India: A Land Shaped by Latitude and Climate
Related Articles: India: A Land Shaped by Latitude and Climate
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to India: A Land Shaped by Latitude and Climate. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
India: A Land Shaped by Latitude and Climate

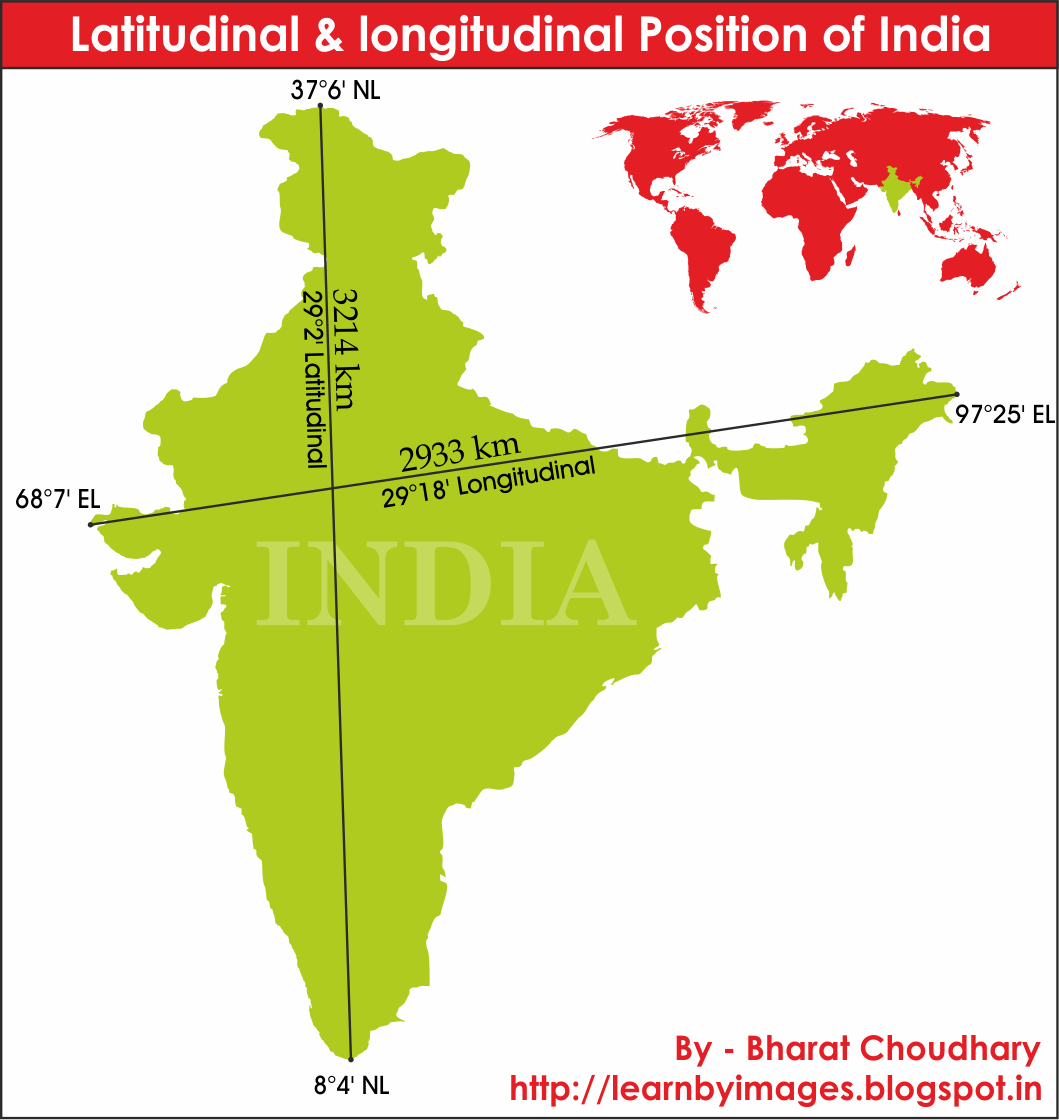
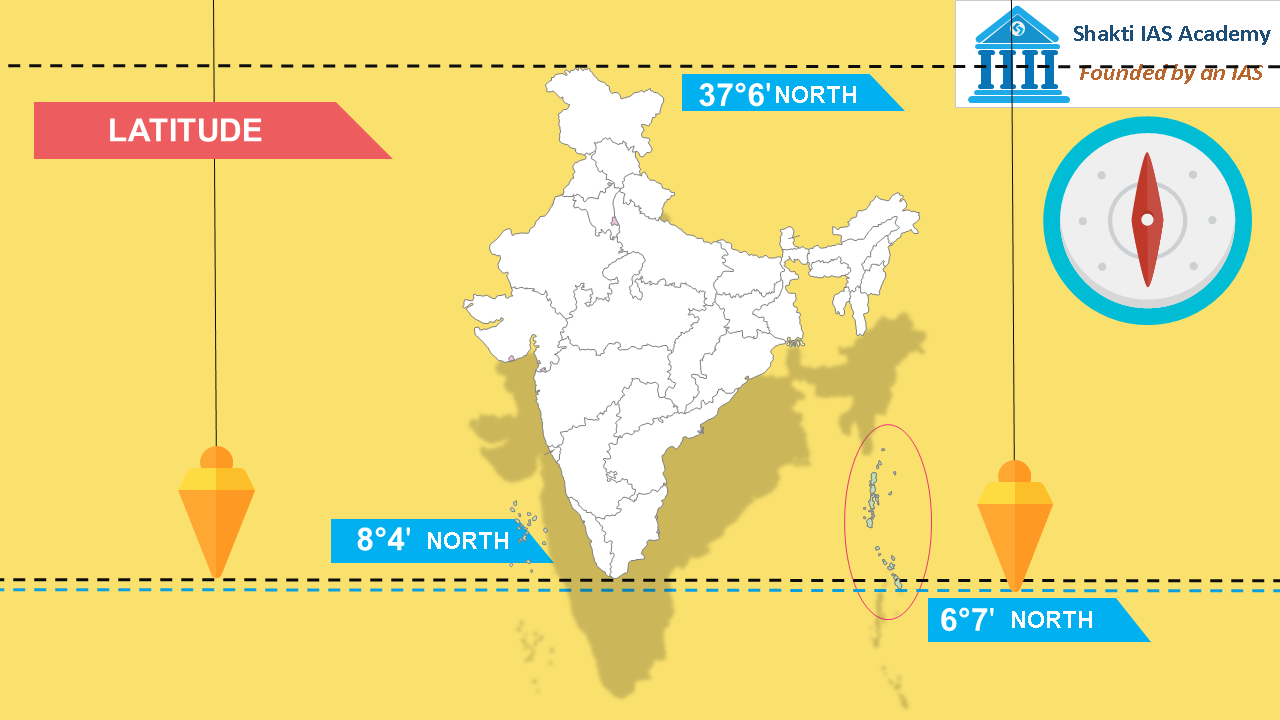
India, a vibrant tapestry of cultures, landscapes, and traditions, is geographically positioned in a way that profoundly influences its climate, biodiversity, and history. The country’s location straddling the Tropic of Cancer and lying north of the Equator plays a pivotal role in shaping its unique characteristics. Understanding the relationship between India’s geographical position and its diverse features offers valuable insights into its natural wonders, cultural heritage, and socio-economic landscape.
