Mapping Multiple Zip Codes: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Analyzing Data
Related Articles: Mapping Multiple Zip Codes: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Analyzing Data
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping Multiple Zip Codes: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Analyzing Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Mapping Multiple Zip Codes: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Analyzing Data
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Mapping Multiple Zip Codes: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Analyzing Data
- 3.1 Understanding the Significance of Zip Codes
- 3.2 Mapping Multiple Zip Codes: Techniques and Tools
- 3.3 Benefits of Mapping Multiple Zip Codes
- 3.4 Considerations for Mapping Multiple Zip Codes
- 3.5 FAQs on Mapping Multiple Zip Codes
- 3.6 Tips for Mapping Multiple Zip Codes
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Mapping Multiple Zip Codes: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Analyzing Data
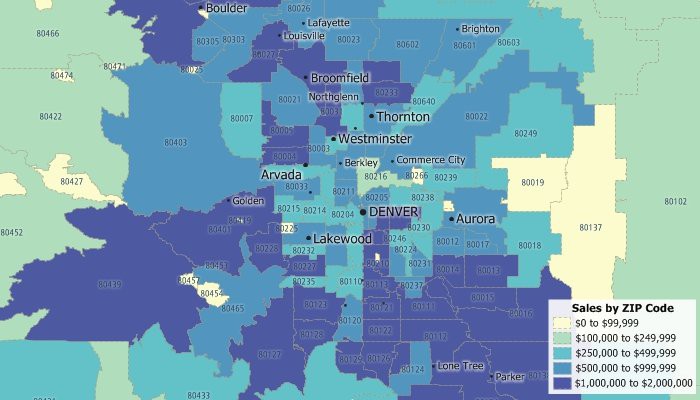
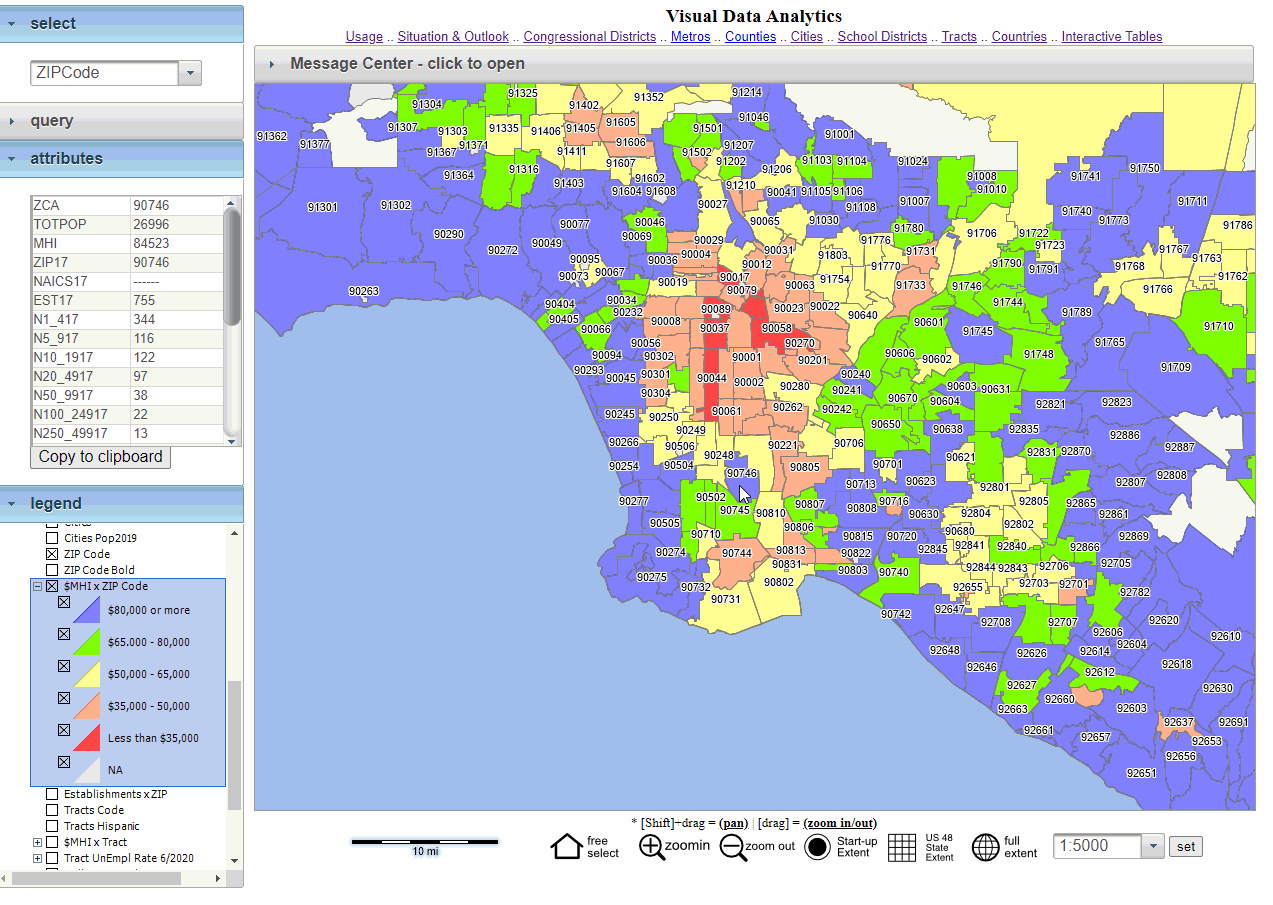
