Deciphering the Earth’s Geography: A Guide to the Equator and Tropic Lines
Related Articles: Deciphering the Earth’s Geography: A Guide to the Equator and Tropic Lines
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Earth’s Geography: A Guide to the Equator and Tropic Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Earth’s Geography: A Guide to the Equator and Tropic Lines
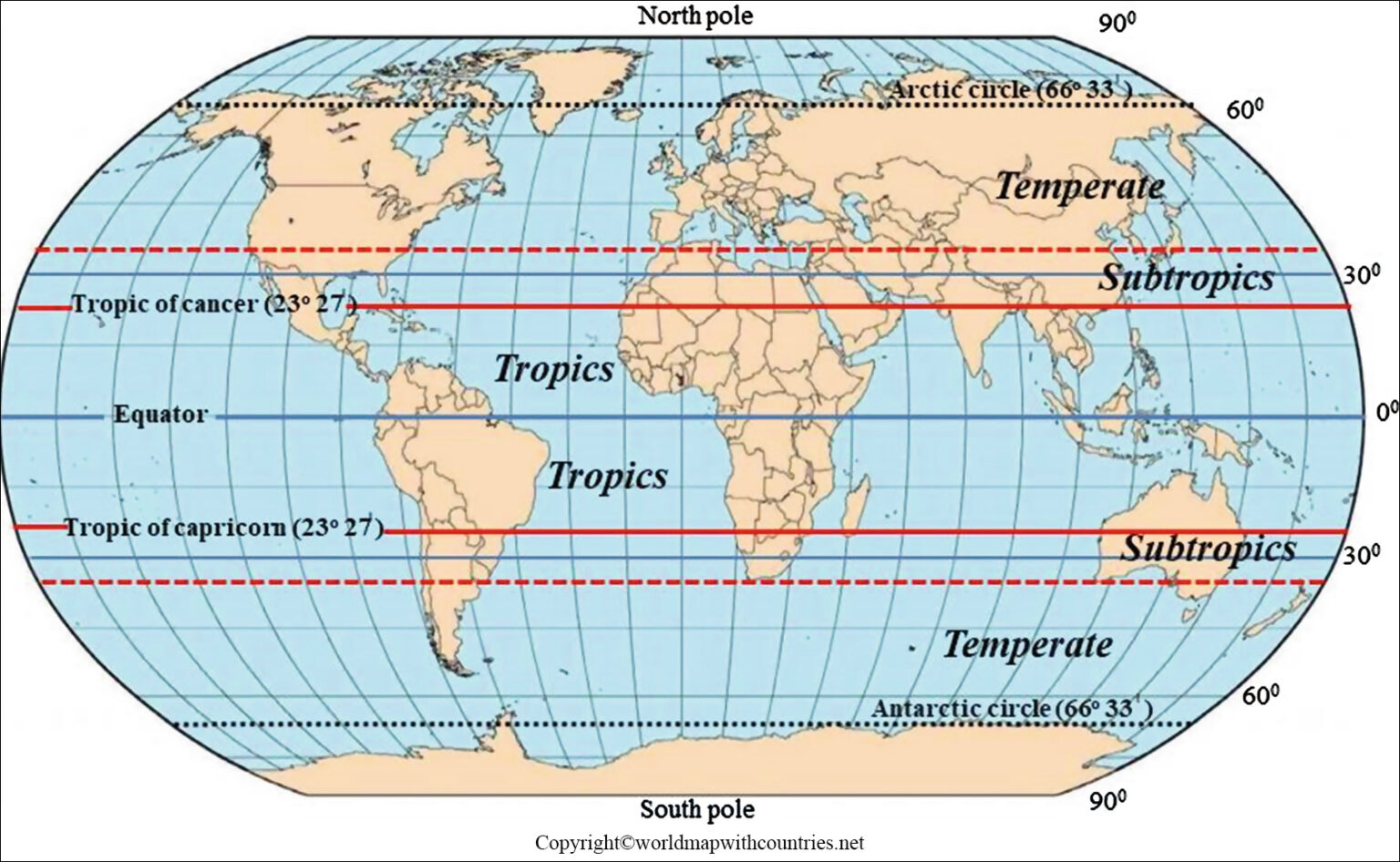
The Earth, a dynamic sphere suspended in space, is home to a diverse array of climates, landscapes, and life forms. Understanding the distribution of these elements is crucial to comprehending the planet’s intricate systems. One essential tool in this endeavor is the world map, particularly when it incorporates the equator and tropic lines. These imaginary lines, while not physically present on the Earth’s surface, serve as vital markers, delineating geographical zones with distinct climatic and ecological characteristics.
