Deciphering the Earth’s Bands: A Guide to the Equator and Tropics
Related Articles: Deciphering the Earth’s Bands: A Guide to the Equator and Tropics
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Earth’s Bands: A Guide to the Equator and Tropics. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Earth’s Bands: A Guide to the Equator and Tropics
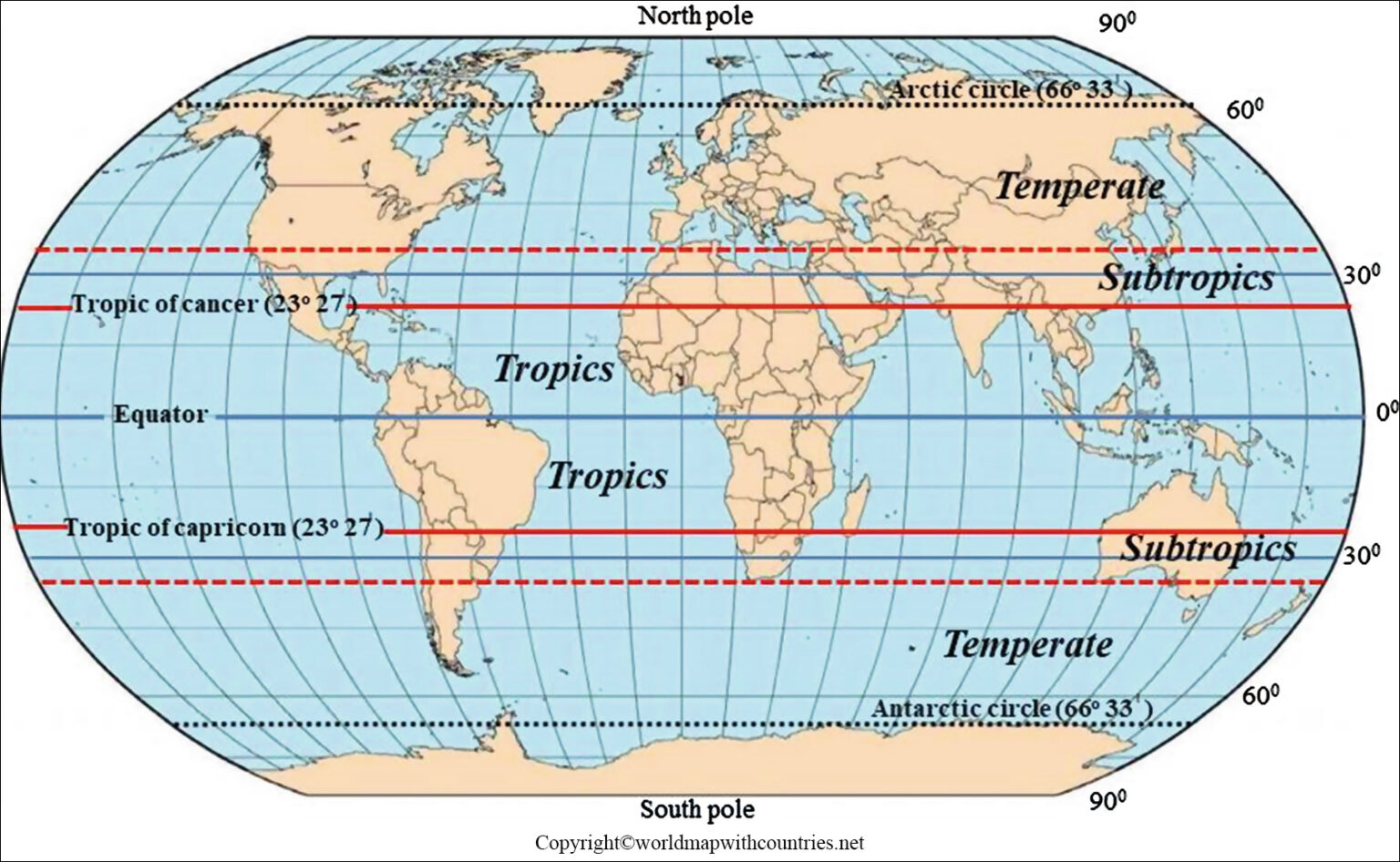
The Earth, a vibrant sphere teeming with life, is not a uniform entity. Its surface is divided into distinct zones, each possessing unique characteristics shaped by the sun’s radiant energy. Among these zones, the equator and tropics hold significant importance, influencing climate, biodiversity, and human civilizations. Understanding these geographical features is crucial for comprehending the Earth’s intricate systems and the diverse tapestry of life it sustains.
