A Reshaped Continent: Europe After World War II
Related Articles: A Reshaped Continent: Europe After World War II
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Reshaped Continent: Europe After World War II. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Reshaped Continent: Europe After World War II
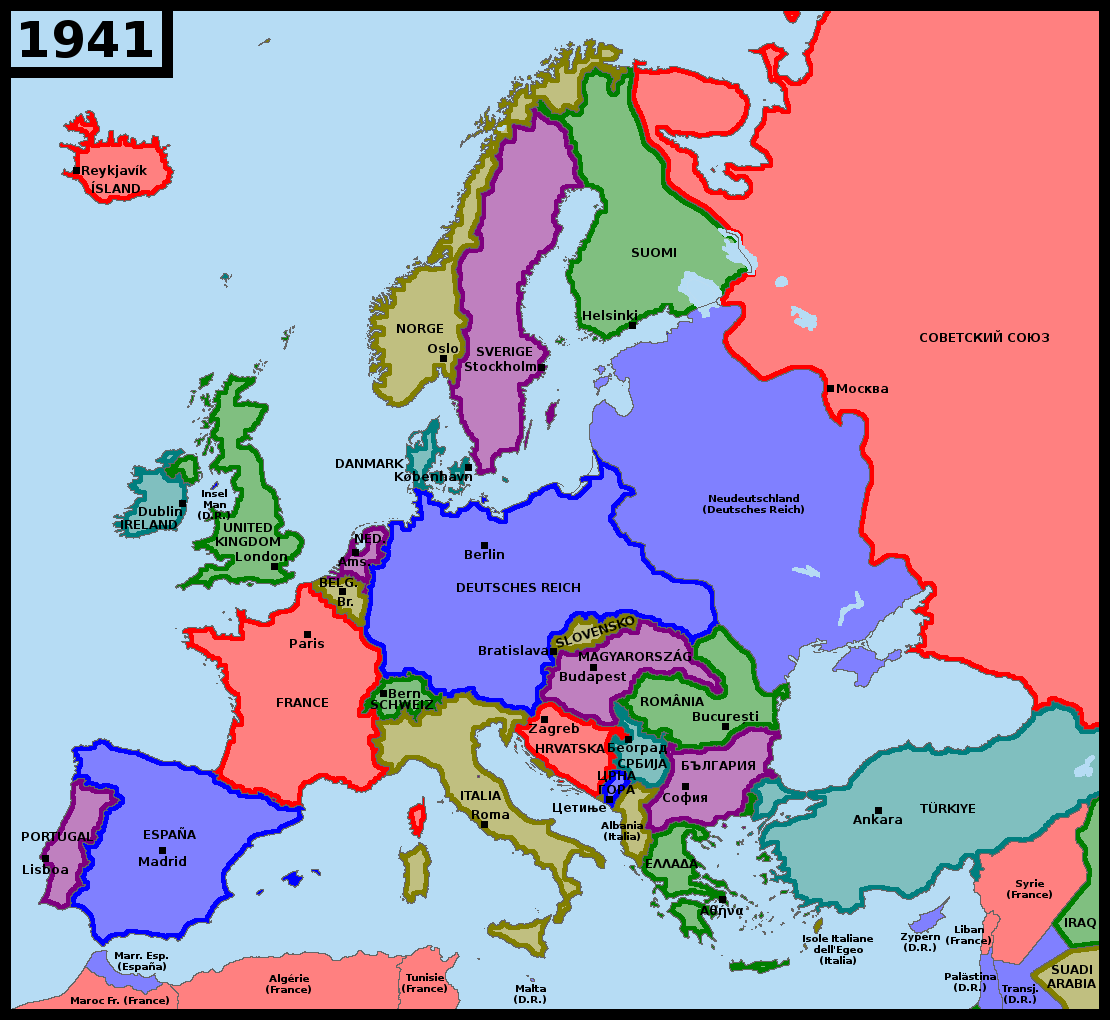
The conclusion of World War II in 1945 marked a profound turning point in European history. The conflict, the most devastating in human history, left the continent scarred, its political landscape dramatically altered, and its social fabric deeply fractured. The map of Europe, once a patchwork of empires and kingdoms, was reshaped, reflecting the geopolitical shifts that followed the war.
The Rise of New Nations and the Fall of Empires:
The war’s aftermath saw the emergence of new nation-states while dismantling the old empires. The Austro-Hungarian, Ottoman, and German empires, which had dominated Europe for centuries, were dissolved. This dismantling led to the creation of new nations like Czechoslovakia, Austria, Hungary, Yugoslavia, Poland, and Romania.