The Equator: A Line of Symmetry and Climate
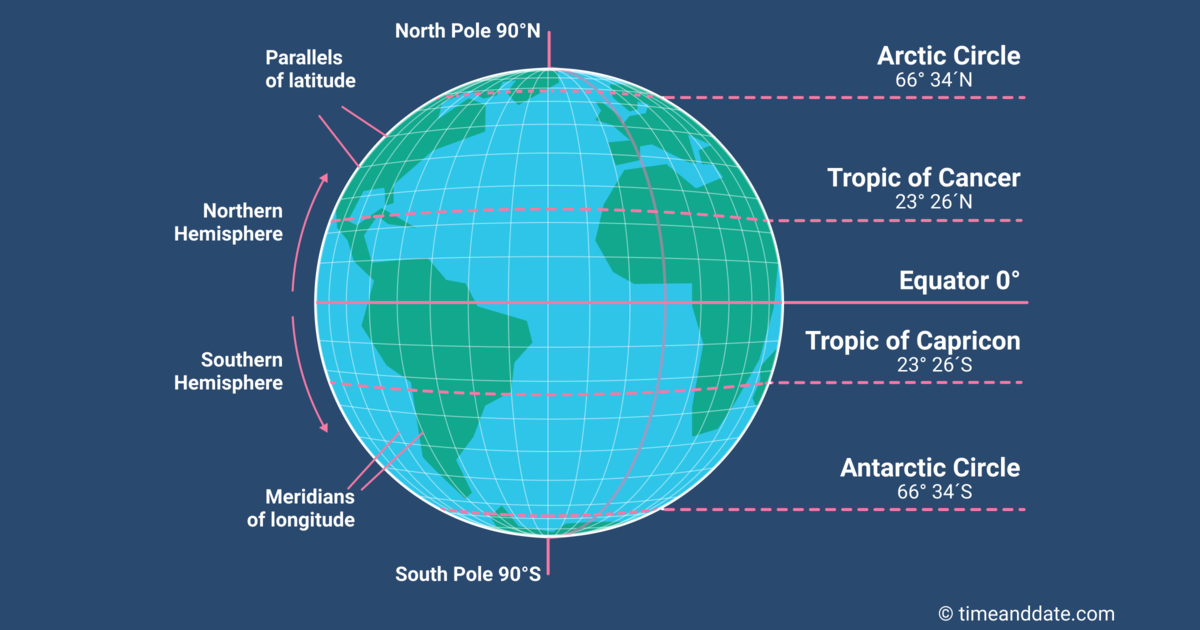
The equator, an imaginary circle that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, is the most fundamental line on a world map. It represents the Earth’s widest circumference and lies at 0 degrees latitude. This line is not just a geographical marker; it holds significant climatic and ecological importance. Due to its position, the equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to consistently high temperatures and a humid, tropical climate.
The equatorial region is characterized by lush rainforests, abundant biodiversity, and a unique ecosystem adapted to the constant warmth and moisture. This region experiences a consistent day length of 12 hours, with minimal variation throughout the year. The equator’s influence extends beyond its immediate vicinity, impacting the distribution of climate zones and weather patterns globally.