The Equator: A Line of Symmetry
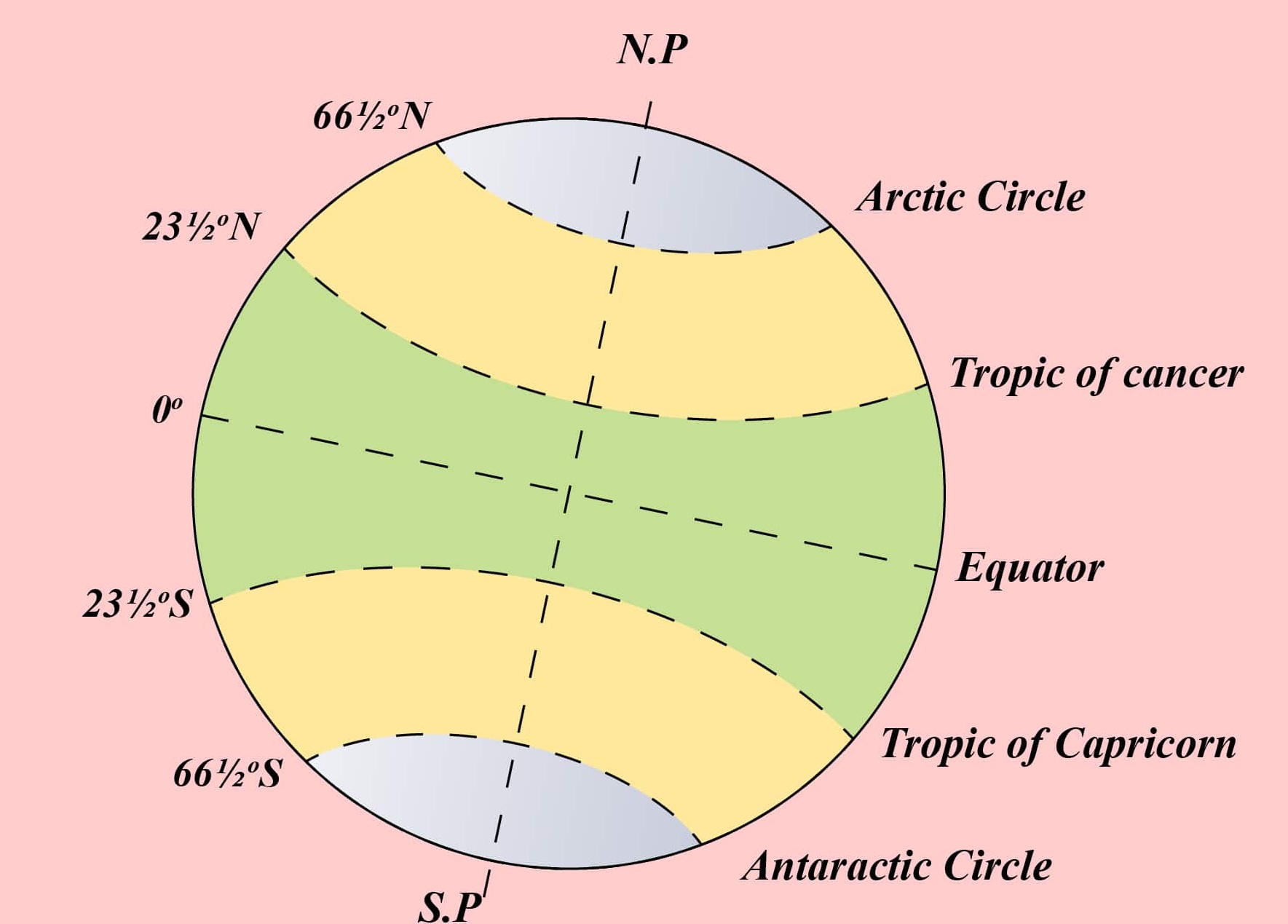
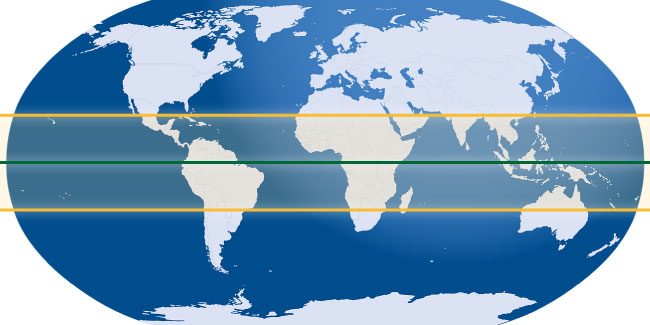
Imagine a circle drawn around the Earth, equidistant from the North and South poles. This imaginary line, known as the equator, serves as the Earth’s zero degree latitude. It divides our planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, marking the point where the sun’s rays strike the Earth at the most direct angle.
