Mapping with Zip Codes: A Comprehensive Guide to Spatial Analysis and Data Visualization
Related Articles: Mapping with Zip Codes: A Comprehensive Guide to Spatial Analysis and Data Visualization
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping with Zip Codes: A Comprehensive Guide to Spatial Analysis and Data Visualization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping with Zip Codes: A Comprehensive Guide to Spatial Analysis and Data Visualization

Zip codes, seemingly simple numerical sequences, hold a wealth of information beyond their primary function of facilitating mail delivery. They serve as a powerful tool for spatial analysis and data visualization, providing a granular level of geographic insight that can inform a wide range of applications. This article delves into the multifaceted world of mapping with zip codes, exploring its utility, benefits, and various applications.
The Significance of Zip Codes in Mapping:
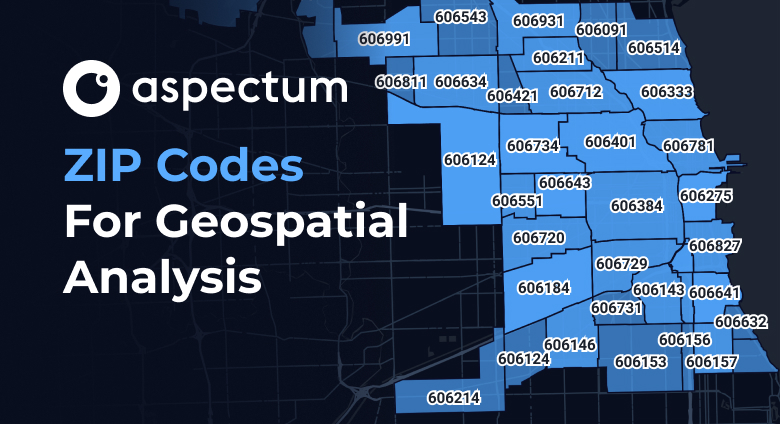
Zip codes, officially known as ZIP Codes (Zone Improvement Plan), represent a hierarchical system of postal codes used in the United States. Each code corresponds to a specific geographic area, typically encompassing a neighborhood, town, or part of a larger city. This spatial association makes zip codes ideal for mapping purposes, offering a structured framework for visualizing and analyzing data geographically.
Advantages of Using Zip Codes for Mapping:
- Granularity and Detail: Zip codes provide a relatively fine-grained level of detail compared to broader geographical divisions like states or counties. This granularity enables a more localized understanding of data distribution and trends.
- Accessibility and Availability: Zip code data is readily accessible and widely available, making it a convenient resource for mapping projects. Numerous public and private databases offer comprehensive zip code information, including geographic boundaries and demographic data.
- Standardization and Consistency: The standardized nature of zip codes ensures consistency across data sets, facilitating accurate mapping and analysis. The consistent structure of zip codes allows for easy integration with other data sources.
- Data Integration and Analysis: Zip codes can be readily integrated with other datasets, enabling comprehensive spatial analysis. By linking zip codes with demographic, economic, or social data, researchers can gain insights into the spatial relationships between different variables.
Applications of Zip Code Mapping:
The versatility of zip code mapping extends across diverse fields, impacting various aspects of our lives. Here are some prominent applications:
- Business and Marketing: Businesses leverage zip code mapping for targeted marketing campaigns, identifying potential customer bases and optimizing delivery routes. Market research firms use zip codes to analyze consumer behavior and market trends within specific geographic areas.
- Real Estate and Urban Planning: Real estate professionals employ zip code mapping to analyze property values, market trends, and identify desirable neighborhoods. Urban planners use zip code data to understand population density, infrastructure needs, and community demographics.
- Healthcare and Public Health: Healthcare providers utilize zip code mapping to assess patient demographics, identify areas with high disease prevalence, and optimize healthcare resource allocation. Public health officials use zip code data to track disease outbreaks, monitor environmental hazards, and implement targeted public health interventions.
- Education and Social Sciences: Educators and social scientists rely on zip code mapping to analyze school performance, identify educational disparities, and understand social and economic trends within specific communities.
- Emergency Response and Disaster Management: Emergency responders and disaster management agencies use zip code mapping to locate affected areas, assess damage, and deploy resources effectively during emergencies.
