Deciphering the Grid: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering the Grid: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Grid: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Grid: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps

Maps are powerful tools, capable of guiding us across continents, navigating intricate city streets, and even charting the vast expanse of the cosmos. At the heart of this navigational power lies a fundamental concept: the geographic coordinate system. This system, based on latitude and longitude, provides a unique address for every point on Earth, enabling precise location identification and navigation.
Latitude: Measuring Distance North or South
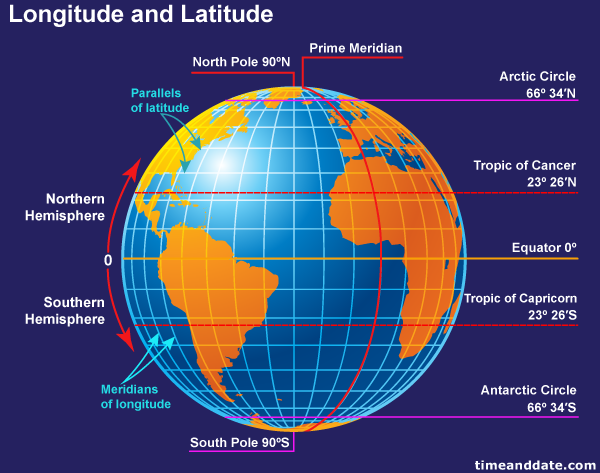
Latitude is akin to a horizontal line drawn around the Earth, parallel to the equator. It measures the angular distance of a point north or south of the equator, expressed in degrees, minutes, and seconds. The equator, serving as the zero-degree latitude line, divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
- Degrees: The Earth is divided into 180 degrees of latitude, with 90 degrees north of the equator and 90 degrees south.
- Minutes: Each degree is further subdivided into 60 minutes.
- Seconds: Each minute is then divided into 60 seconds.
For example, a location with a latitude of 40° 45′ 15" N is 40 degrees, 45 minutes, and 15 seconds north of the equator.
Longitude: Measuring Distance East or West
Longitude, on the other hand, is represented by vertical lines that converge at the poles. It measures the angular distance of a point east or west of the prime meridian, also expressed in degrees, minutes, and seconds. The prime meridian, passing through Greenwich, England, is designated as the zero-degree longitude line.
- Degrees: The Earth is divided into 360 degrees of longitude, with 180 degrees east of the prime meridian and 180 degrees west.
- Minutes: Each degree is further subdivided into 60 minutes.
- Seconds: Each minute is then divided into 60 seconds.
For example, a location with a longitude of 74° 00′ 30" W is 74 degrees, 00 minutes, and 30 seconds west of the prime meridian.
Navigating the Grid: Using Latitude and Longitude
Understanding latitude and longitude is crucial for various applications, including:
- Navigation: GPS devices, maps, and navigation apps rely heavily on latitude and longitude to pinpoint locations and guide users to their destinations.
- Mapping: Cartographers use latitude and longitude to create accurate maps, ensuring consistent representation of geographical features.
- Geospatial Analysis: Researchers and analysts utilize latitude and longitude to analyze spatial data, studying patterns and trends across various locations.
- Data Visualization: Visualizing data on maps, incorporating latitude and longitude, allows for insightful representation of geographical distributions and relationships.
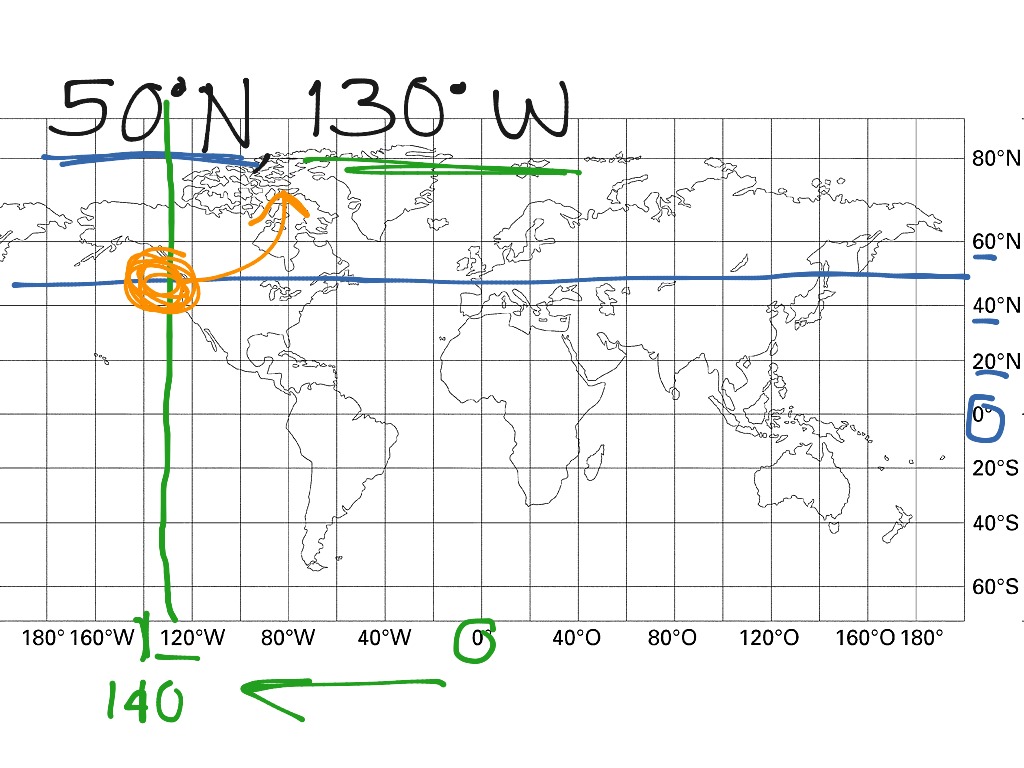
Calculating Latitude and Longitude: A Practical Approach
While modern technology seamlessly provides latitude and longitude coordinates, understanding how to calculate them manually can enhance map interpretation and navigation skills. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
1. Identifying Reference Points:
- Equator: The equator serves as the starting point for latitude measurements.