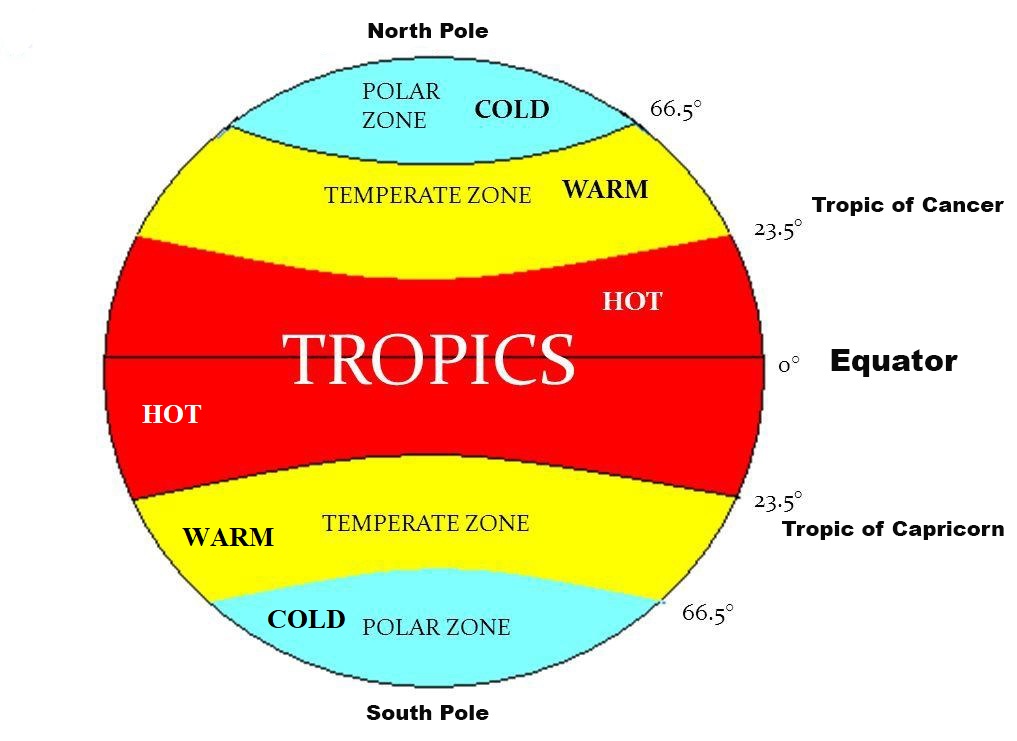
The Tropic of Cancer: A Line of Influence
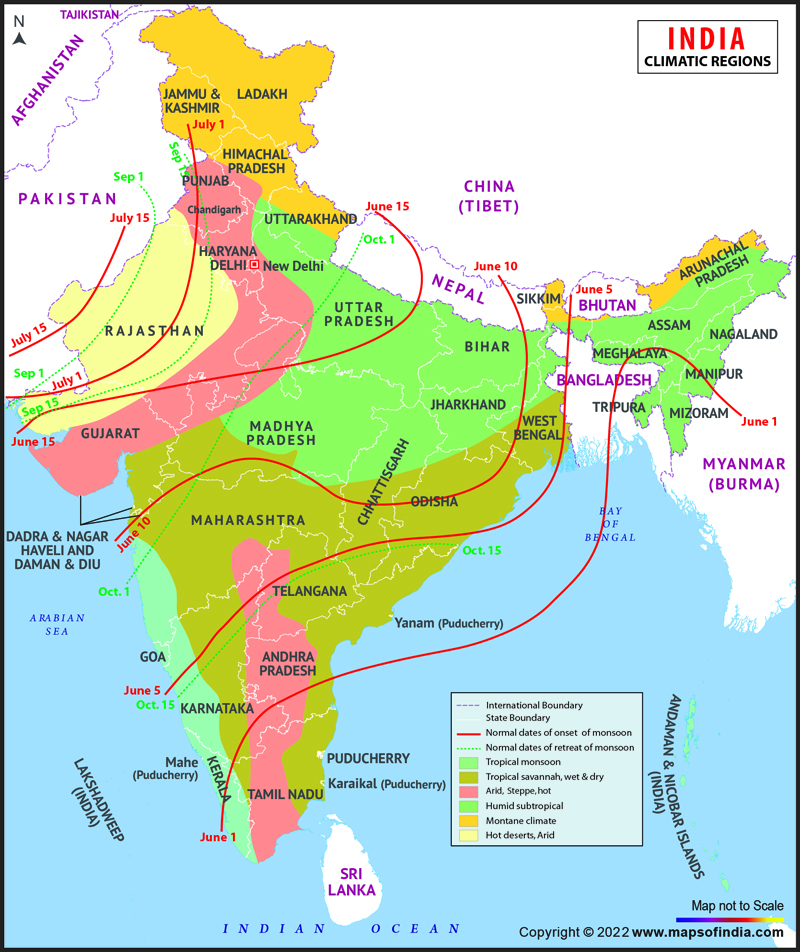
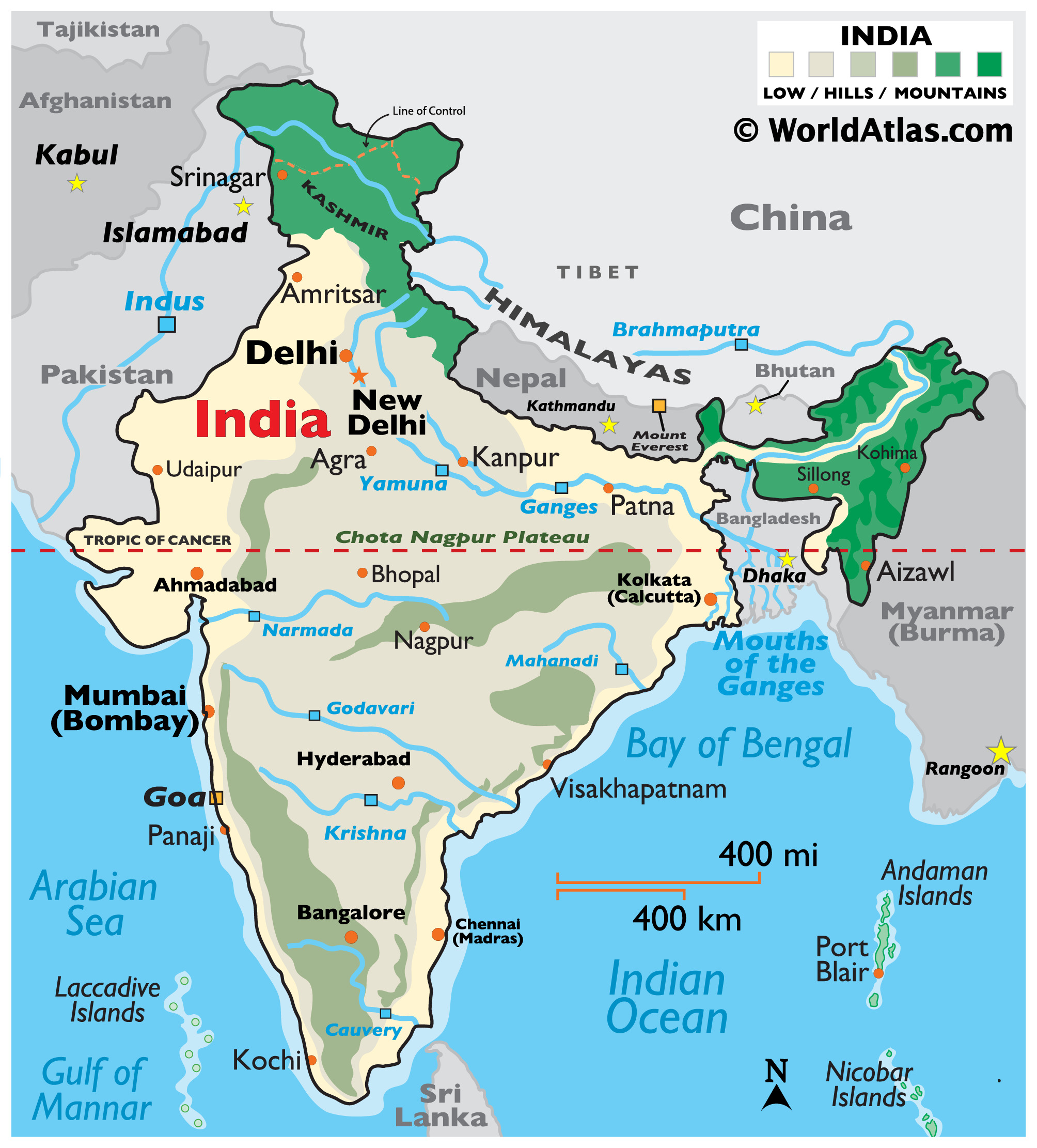
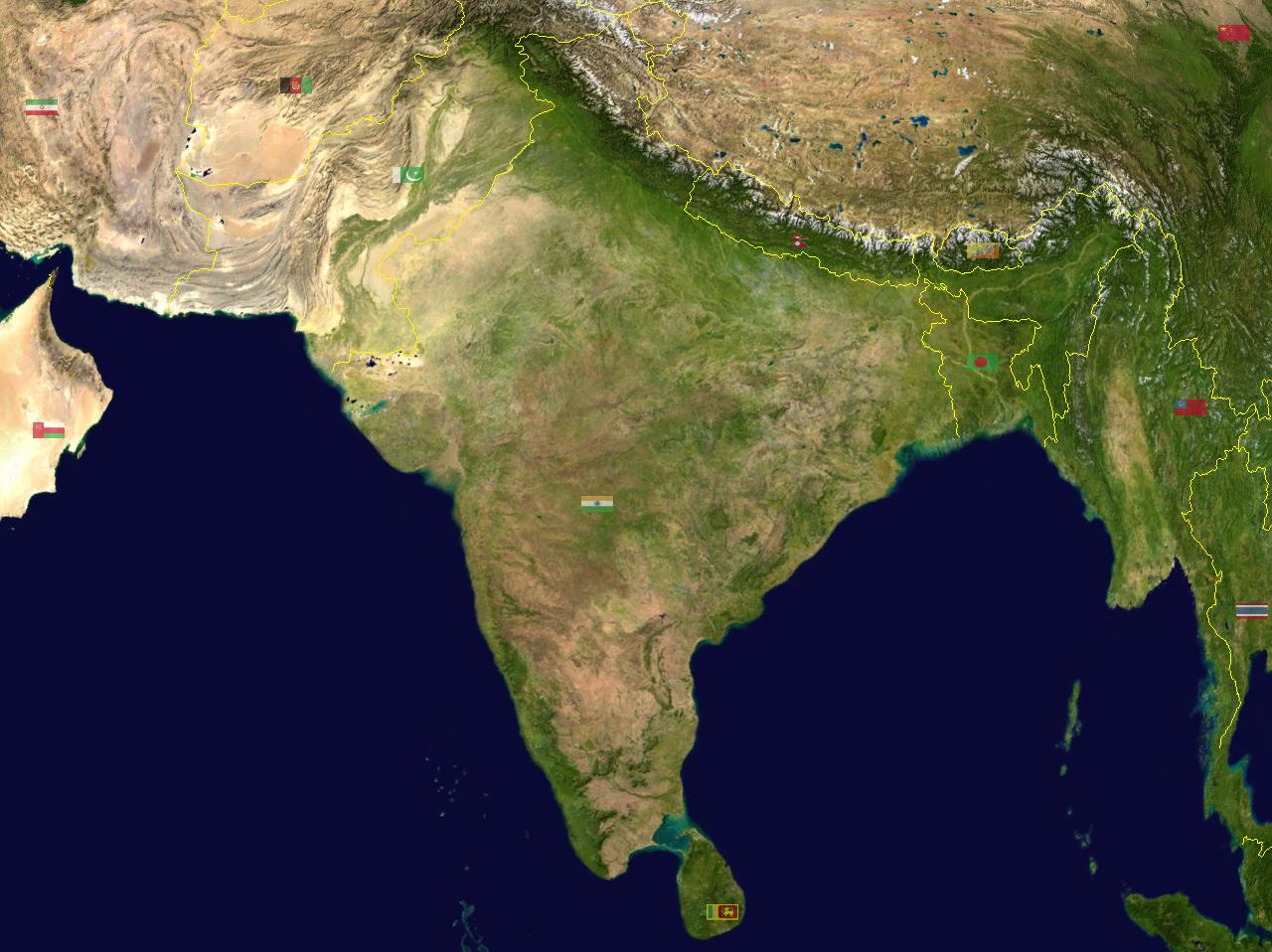
The Tropic of Cancer, an imaginary line encircling the Earth at approximately 23.5 degrees north latitude, cuts through India, passing through states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, and Tripura. This line marks the northernmost point where the sun can be directly overhead at noon, signifying the influence of the tropical climate on India.
The Equator: A Line of Distance
While the Equator does not pass through India, its influence is felt in the southernmost parts of the country, particularly in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. These islands, located south of the mainland, experience a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. This proximity to the Equator contributes to the islands’ unique biodiversity and lush vegetation.
Impact on Climate
The Tropic of Cancer’s passage through India has a profound impact on the country’s climate. The region north of this line experiences a predominantly subtropical climate, characterized by hot summers and mild winters. The southern parts of India, influenced by the Equator, experience a tropical climate with high temperatures and humidity year-round. This variation in climate results in a wide range of ecosystems, from the snow-capped Himalayas in the north to the lush rainforests of the south.
