A World Divided: Understanding the Significance of the Equator
Related Articles: A World Divided: Understanding the Significance of the Equator
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A World Divided: Understanding the Significance of the Equator. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A World Divided: Understanding the Significance of the Equator
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1280px-World_map_with_equator-5c4e470b46e0fb00014c3710.jpg)
The Earth, a vast and intricate sphere, is divided by an invisible line known as the equator. This imaginary circle, equidistant from the North and South poles, plays a crucial role in understanding our planet’s geography, climate, and cultural diversity. While often depicted on maps as a simple line, the equator represents a fundamental boundary that influences life across the globe.
The Equator: A Line of Division and Unity
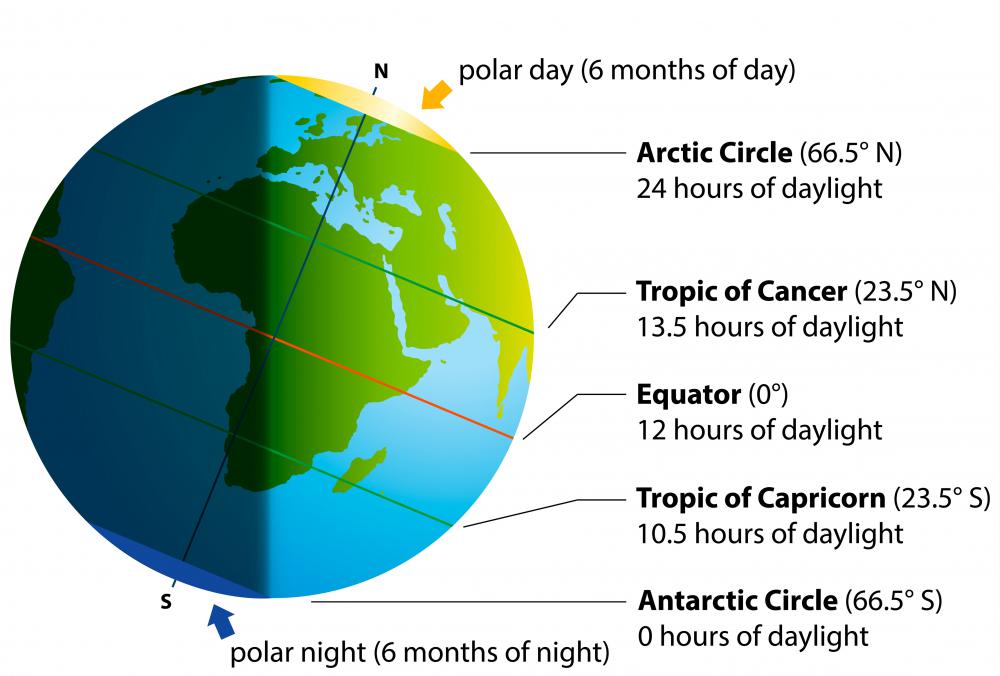
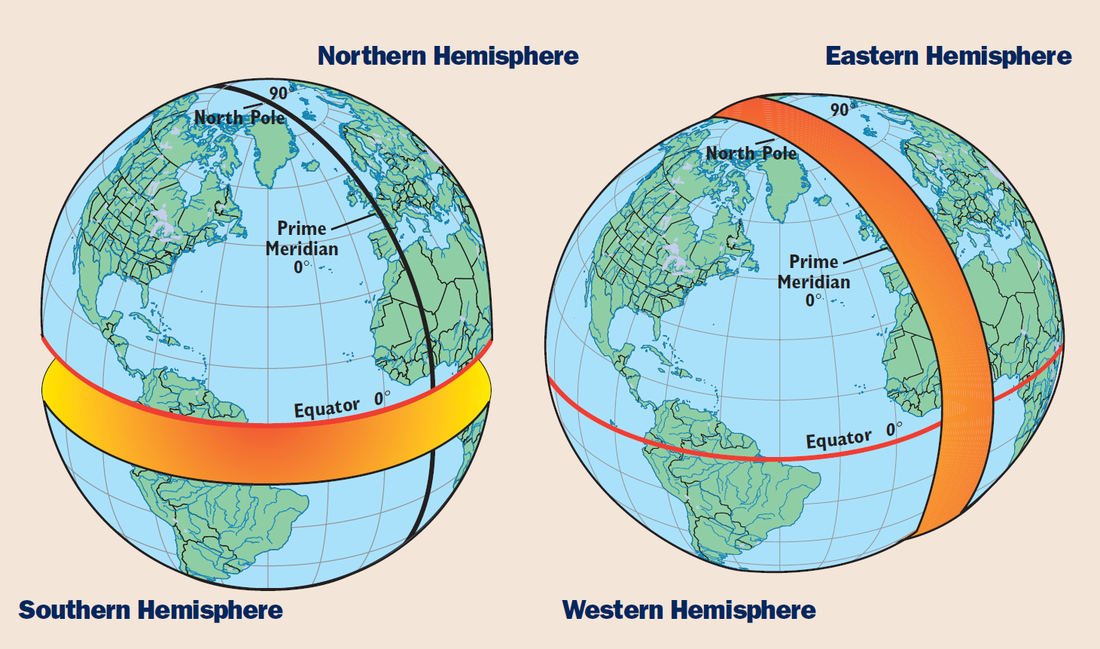
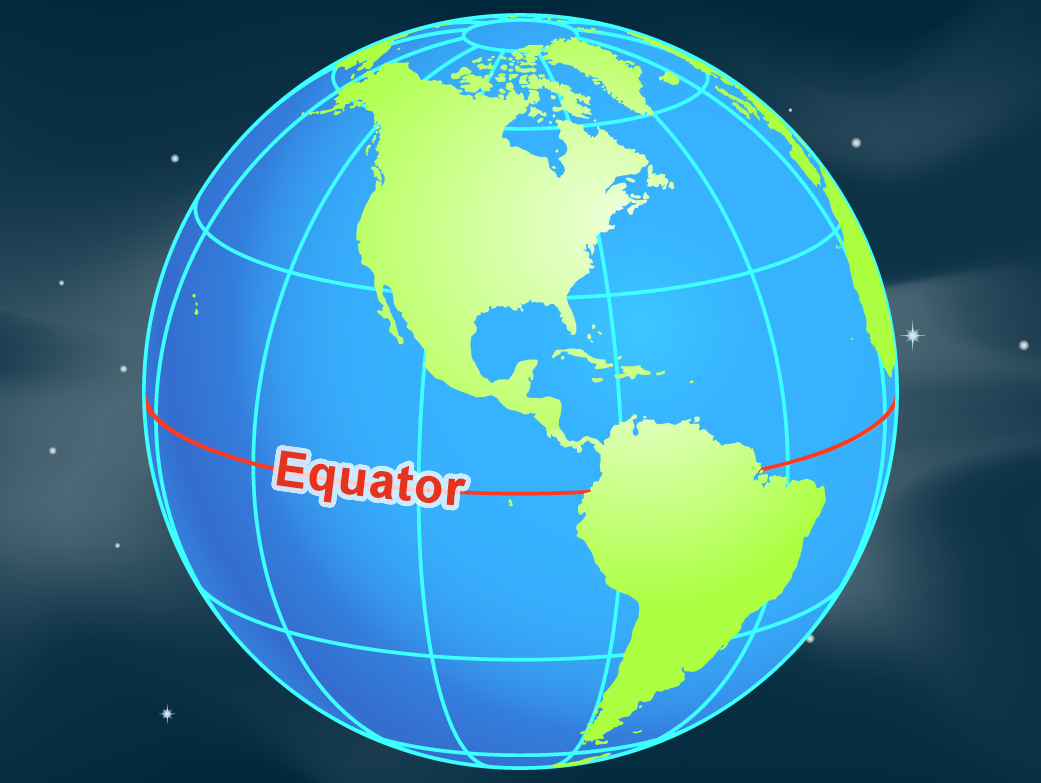
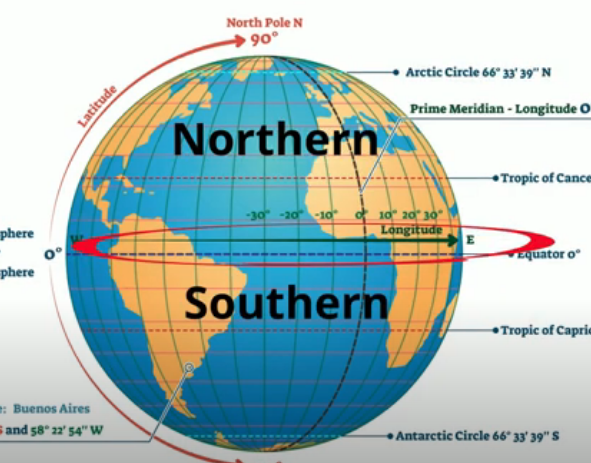
The equator is a line of latitude that marks 0 degrees latitude. It divides the Earth into two hemispheres: the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. This division has profound implications for the planet’s climate, seasons, and even the distribution of landmasses.