The Tropic Lines: Boundaries of Tropical Climates
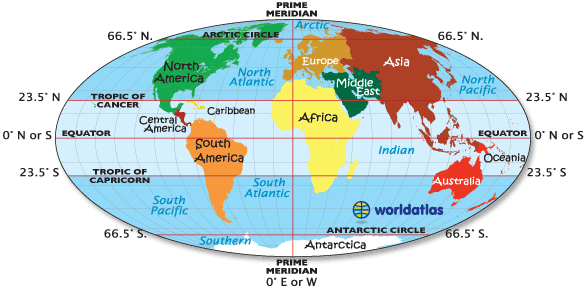
The tropics, encompassing the regions between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, are defined by their proximity to the equator and the resulting warm, tropical climates. These lines, located at approximately 23.5 degrees north and south of the equator respectively, mark the boundaries of the zone where the sun’s rays can strike the Earth at a 90-degree angle at least once during the year. This phenomenon contributes to the high temperatures and distinct seasons characteristic of the tropics.
The Tropic of Cancer: Situated in the Northern Hemisphere, the Tropic of Cancer is named after the constellation Cancer, where the sun appears to be positioned during the summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere. This line passes through countries like Mexico, India, and China, influencing their climate and vegetation.
The Tropic of Capricorn: Located in the Southern Hemisphere, the Tropic of Capricorn is named after the constellation Capricorn, where the sun appears during the summer solstice in the Southern Hemisphere. This line traverses countries like Australia, Brazil, and South Africa, shaping their unique climates and ecosystems.
Understanding the Importance of the Equator and Tropic Lines
The equator and tropic lines play a crucial role in understanding global climate patterns, biodiversity distribution, and even human civilization. Their significance can be summarized as follows:
- Climate Zones: These lines delineate distinct climate zones, influencing temperature, rainfall, and vegetation patterns. This understanding is critical for agriculture, resource management, and disaster preparedness.
- Biodiversity: The equator and tropics are renowned for their exceptional biodiversity, hosting a vast array of flora and fauna. These regions are hotspots for conservation efforts, as they hold a significant portion of the Earth’s genetic diversity.
- Human Settlement: The equator and tropics have been home to human civilizations for millennia, shaping cultural practices, agricultural techniques, and architectural styles. Understanding these regions’ unique characteristics is essential for sustainable development and cultural preservation.
- Global Circulation Patterns: The equator and tropics play a pivotal role in driving global atmospheric circulation patterns. These patterns influence weather systems, ocean currents, and the distribution of precipitation across the globe.
FAQs about the Equator and Tropic Lines
Q: Why are the Tropic lines located at 23.5 degrees?
A: The Earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of approximately 23.5 degrees. This tilt causes the sun’s rays to strike different parts of the Earth at varying angles throughout the year. The Tropic lines mark the boundaries where the sun’s rays can strike the Earth at a 90-degree angle at least once during the year.
Q: What are the differences between the climates of the equator and the tropics?
A: The equator experiences a consistently hot and humid tropical climate, with minimal seasonal variation. The tropics, while also generally warm, experience more distinct seasons, with periods of wet and dry weather.
Q: What are the benefits of understanding the equator and tropic lines?
A: Understanding these lines helps us comprehend global climate patterns, biodiversity distribution, and human settlement patterns. This knowledge is crucial for sustainable development, resource management, and conservation efforts.
Tips for Using the Equator and Tropic Lines
- Reference a World Map: Always refer to a world map with the equator and tropic lines clearly marked for accurate geographical understanding.
- Relate to Climate and Vegetation: Observe the correlation between the equator and tropic lines and the distribution of different climate zones and vegetation types.
- Explore Cultural Significance: Research how these lines have influenced human settlements, cultural practices, and agricultural techniques in different regions.
- Engage with Global Issues: Understand how these lines play a role in global issues like climate change, biodiversity loss, and sustainable development.
Conclusion
The equator and tropic lines, while invisible on the Earth’s surface, are powerful tools for understanding the planet’s geography and the distribution of life. They provide a framework for comprehending climate patterns, biodiversity hotspots, and the influence of these factors on human civilization. By utilizing these lines as navigational markers, we gain valuable insights into the interconnectedness of the Earth’s systems and the challenges and opportunities they present for humanity. The world map, with its equator and tropic lines, serves as a vital guide for exploring our planet’s intricate tapestry of geography, climate, and life.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1280px-World_map_with_equator-5c4e470b46e0fb00014c3710.jpg)


/wov007-58b9cea93df78c353c388df1.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Earth’s Geography: A Guide to the Equator and Tropic Lines. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!