Monsoon Winds: A Vital Lifeline
India’s position relative to the Equator and the Tropic of Cancer also influences the country’s monsoon season. The monsoon winds, originating over the Indian Ocean, bring life-giving rain to the Indian subcontinent, sustaining agriculture and replenishing water resources. The arrival of the monsoon is a time of celebration and relief, marking the end of the dry season and heralding a period of renewed growth.
Biodiversity: A Rich Tapestry
The diverse climate zones created by India’s geographical position contribute to its remarkable biodiversity. From the snow leopards of the Himalayas to the Bengal tigers of the Sundarbans, India is home to a wide range of flora and fauna. The country’s rich biodiversity is a testament to the intricate relationship between its geographical location and its natural world.
Cultural Influence:
The influence of India’s geographical position extends beyond its natural environment. The distinct climate zones and their associated agricultural practices have shaped the country’s cultural landscape. From the vibrant festivals celebrating the monsoon season to the traditional clothing and cuisine adapted to different climatic conditions, India’s cultural tapestry reflects the intricate interplay between geography and human life.
Economic Significance:
India’s location and climate have significant economic implications. The country’s fertile land, abundant water resources, and diverse ecosystems provide a foundation for a thriving agricultural sector. The monsoon winds, while sometimes causing flooding, also support the cultivation of a wide range of crops, contributing to India’s food security.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While India’s geographical position offers numerous advantages, it also presents certain challenges. The country is prone to natural disasters like floods, droughts, and cyclones, which can cause significant damage and disrupt economic activities. However, India’s geographical location also presents opportunities for sustainable development, harnessing renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
FAQs
Q1: Why is India called a "subcontinent"?
A: India is often referred to as a "subcontinent" due to its vast size and distinct geographical features. It is separated from the rest of Asia by the Himalayas, creating a unique landmass with its own distinctive geological, climatic, and cultural characteristics.
Q2: How does the Tropic of Cancer influence India’s climate?
A: The Tropic of Cancer, passing through India, signifies the influence of the tropical climate. The region north of this line experiences a subtropical climate with hot summers and mild winters. This influence creates diverse ecosystems and agricultural practices across the country.
Q3: What is the significance of the monsoon season in India?
A: The monsoon season is crucial for India’s agricultural economy, providing life-giving rain and replenishing water resources. It is a time of celebration and renewal, marking the end of the dry season and heralding a period of growth.
Q4: How does India’s geographical position affect its biodiversity?
A: The diverse climate zones created by India’s location contribute to its rich biodiversity. The country’s wide range of ecosystems, from the snow-capped Himalayas to the lush rainforests, supports a vast array of flora and fauna.
Q5: What are some of the economic implications of India’s geographical position?
A: India’s location and climate provide fertile land, abundant water resources, and diverse ecosystems, supporting a thriving agricultural sector. The monsoon winds, while sometimes causing flooding, also support the cultivation of various crops, contributing to food security.
Tips
- Use maps and visuals: Utilize maps and diagrams to illustrate India’s geographical position relative to the Equator and the Tropic of Cancer. This will help viewers understand the concepts more effectively.
- Highlight specific examples: Provide concrete examples of how India’s geographical position influences its climate, biodiversity, and culture. This will make the information more relatable and engaging.
- Connect the dots: Emphasize the interconnectedness of India’s geographical location, climate, and cultural practices. This will demonstrate the complex and multifaceted nature of the relationship.
- Address challenges and opportunities: Acknowledge the challenges posed by India’s geographical position, such as natural disasters. However, also highlight the opportunities for sustainable development and economic growth.
Conclusion
India’s geographical position, straddling the Tropic of Cancer and lying north of the Equator, plays a crucial role in shaping its diverse natural environment, cultural heritage, and socio-economic landscape. From the influence of the monsoon winds to the rich biodiversity and the unique climatic zones, India’s location is a defining factor in its unique identity. Understanding the interplay between geography, climate, and human life in India offers valuable insights into the country’s past, present, and future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into India: A Land Shaped by Latitude and Climate. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!