Charting the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Charting the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Charting the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude

The world is a vast and intricate tapestry, and to navigate its complexities, we rely on a system of precise measurement. Latitude and longitude, two fundamental concepts in geography, provide the framework for understanding location and charting the Earth’s surface. This system, often visualized through maps, has been instrumental in facilitating exploration, navigation, and communication across the globe.
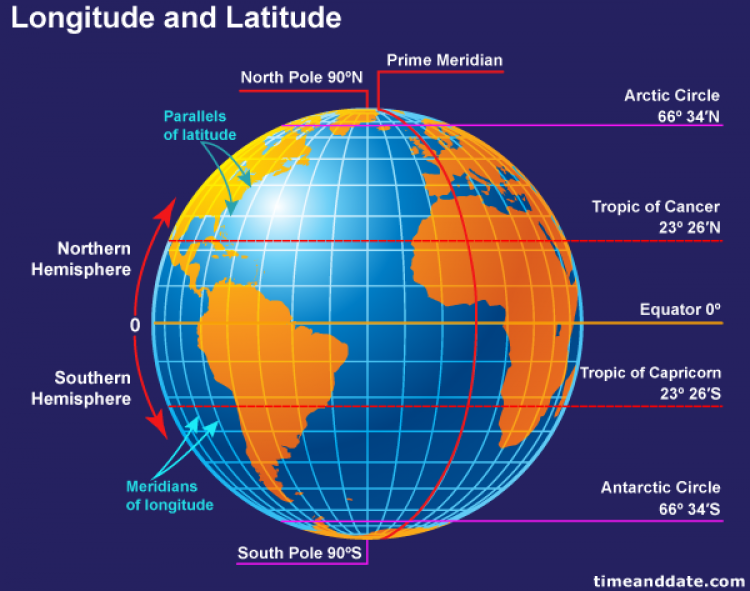
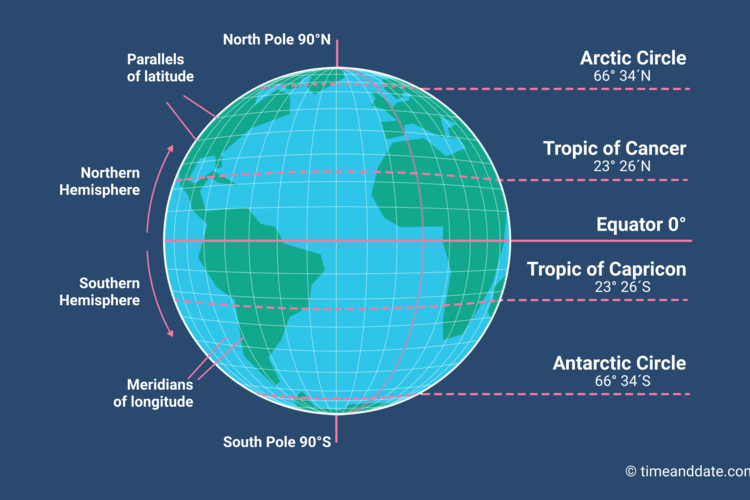
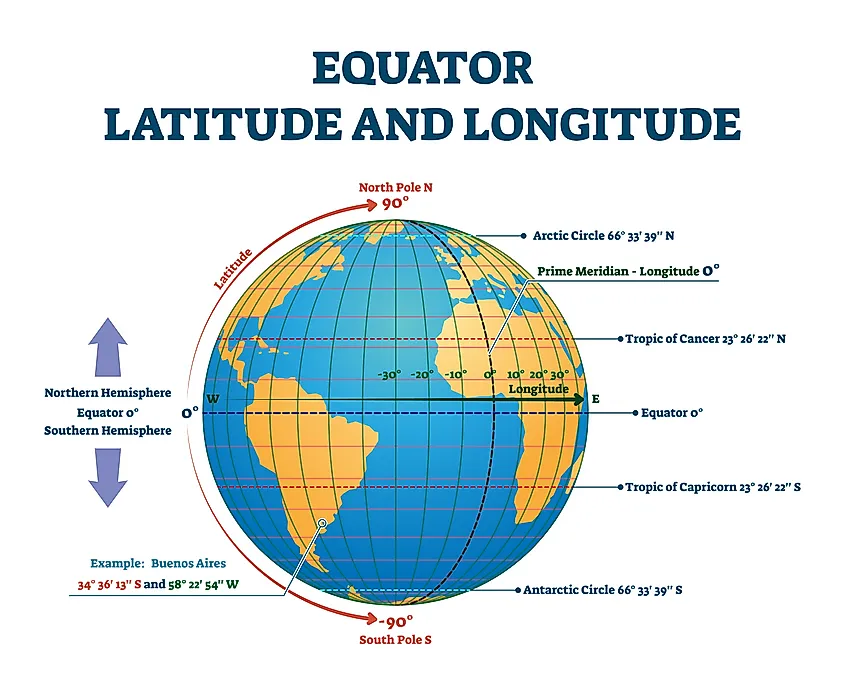
Latitude: Measuring North and South
Latitude lines, also known as parallels, are imaginary circles that run east to west around the Earth, parallel to the equator. They measure the angular distance of a point north or south of the equator. The equator, situated at 0 degrees latitude, serves as the baseline, with latitude increasing towards the poles. Each degree of latitude is approximately 111 kilometers (69 miles) apart, a distance that remains consistent across the globe.