The ability to map multiple zip codes simultaneously is a versatile tool that unlocks valuable insights across various fields. From business development and market research to urban planning and public health initiatives, visualizing geographical data associated with zip codes offers a powerful lens for understanding patterns, trends, and relationships. This article delves into the practical applications, benefits, and considerations involved in mapping multiple zip codes.
Understanding the Significance of Zip Codes
Zip codes, established by the United States Postal Service, are five-digit numerical codes that designate specific geographical areas. They serve as a fundamental building block for organizing and categorizing data. While initially designed for mail delivery, zip codes have evolved into a valuable identifier for a multitude of purposes:
- Demographic Analysis: Zip codes often correlate with demographic data, including population density, age distribution, income levels, and educational attainment. This information allows for targeted marketing campaigns, tailored product offerings, and effective resource allocation.
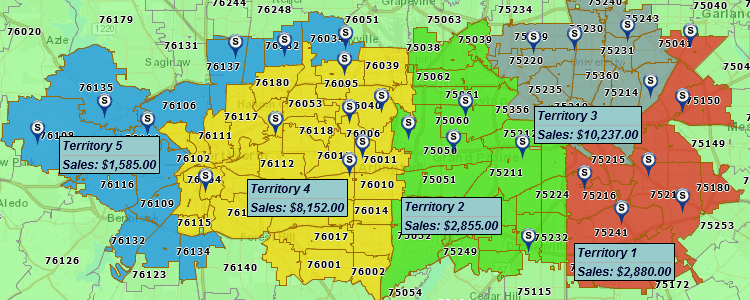
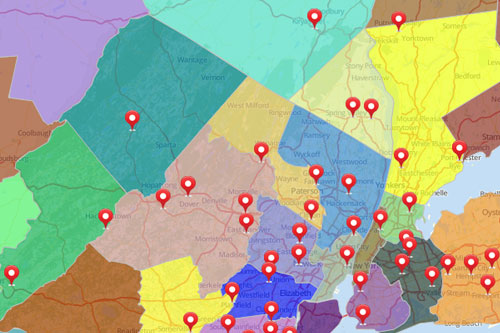
- Market Research: Businesses utilize zip code data to identify potential customer bases, analyze market competition, and understand consumer preferences. Mapping multiple zip codes reveals market penetration, customer clustering, and potential growth opportunities.