Types of Maps Using Zip Codes:
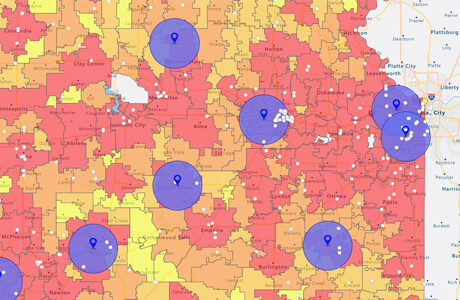
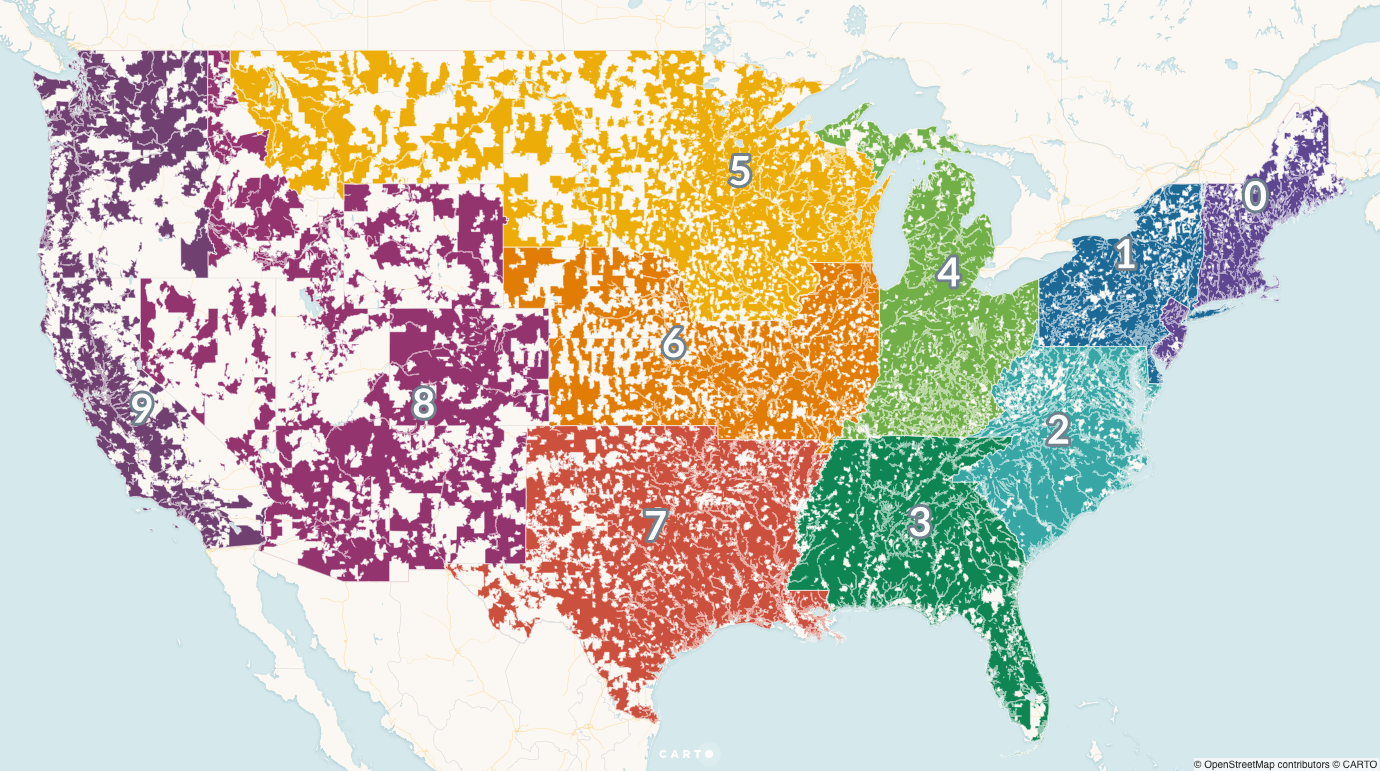
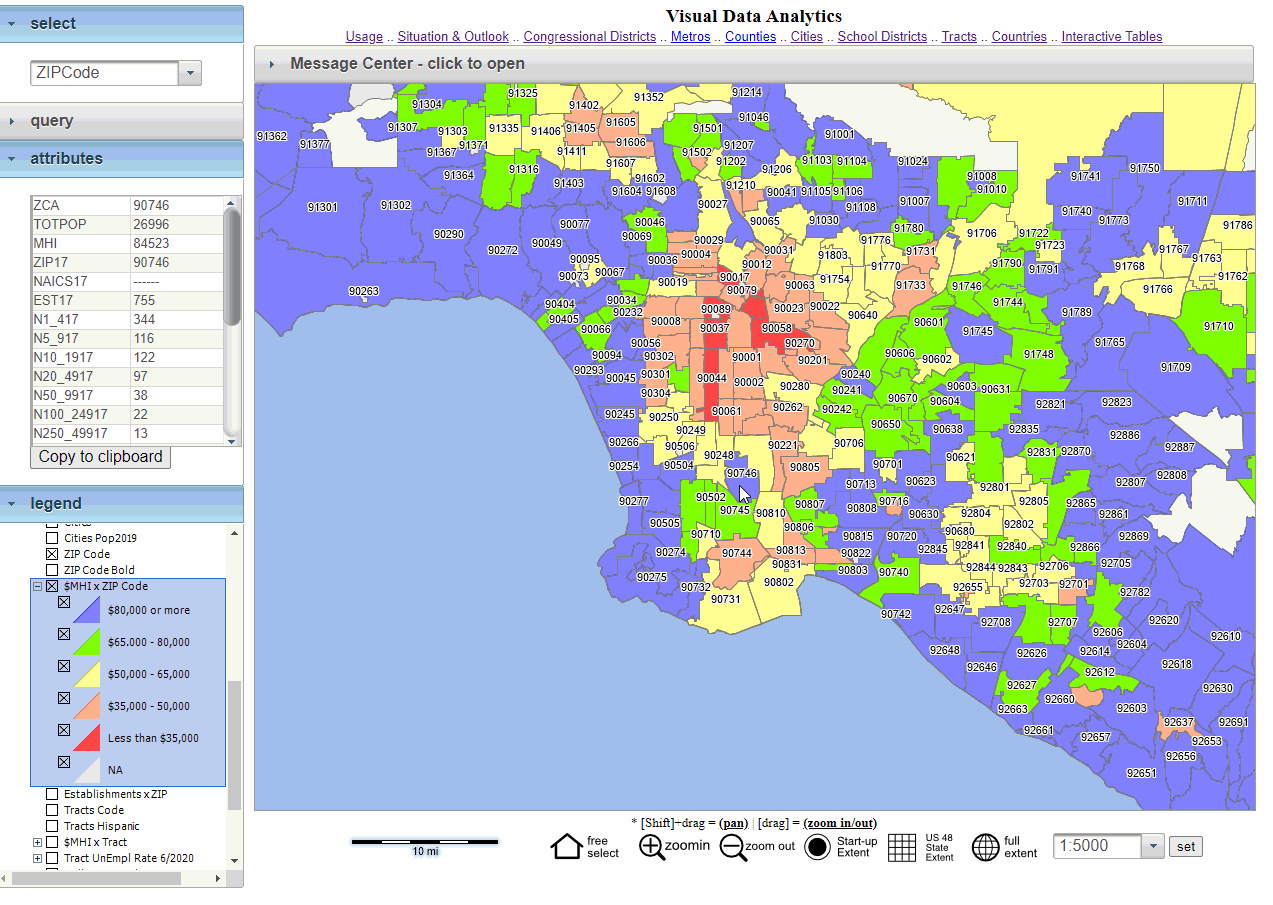
- Choropleth Maps: These maps use color variations to represent data values across different zip code areas. Darker shades typically indicate higher values, while lighter shades represent lower values. Choropleth maps are useful for visualizing data distributions, identifying patterns, and highlighting spatial disparities.
- Dot Density Maps: These maps use dots to represent data points, with the density of dots indicating the concentration of data within each zip code area. Dot density maps are effective for visualizing data clusters, identifying areas with high or low concentrations, and providing a visual representation of data distribution.
