Japan and the Equator: A Geographic Exploration
Related Articles: Japan and the Equator: A Geographic Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Japan and the Equator: A Geographic Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Japan and the Equator: A Geographic Exploration

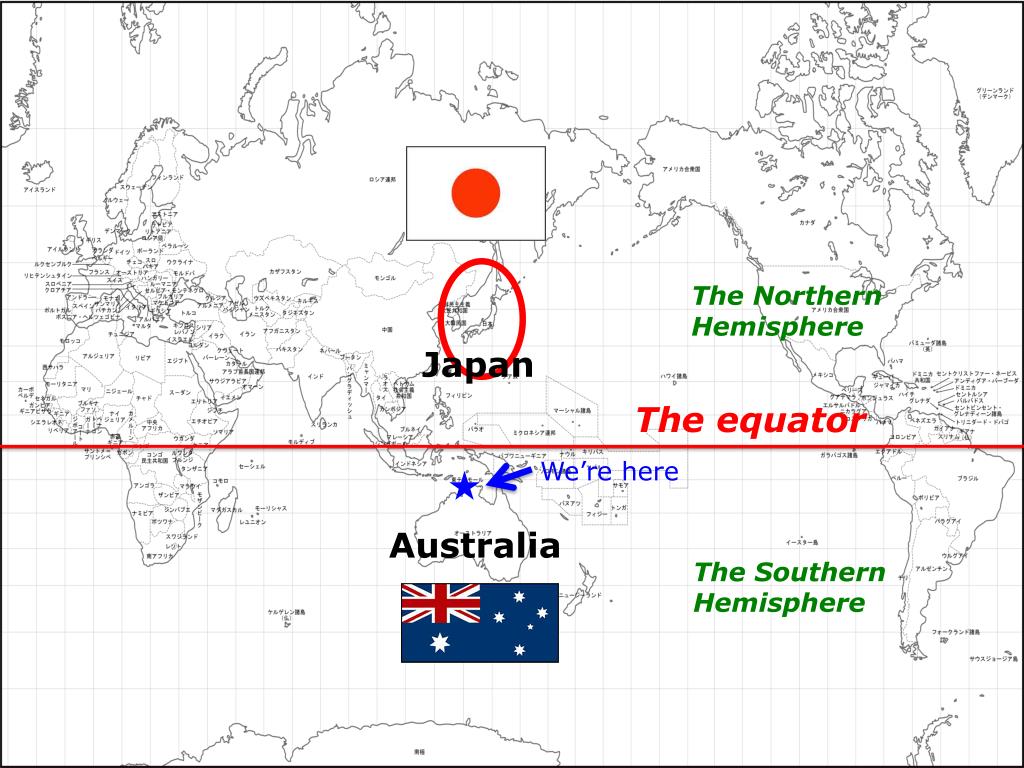
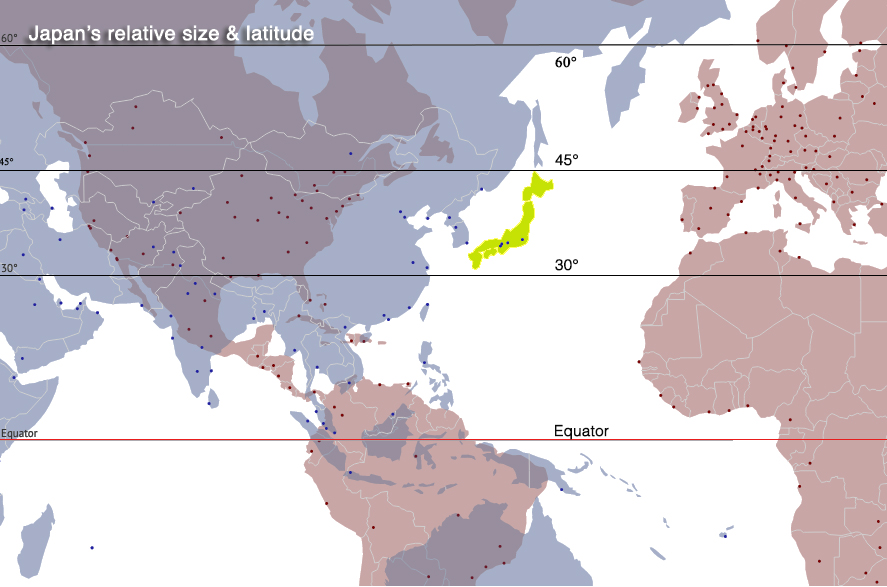
The concept of Japan being situated on the equator is a misconception. Japan, an archipelago nation, is located in the Northern Hemisphere and is not intersected by the equator. This geographical reality has a profound impact on Japan’s climate, biodiversity, and cultural development.