The Iron Curtain and the Cold War:
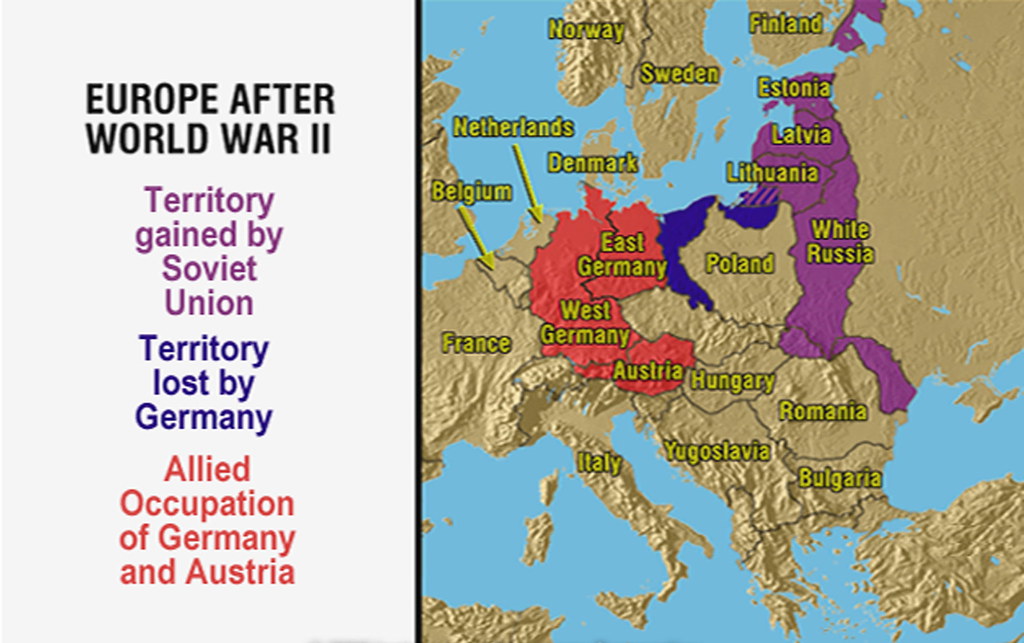
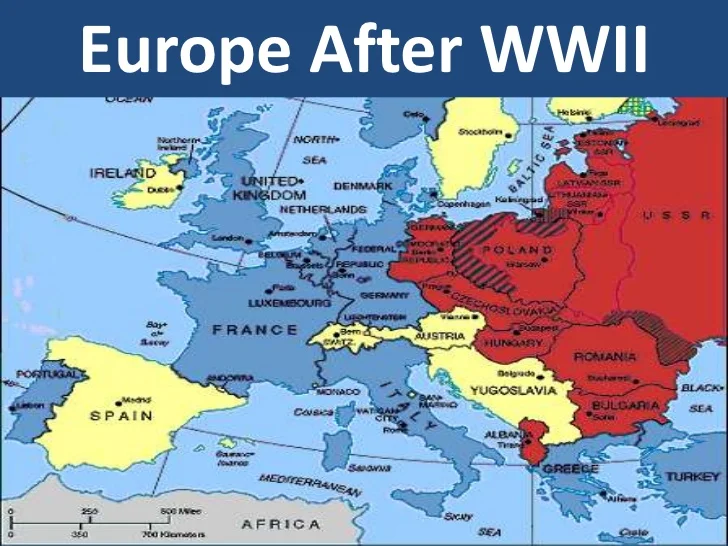
The war’s conclusion also ushered in a new era of ideological division: the Cold War. The Soviet Union, a major victor in the war, expanded its influence in Eastern Europe, imposing communist regimes in countries like Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, East Germany, Bulgaria, and Romania. This division solidified into the "Iron Curtain," a metaphorical barrier separating communist Eastern Europe from the capitalist West.
The Creation of NATO and the Warsaw Pact:
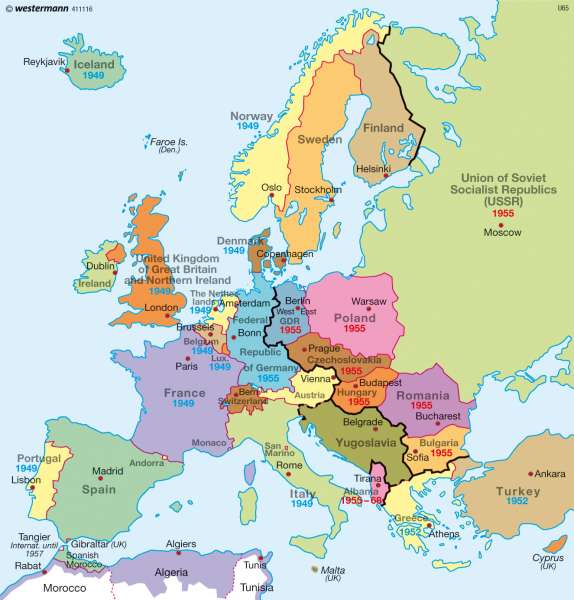
The Cold War rivalry led to the formation of two opposing military alliances. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was established in 1949 by Western European nations and the United States to counter the Soviet threat. In response, the Soviet Union formed the Warsaw Pact in 1955, uniting its Eastern European allies.