- Prime Meridian: The prime meridian is the starting point for longitude measurements.
2. Measuring Angular Distance:
- Latitude: Measure the angular distance of the target location north or south of the equator using a protractor or a compass.
- Longitude: Measure the angular distance of the target location east or west of the prime meridian using a protractor or a compass.
3. Converting to Degrees, Minutes, and Seconds:
- Degrees: The measured angle directly corresponds to the degrees of latitude or longitude.
- Minutes: Divide the remaining fractional part of the angle by 60 to obtain the minutes.
- Seconds: Divide the remaining fractional part of the minutes by 60 to obtain the seconds.
4. Specifying Hemisphere:
- Latitude: Indicate whether the location is north or south of the equator (N or S).
- Longitude: Indicate whether the location is east or west of the prime meridian (E or W).
Example:
Let’s say we want to find the latitude and longitude of a point on a map. We measure the angular distance from the equator as 30 degrees, 15 minutes, and 30 seconds north. We also measure the angular distance from the prime meridian as 75 degrees, 45 minutes, and 15 seconds west. Therefore, the latitude and longitude of the point are 30° 15′ 30" N and 75° 45′ 15" W, respectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How accurate are latitude and longitude coordinates?
A: The accuracy of latitude and longitude coordinates depends on the precision of the measuring instruments and the scale of the map. Modern GPS devices can achieve accuracy within a few meters, while traditional methods using compasses and protractors may result in less accurate measurements.
Q: Can latitude and longitude be used to locate points in space?
A: While latitude and longitude are specific to Earth, similar coordinate systems are used to locate points in space. Celestial coordinates, for instance, utilize declination (analogous to latitude) and right ascension (analogous to longitude) to pinpoint the position of stars and other celestial objects.
Q: How do latitude and longitude relate to time zones?
A: Time zones are directly related to longitude. As the Earth rotates, different longitudes experience sunrise and sunset at different times. Each time zone covers a specific range of longitudes, with the time difference between adjacent zones typically being one hour.
Q: What are some common applications of latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude and longitude are crucial in various applications, including:
- Navigation: GPS devices, maps, and navigation apps rely heavily on latitude and longitude to pinpoint locations and guide users to their destinations.
- Mapping: Cartographers use latitude and longitude to create accurate maps, ensuring consistent representation of geographical features.
- Geospatial Analysis: Researchers and analysts utilize latitude and longitude to analyze spatial data, studying patterns and trends across various locations.
- Data Visualization: Visualizing data on maps, incorporating latitude and longitude, allows for insightful representation of geographical distributions and relationships.
Tips for Using Latitude and Longitude Effectively
- Use high-quality maps: Ensure the map you’re using is accurate and up-to-date, as outdated maps may have inaccurate coordinates.
- Understand the scale: Pay attention to the map scale, as it determines the level of precision you can achieve when measuring latitude and longitude.
- Practice your measuring skills: Practice using protractors and compasses to improve your accuracy in measuring angular distances.
- Use online tools: Utilize online tools like Google Maps or other mapping software to verify and refine your calculated coordinates.
- Always double-check: Always double-check your measurements and calculations to minimize errors.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude form the backbone of the geographic coordinate system, providing a universal language for describing locations on Earth. Understanding this system empowers us to navigate our surroundings, analyze geographical data, and visualize spatial relationships with greater clarity. By mastering the principles of latitude and longitude, we unlock the potential of maps to guide us, inform us, and connect us to the world around us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Grid: Understanding Latitude and Longitude on Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!