Japan’s Geographic Position:
Japan’s archipelago extends from north to south, spanning approximately 3,000 kilometers. The northernmost point, Cape Soya, is located at 45°31′ N, while the southernmost point, Okinotorishima, lies at 20°25′ N. This geographical spread places Japan entirely within the temperate zone, with distinct seasons and a diverse range of climates.
Equatorial Influences and Their Absence:
The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0° latitude, marks the boundary between the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. This line is associated with a unique set of climatic conditions, including:
- High Temperatures: The equator receives direct sunlight throughout the year, resulting in consistently high temperatures.
- Heavy Rainfall: The equator experiences significant rainfall due to the convergence of trade winds and the formation of low-pressure zones.
- Tropical Vegetation: The equatorial climate fosters lush vegetation, including rainforests and diverse ecosystems.
While Japan is not located on the equator, it experiences seasonal variations in temperature and precipitation due to its latitude and the influence of the East Asian monsoon. This monsoon system brings heavy rainfall to Japan during the summer months, while winters are characterized by dry and cold conditions.
Impact of Japan’s Location on Climate and Biodiversity:
Japan’s temperate climate, influenced by its location north of the equator, creates a unique environment that supports a rich diversity of flora and fauna. The country boasts a variety of ecosystems, including:
- Temperate Forests: These forests, dominated by deciduous trees, cover a significant portion of Japan and are home to diverse wildlife.
- Mountainous Regions: Japan’s mountainous terrain, including the Japanese Alps, provides a habitat for unique species adapted to high altitudes.
- Coastal Regions: Japan’s extensive coastline supports a variety of marine life, including fish, seabirds, and marine mammals.
The absence of equatorial influences has shaped Japan’s biodiversity, leading to the evolution of distinct species adapted to the country’s unique climate and geographical features.
Cultural Influences:
Japan’s location north of the equator has also played a role in shaping its cultural development. The temperate climate has allowed for the development of agriculture and the growth of a vibrant society. Japan’s cultural traditions, including its art, literature, and cuisine, are influenced by its unique geographical position and the seasonal changes it experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: Why is it important to understand Japan’s location relative to the equator?
A: Understanding Japan’s location is crucial for understanding its climate, biodiversity, and cultural development. It helps us appreciate the unique characteristics of the country and its distinct position within the global context.
Q: How does Japan’s climate differ from equatorial regions?
A: Japan experiences distinct seasons, with warm and humid summers and cold and dry winters. Equatorial regions, in contrast, have consistently high temperatures and heavy rainfall throughout the year.
Q: Does Japan have any equatorial influences?
A: While Japan is not located on the equator, it experiences some influence from the East Asian monsoon, which brings heavy rainfall during the summer months.
Q: What are the benefits of Japan’s location north of the equator?
A: Japan’s temperate climate allows for diverse ecosystems, agriculture, and a rich cultural development. Its unique location also fosters a unique biodiversity.
Tips for Understanding Japan’s Geography:
- Use a map: Visualizing Japan’s location on a map helps understand its position relative to the equator and other geographical features.
- Explore Japanese culture: Understanding Japanese culture can provide insights into the influence of climate and geography on its development.
- Learn about the East Asian monsoon: Understanding the monsoon system helps explain the seasonal variations in Japan’s climate.
Conclusion:
Japan’s location north of the equator plays a significant role in shaping its climate, biodiversity, and cultural development. The country’s temperate climate, diverse ecosystems, and unique cultural traditions are all influenced by its geographical position. Understanding Japan’s location relative to the equator provides a deeper appreciation for this fascinating archipelago nation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Japan and the Equator: A Geographic Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!