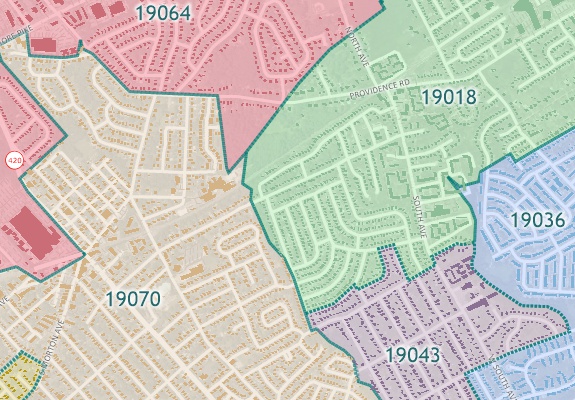
- Urban Planning: City planners rely on zip code data to assess infrastructure needs, plan transportation routes, and identify areas requiring development or revitalization. Visualizing multiple zip codes highlights population distribution, traffic patterns, and areas with high demand for services.
- Public Health: Health organizations use zip codes to track disease outbreaks, monitor health disparities, and allocate resources effectively. Mapping multiple zip codes helps identify areas with high disease prevalence, understand environmental factors, and tailor public health interventions.
Mapping Multiple Zip Codes: Techniques and Tools
Mapping multiple zip codes involves several techniques and tools, each offering unique capabilities and advantages:
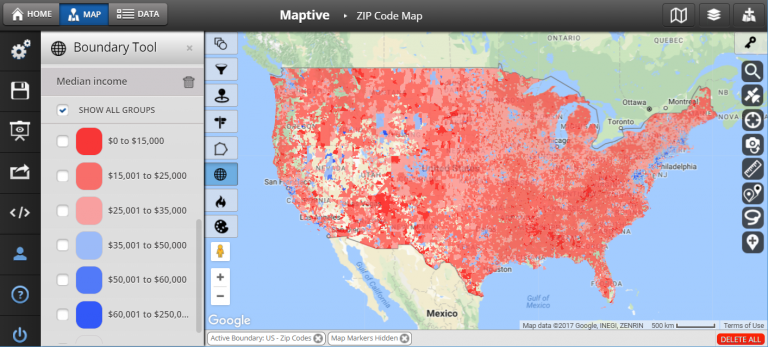
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software provides comprehensive tools for visualizing and analyzing spatial data. Users can import zip code data, create thematic maps, and perform spatial analysis to identify relationships, patterns, and trends. Popular GIS platforms include ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo.
- Mapping APIs: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) from companies like Google Maps, Mapbox, and Esri allow developers to integrate mapping functionality into their applications. These APIs offer access to map data, visualization tools, and routing capabilities, enabling dynamic and interactive mapping experiences.
- Spreadsheets and Data Visualization Tools: Spreadsheet programs like Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets, along with data visualization tools like Tableau and Power BI, offer basic mapping capabilities. These tools enable users to create simple maps highlighting zip code boundaries and associated data.
Benefits of Mapping Multiple Zip Codes
The ability to map multiple zip codes offers several significant benefits:
- Data Visualization: Mapping provides a clear and intuitive way to visualize spatial data. It helps identify clusters, outliers, and spatial relationships that might not be apparent from raw data alone.
- Trend Analysis: By mapping data over time, users can identify trends and patterns, such as population growth, economic development, or disease prevalence. This information facilitates informed decision-making and strategic planning.
- Spatial Analysis: Mapping tools enable users to perform various spatial analysis techniques, such as proximity analysis, network analysis, and spatial statistics. These analyses provide deeper insights into relationships between data points and their spatial context.
- Targeted Communication: Mapping multiple zip codes helps target communication efforts to specific audiences based on their location and associated data. This allows for more effective marketing campaigns, public health outreach, and community engagement.
- Improved Decision-Making: By visualizing and analyzing spatial data, stakeholders gain a comprehensive understanding of their environment. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
Considerations for Mapping Multiple Zip Codes
While mapping multiple zip codes offers valuable insights, several considerations are crucial for ensuring accurate and meaningful analysis:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the data used for mapping is paramount. Ensure data sources are reliable, up-to-date, and consistent with the intended analysis.
- Data Privacy: When working with sensitive data, ensure compliance with privacy regulations and ethical guidelines. Avoid sharing or displaying information that could compromise individuals’ privacy.
- Map Projections: Different map projections distort spatial relationships in various ways. Choose a projection appropriate for the geographic area and intended analysis.