The Post-War Economic Recovery and the Marshall Plan:
The war’s devastation left Europe facing immense economic challenges. The United States, under the Marshall Plan, provided significant financial aid to Western European nations, helping them rebuild their economies and recover from the war’s destruction. This economic assistance played a crucial role in promoting stability and economic growth in Western Europe.
The European Union: Integration and Cooperation:
The desire for peace and economic prosperity led to the formation of the European Economic Community (EEC) in 1957. This initiative, later renamed the European Union (EU), aimed to integrate European economies through free trade and cooperation. The EU has expanded significantly since its inception, encompassing most of Western Europe and becoming a major economic and political force in the world.
The Legacy of the Blank Map:
The blank map of Europe after World War II serves as a potent visual representation of the continent’s turbulent past. It highlights the significant geopolitical changes that reshaped the continent, the emergence of new nations, the division of Europe along ideological lines, and the subsequent efforts towards integration and cooperation.
Benefits of Studying the Blank Map:
Understanding the post-war map of Europe offers numerous benefits:
- Historical Perspective: It provides a visual context for understanding the profound changes that reshaped Europe after the war, including the rise and fall of empires, the creation of new nations, and the emergence of the Cold War.
- Geopolitical Understanding: It sheds light on the geopolitical dynamics of the region, including the formation of alliances, the division of Europe into East and West, and the subsequent efforts towards integration.
- Economic Insights: It helps to grasp the economic challenges faced by Europe after the war and the role of initiatives like the Marshall Plan in facilitating economic recovery and growth.
- Contemporary Relevance: The blank map serves as a reminder of the fragility of peace and the importance of international cooperation in addressing global challenges.
FAQs:
Q: Why is the blank map of Europe after World War II significant?
A: The blank map provides a visual representation of the profound changes that reshaped the continent after the war, including the emergence of new nations, the division of Europe along ideological lines, and the subsequent efforts towards integration.
Q: What are the key geopolitical changes that occurred in Europe after World War II?
A: The key changes include the fall of empires, the rise of new nations, the division of Europe into East and West, the creation of NATO and the Warsaw Pact, and the subsequent efforts towards integration through the European Union.
Q: How did the Cold War impact the map of Europe?
A: The Cold War led to the division of Europe along ideological lines, with the Soviet Union imposing communist regimes in Eastern Europe. This division solidified into the "Iron Curtain," a metaphorical barrier separating communist Eastern Europe from the capitalist West.
Q: What was the significance of the Marshall Plan?
A: The Marshall Plan provided significant financial aid to Western European nations, helping them rebuild their economies and recover from the war’s destruction. This economic assistance played a crucial role in promoting stability and economic growth in Western Europe.
Q: What is the importance of the European Union?
A: The European Union, formed through the integration of European economies, has become a major economic and political force in the world. It promotes peace, economic prosperity, and cooperation among its member states.
Tips for Using the Blank Map:
- Visualize the Changes: Use the blank map to visualize the key changes that occurred in Europe after World War II, such as the emergence of new nations, the division of Europe into East and West, and the expansion of the European Union.
- Research and Fill in the Details: Use the blank map as a starting point for research, filling in the details of each country’s history, political system, and economic development.
- Compare and Contrast: Use the blank map to compare and contrast the different regions of Europe, highlighting their unique characteristics and historical experiences.
- Connect to Contemporary Issues: Use the blank map to explore contemporary issues in Europe, such as the rise of nationalism, the refugee crisis, and the challenges of globalization.
Conclusion:
The blank map of Europe after World War II serves as a powerful reminder of the continent’s turbulent past and its subsequent journey towards integration and cooperation. It highlights the profound changes that reshaped the continent, the challenges faced by European nations, and the enduring legacy of the war’s aftermath. By studying this map, we gain a deeper understanding of the historical forces that shaped modern Europe and the complex geopolitical landscape that continues to evolve today.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Reshaped Continent: Europe After World War II. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!