: Advanced techniques include spatial analysis, geostatistical modeling, and network analysis. These methods allow for the identification of spatial patterns, the prediction of data values, and the analysis of geographic relationships.
Tips for Effective Zip Code Mapping
- Start with a clear objective: Determine the specific information you want to convey with your map.
- Use a consistent data source: Ensure all zip code data originates from a single reliable source to maintain accuracy and consistency.
- Explore different map types: Experiment with various map types to find the most effective representation for your data.
- Pay attention to map design: Use clear labeling, appropriate colors, and visually appealing elements to enhance clarity and impact.
- Always acknowledge limitations: Clearly communicate any data limitations or potential biases in your map.
Conclusion
Mapping zip codes is a powerful tool for visualizing geographic data and gaining insights into spatial relationships. By understanding the different methods, data sources, and best practices, individuals and organizations can create effective maps that inform decision-making, enhance research, and drive business strategies. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of zip code mapping will further expand, providing even more opportunities for exploring and understanding the world around us.


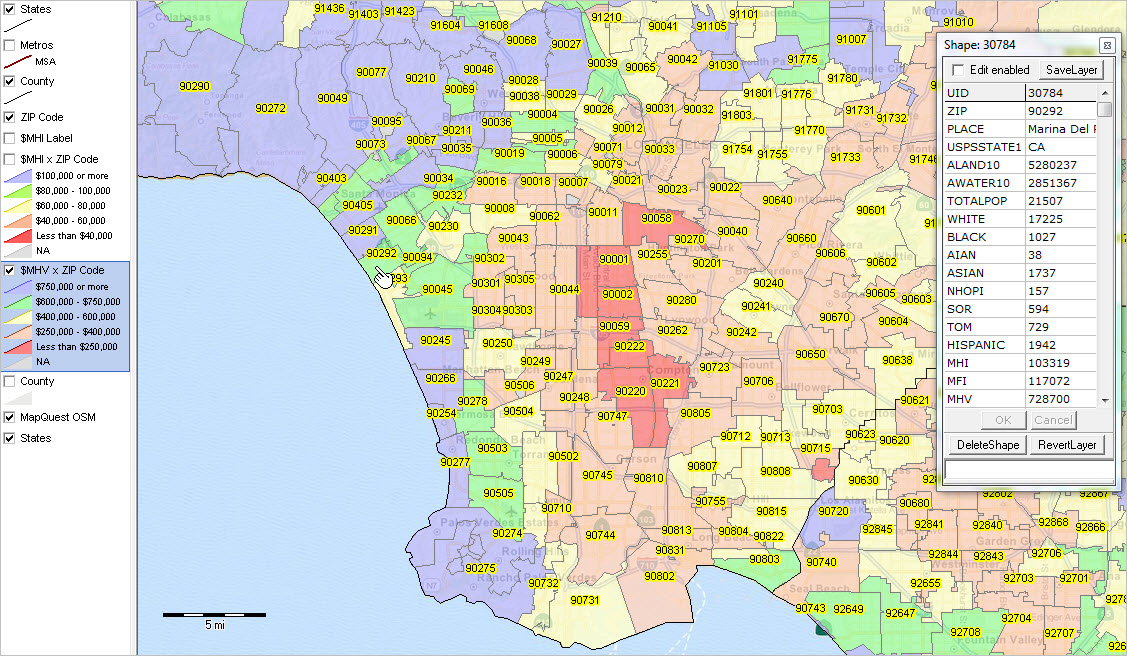
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Zip Codes: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Geographic Data. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!