The equator’s significance extends beyond its geometrical role. It is a zone of consistent solar radiation, receiving almost 12 hours of daylight throughout the year. This constant influx of energy creates a distinct climate characterized by high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and lush vegetation. The equatorial regions are home to some of the most diverse ecosystems on Earth, including the Amazon rainforest, the Congo Basin, and the Indonesian archipelago.
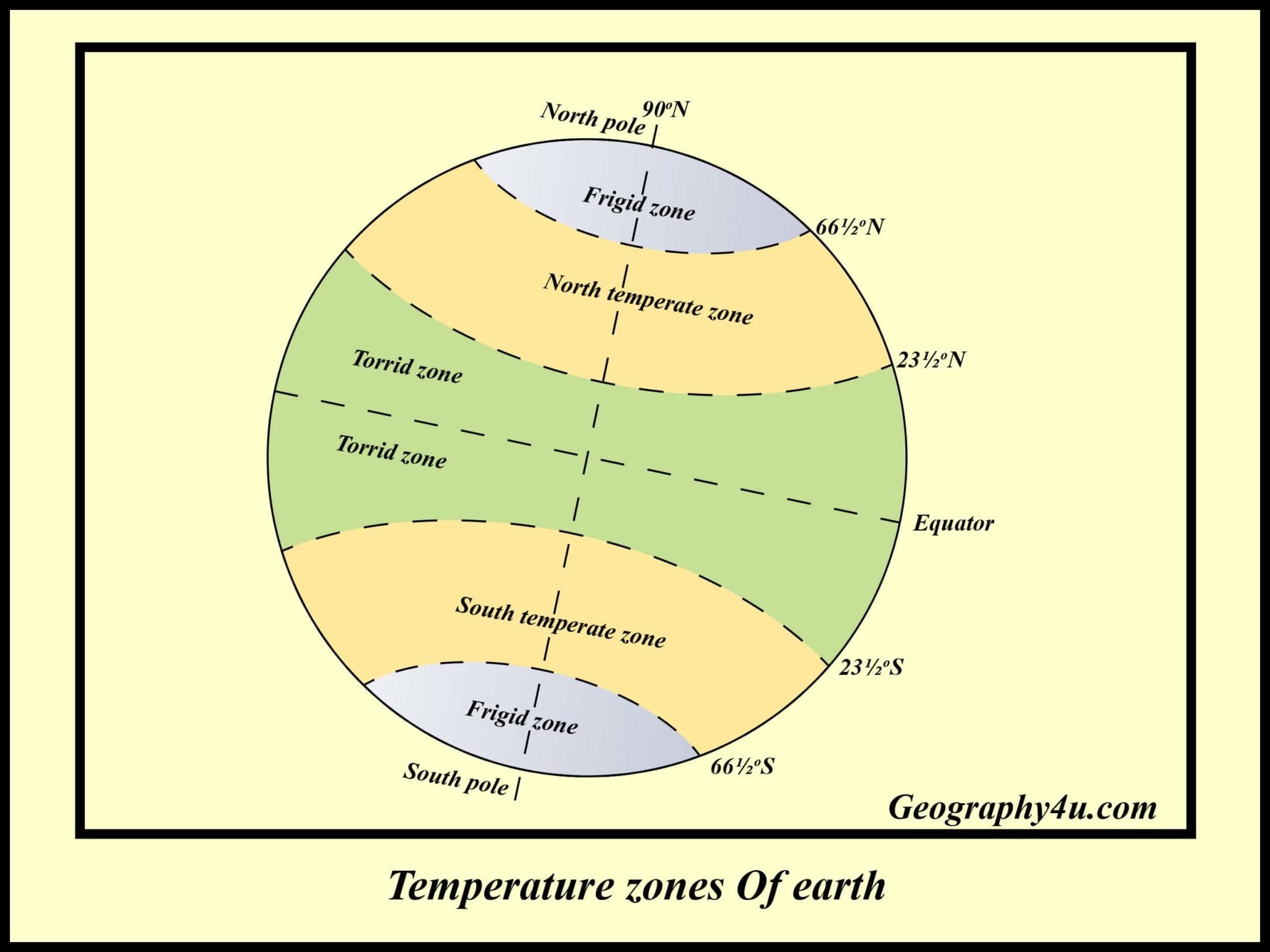
The Tropics: Zones of Intense Sunlight
The tropics, encompassing the areas between the Tropic of Cancer (23.5 degrees North) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5 degrees South), are defined by their proximity to the equator. These regions receive high solar radiation, leading to consistently warm temperatures and a distinct climate.
Within the tropics, several sub-regions exist, each with its unique characteristics. The tropical rainforests, located near the equator, experience heavy rainfall throughout the year. These dense forests, like the Amazon, are biodiversity hotspots, harboring a vast array of flora and fauna. Further away from the equator, the tropical savannas, characterized by grasslands interspersed with trees, are home to diverse animal populations, including the iconic African savanna.
Understanding the Significance
The equator and tropics are not merely geographical lines on a map; they are dynamic zones that play a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s climate, ecosystems, and human societies.
-
Climate Regulation: The equator and tropics act as heat reservoirs, influencing global weather patterns. The warm, moist air rising from these regions creates low-pressure systems, leading to cloud formation and rainfall. This atmospheric circulation system helps distribute heat and moisture across the globe.
-
Biodiversity Hotspots: The equator and tropics are renowned for their exceptional biodiversity. The abundance of sunlight, rainfall, and fertile soil creates ideal conditions for a vast array of plant and animal life. These regions are home to a significant portion of the world’s species, many of which are endemic to these specific locations.
-
Human Civilization: The equator and tropics have been home to human civilizations for millennia. Their fertile lands and abundant resources have supported thriving agricultural societies. The tropical regions are also major producers of agricultural commodities, contributing significantly to global food security.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between the equator and the tropics?