The North Pole is located at 90 degrees north latitude, while the South Pole resides at 90 degrees south latitude. This system provides a standardized way to pinpoint the location of any point on Earth in relation to the equator, facilitating accurate representation and understanding of geographical positioning.
Longitude: Measuring East and West
Longitude lines, also known as meridians, are imaginary semicircles that run from the North Pole to the South Pole, intersecting at the poles. They measure the angular distance of a point east or west of the Prime Meridian, a reference meridian that passes through Greenwich, England. The Prime Meridian is designated as 0 degrees longitude, with longitude increasing eastward and westward to 180 degrees.
Unlike latitude, the distance between longitude lines varies depending on the latitude. At the equator, each degree of longitude is approximately 111 kilometers (69 miles) apart, but this distance decreases as one moves closer to the poles.
The Power of Coordinates: Latitude and Longitude in Action
The combination of latitude and longitude forms a coordinate system, providing a unique address for every point on Earth. This system, known as the geographic coordinate system, is the foundation of global navigation and mapping.
Benefits of Latitude and Longitude:
- Precise Location Determination: Latitude and longitude provide a precise and unambiguous way to pinpoint the location of any point on Earth. This is essential for navigation, surveying, and a wide range of applications requiring accurate location data.
- Global Standardization: The system of latitude and longitude offers a universally recognized and standardized method for representing location, facilitating communication and collaboration across geographical boundaries.
- Mapping and Visualization: Latitude and longitude are crucial for creating maps, which provide a visual representation of the Earth’s surface and aid in understanding spatial relationships.
- Navigation and Travel: Navigation systems, including GPS, rely on latitude and longitude to determine location and guide users to their destination.
- Scientific Research: Latitude and longitude are essential for scientific research, enabling researchers to analyze data, study patterns, and understand environmental changes across different geographical locations.
FAQs about Latitude and Longitude:
Q: How are latitude and longitude measured?
A: Latitude and longitude are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. A degree is divided into 60 minutes, and a minute is divided into 60 seconds. For example, the coordinates of the Eiffel Tower are 48°51’29.9" N, 2°17’40.2" E, indicating its location at 48 degrees, 51 minutes, and 29.9 seconds north of the equator and 2 degrees, 17 minutes, and 40.2 seconds east of the Prime Meridian.
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude measures the angular distance of a point north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the angular distance of a point east or west of the Prime Meridian. Latitude lines run east to west, parallel to the equator, while longitude lines run from the North Pole to the South Pole.
Q: Why is the Prime Meridian located in Greenwich, England?
A: The Prime Meridian’s location in Greenwich was established by international agreement in 1884. Before this, different countries used their own reference meridians, leading to confusion and inconsistency. The choice of Greenwich was based on the prominence of the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, which had been a leading center for astronomical research and timekeeping.
Q: How are latitude and longitude used in GPS?
A: GPS devices use a network of satellites orbiting Earth to determine location. These satellites transmit signals that contain information about their position and time. By receiving signals from multiple satellites, GPS receivers can calculate their latitude, longitude, and altitude.
Tips for Understanding Latitude and Longitude:
- Visualize the Grid System: Imagine the Earth as a globe covered by a grid of latitude and longitude lines. This mental image can help you grasp the concept of coordinates and understand how they relate to location.
- Use Online Mapping Tools: Interactive online mapping tools like Google Maps allow you to explore different locations and visualize how latitude and longitude are used to pinpoint specific points on the Earth.
- Practice Using Coordinates: Try finding the latitude and longitude of familiar places in your surroundings. This hands-on experience can help you solidify your understanding of the coordinate system.
- Explore Historical Maps: Studying historical maps can provide insights into how latitude and longitude were used in the past and how mapping techniques have evolved over time.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude are fundamental concepts in geography that provide a framework for understanding and navigating the Earth’s surface. Their significance extends far beyond simply pinpointing locations; they are essential for a wide range of applications, including navigation, mapping, scientific research, and communication. As our world becomes increasingly interconnected, the importance of latitude and longitude continues to grow, enabling us to explore, understand, and interact with our planet in increasingly sophisticated ways.

/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!