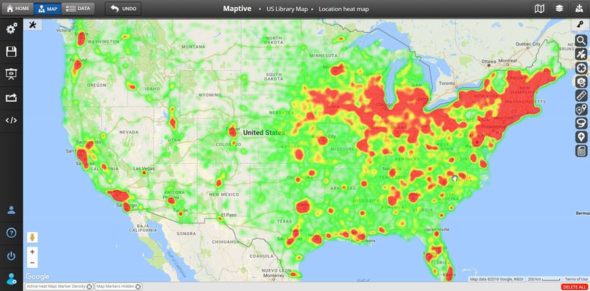
- Heat Maps: These maps use color gradients to depict data density or intensity across different zip code areas. Warmer colors typically represent higher values, while cooler colors represent lower values. Heat maps are useful for identifying areas with high data concentration, highlighting areas of interest, and visualizing data trends.
- Flow Maps: These maps illustrate the movement of people, goods, or information between different zip code areas. Flow maps use lines or arrows to represent the direction and volume of movement. They are valuable for understanding transportation patterns, migration trends, and the flow of goods and services.
Challenges and Considerations:
While zip code mapping offers a powerful analytical tool, it is essential to acknowledge potential limitations:
- Spatial Heterogeneity: Zip codes represent a broad geographic area, and data values within a single zip code may vary significantly. This heterogeneity can affect the accuracy of analyses and interpretations.
- Data Availability and Accuracy: Data availability and accuracy can vary across different zip codes and datasets. It is crucial to verify data sources and ensure data quality for accurate and reliable mapping.
- Privacy Concerns: Zip codes can be used to identify individuals, raising concerns about privacy and data security. It is essential to handle zip code data responsibly and ethically, ensuring data anonymization and appropriate usage.
FAQs about Mapping with Zip Codes:
Q: What are the best software tools for mapping with zip codes?
A: Numerous software tools cater to mapping with zip codes. Some popular options include:
- ArcGIS: A comprehensive geographic information system (GIS) software with advanced mapping and analytical capabilities.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software that provides a user-friendly interface and supports a wide range of mapping functionalities.
- Google Maps: A widely used online mapping platform that offers basic mapping tools and integration with zip code data.
- Tableau: A data visualization software that enables interactive maps and data exploration using zip code data.
Q: How can I obtain zip code boundary data for mapping?
A: Zip code boundary data can be obtained from various sources:
- U.S. Census Bureau: The Census Bureau provides shapefiles and other geographic data, including zip code boundaries.
- Tiger/Line Shapefiles: The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) offers Tiger/Line shapefiles that contain zip code boundaries and other geographic features.
- Online GIS Data Repositories: Websites like OpenStreetMap and Geofabrik provide free and open-source zip code boundary data.
- Commercial Data Providers: Companies like ESRI and Mapbox offer commercial datasets that include zip code boundaries and other geographic data.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when mapping with zip codes?
A: Avoid these common mistakes to ensure accurate and meaningful maps:
- Using outdated data: Ensure your zip code data is up-to-date, as zip code boundaries can change over time.
- Assuming uniformity within zip codes: Recognize that data values within a single zip code can vary significantly.
- Over-reliance on single data sources: Cross-reference data from multiple sources to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Ignoring spatial context: Consider the spatial relationships between different zip codes and how they influence data patterns.
Tips for Effective Zip Code Mapping:
- Define your objectives: Clearly outline your mapping goals and the information you aim to convey.
- Choose appropriate data sources: Select reliable and relevant data sources for your mapping project.
- Select appropriate map types: Choose the map type that best suits your data and objectives, considering choropleth, dot density, heat maps, and flow maps.
- Use clear and consistent legends: Ensure your map legend is easy to understand and provides clear information about the data being visualized.
- Consider map aesthetics: Use colors, symbols, and other visual elements effectively to enhance map readability and visual appeal.
- Communicate insights effectively: Clearly communicate the findings and insights derived from your zip code mapping analysis.
Conclusion:
Mapping with zip codes offers a powerful tool for spatial analysis and data visualization, providing a granular level of geographic insight that can inform various applications across diverse fields. By leveraging the accessibility, standardization, and versatility of zip code data, researchers, businesses, and policymakers can gain valuable insights into geographic patterns, trends, and relationships. While recognizing potential challenges and limitations, effective zip code mapping can contribute to informed decision-making, improved resource allocation, and a deeper understanding of our world.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping with Zip Codes: A Comprehensive Guide to Spatial Analysis and Data Visualization. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!