A: The equator is a single line that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The tropics are a wider band encompassing the areas between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
Q: Why are the tropics so warm?
A: The tropics receive the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to consistently high temperatures.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by people living in the tropics?
A: Tropical regions often face challenges related to extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and droughts. Deforestation and climate change are also significant threats to the delicate ecosystems of these regions.
Q: How do the equator and tropics affect global climate patterns?
A: The equator and tropics are key drivers of global atmospheric circulation. The rising warm air from these regions creates low-pressure systems, leading to the formation of clouds and precipitation. This circulation system helps distribute heat and moisture across the globe.
Tips for Understanding the Equator and Tropics
- Use a globe or an online map: Visualizing the Earth’s curvature and the position of the equator and tropics helps in understanding their significance.
- Explore online resources: Numerous websites and articles provide detailed information about the equator, tropics, and their impact on the Earth’s systems.
- Study climate data: Examining temperature and precipitation patterns in different regions can help understand the influence of the equator and tropics on climate.
- Learn about the biodiversity of these regions: Researching the unique flora and fauna found in the equator and tropics provides insights into the importance of these ecosystems.
Conclusion
The equator and tropics are not simply geographical lines; they are dynamic zones that play a critical role in shaping the Earth’s climate, ecosystems, and human societies. Understanding these features is crucial for comprehending the intricate interconnectedness of our planet and the importance of protecting its diverse ecosystems. As we navigate the challenges of a changing climate, understanding the equator and tropics becomes even more critical, guiding our efforts to sustain life and preserve the delicate balance of our planet.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Earth’s Bands: A Guide to the Equator and Tropics. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!