- Map Scale: The scale of the map influences the level of detail and the visibility of spatial relationships. Choose an appropriate scale based on the data and the intended message.
- Map Legend and Symbols: Use clear and consistent legends and symbols to ensure accurate interpretation of the map.
FAQs on Mapping Multiple Zip Codes
Q: What are the most common uses of mapping multiple zip codes?
A: Mapping multiple zip codes is widely used in various fields, including:
- Business Development: Identifying potential customer bases, analyzing market competition, and understanding consumer preferences.
- Market Research: Analyzing market penetration, customer clustering, and potential growth opportunities.
- Urban Planning: Assessing infrastructure needs, planning transportation routes, and identifying areas requiring development or revitalization.
- Public Health: Tracking disease outbreaks, monitoring health disparities, and allocating resources effectively.
- Real Estate: Analyzing property values, identifying desirable neighborhoods, and understanding market trends.
- Education: Understanding school district boundaries, identifying areas with high student populations, and analyzing educational disparities.
Q: What are some tools for mapping multiple zip codes?
A: Several tools are available for mapping multiple zip codes, including:
- GIS Software: ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo.
- Mapping APIs: Google Maps, Mapbox, and Esri.
- Spreadsheets and Data Visualization Tools: Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, Tableau, and Power BI.
Q: What are the limitations of mapping multiple zip codes?
A: While powerful, mapping multiple zip codes has some limitations:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the data used for mapping is paramount. Ensure data sources are reliable, up-to-date, and consistent with the intended analysis.
- Data Privacy: When working with sensitive data, ensure compliance with privacy regulations and ethical guidelines. Avoid sharing or displaying information that could compromise individuals’ privacy.
- Map Projections: Different map projections distort spatial relationships in various ways. Choose a projection appropriate for the geographic area and intended analysis.
- Map Scale: The scale of the map influences the level of detail and the visibility of spatial relationships. Choose an appropriate scale based on the data and the intended message.
- Map Legend and Symbols: Use clear and consistent legends and symbols to ensure accurate interpretation of the map.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy of my map?
A: To ensure the accuracy of your map, consider the following:
- Use reliable data sources: Verify the source of your data and ensure its accuracy and relevance.
- Check data consistency: Ensure that the data used for mapping is consistent with the intended analysis and geographic boundaries.
- Verify map projections: Choose a projection appropriate for the geographic area and intended analysis.
- Review map scale: Ensure that the chosen map scale allows for clear visualization of the data and spatial relationships.
- Validate map features: Verify the accuracy of map features, such as zip code boundaries, roads, and landmarks.
Q: What are some ethical considerations when mapping multiple zip codes?
A: Ethical considerations include:
- Data privacy: Ensure compliance with privacy regulations and ethical guidelines. Avoid sharing or displaying information that could compromise individuals’ privacy.
- Transparency: Clearly identify data sources and any limitations of the map.
- Bias: Avoid using data that perpetuates biases or stereotypes.
- Context: Provide context for the data and map to avoid misinterpretation.
- Impact: Consider the potential impact of the map on individuals and communities.
Tips for Mapping Multiple Zip Codes
- Define your purpose: Clearly identify the objectives of your map and the questions you aim to answer.
- Choose appropriate tools: Select tools that align with your data, technical skills, and project requirements.
- Use clear and consistent legends and symbols: Ensure the map is easily understandable and interpretable.
- Consider data visualization techniques: Experiment with different visualization techniques to enhance the clarity and impact of your map.
- Share your map responsibly: Consider the ethical implications of sharing your map and ensure that it is used appropriately.
Conclusion
Mapping multiple zip codes provides a powerful tool for understanding and analyzing data across various fields. By visualizing spatial relationships and patterns, users can gain valuable insights, identify trends, and make informed decisions. While mapping offers numerous benefits, it is crucial to consider data accuracy, privacy, and ethical implications to ensure responsible and meaningful analysis. By embracing the power of mapping multiple zip codes, individuals and organizations can unlock a deeper understanding of their environment and make informed decisions to drive progress and improve outcomes.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Multiple Zip Codes: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Analyzing Data. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!