Climate and Seasons:
The equator is a region of intense solar radiation. The sun’s rays hit the Earth at a near-perpendicular angle, resulting in consistently warm temperatures throughout the year. This leads to tropical climates characterized by high humidity, abundant rainfall, and lush vegetation. As one moves away from the equator towards the poles, the angle of the sun’s rays decreases, resulting in colder temperatures and distinct seasons.
Landmasses and Oceans:
The equator is also a significant feature in the distribution of landmasses and oceans. The majority of the Earth’s landmass is situated in the Northern Hemisphere, while the Southern Hemisphere is dominated by water. This distribution contributes to differences in biodiversity, climate patterns, and global trade routes.
Cultural Diversity:
The equator is home to a vast array of cultures and civilizations. From the rainforests of the Amazon to the savannas of Africa, the equatorial region boasts a diverse tapestry of languages, traditions, and ways of life. This diversity is a testament to the adaptability of human societies to different environments and the interconnectedness of the world.
Navigational Significance:
The equator serves as a key reference point for navigation. Sailors and pilots use the equator as a starting point for measuring latitude, which is essential for determining location and direction. The equator also plays a role in the establishment of international time zones, with the Greenwich Meridian serving as the prime meridian at 0 degrees longitude.
The Equator: A Global Perspective
Understanding the equator’s significance goes beyond mere geography. It offers a unique perspective on the interconnectedness of our planet and the diverse ways in which life adapts to different environments. Studying the equator allows us to appreciate the global implications of climate change, the importance of biodiversity conservation, and the challenges of sustainable development.
Understanding the Equator: FAQs
Q: Why is the equator important?
A: The equator is important because it divides the Earth into two hemispheres, influences climate and seasons, shapes landmass distribution, and serves as a reference point for navigation.
Q: What is the climate like at the equator?
A: The equator experiences a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures, high humidity, and abundant rainfall throughout the year.
Q: What are some of the cultural features of equatorial regions?
A: Equatorial regions are home to a wide range of cultures, including indigenous communities, diverse languages, and unique traditions.
Q: How does the equator influence navigation?
A: The equator serves as a starting point for measuring latitude, which is essential for determining location and direction.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by equatorial regions?
A: Equatorial regions face challenges such as deforestation, climate change, and poverty, which require global attention and cooperation.
Tips for Understanding the Equator:
- Use a globe or world map: Visualizing the equator on a globe or world map helps to understand its position and significance.
- Study climate zones: Explore the different climate zones of the Earth and how they relate to the equator.
- Research equatorial cultures: Learn about the diverse cultures and traditions of equatorial regions.
- Engage in discussions: Share your knowledge of the equator with others and encourage discussions about its importance.
Conclusion
The equator, while an imaginary line, is a powerful symbol of Earth’s interconnectedness. It serves as a reminder of the planet’s diverse climates, cultures, and ecosystems. By understanding the significance of the equator, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of our planet and the importance of global cooperation in addressing shared challenges. As we navigate the challenges of the 21st century, the equator serves as a powerful reminder of our shared responsibility to protect and preserve our planet for future generations.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A World Divided: Understanding the Significance of the Equator. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!