A Journey Across the Equator: Exploring the Significance of Brazil’s Geographic Divide
Related Articles: A Journey Across the Equator: Exploring the Significance of Brazil’s Geographic Divide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Across the Equator: Exploring the Significance of Brazil’s Geographic Divide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Across the Equator: Exploring the Significance of Brazil’s Geographic Divide
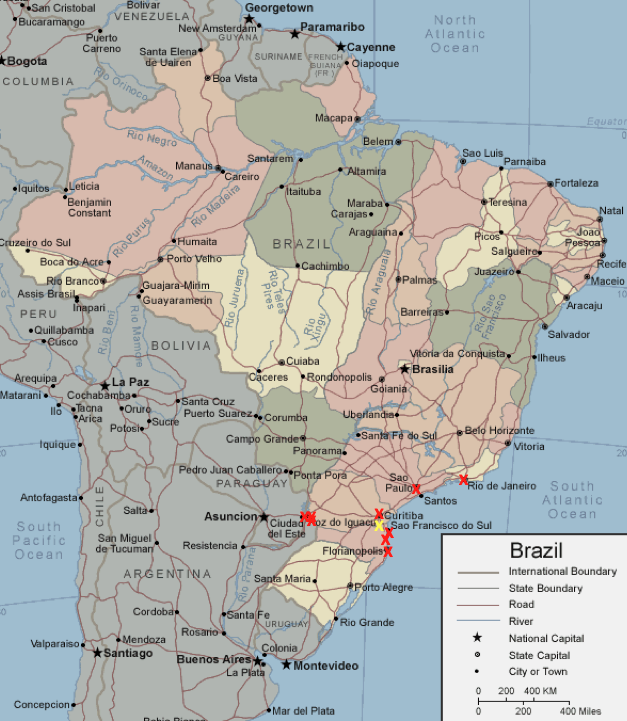
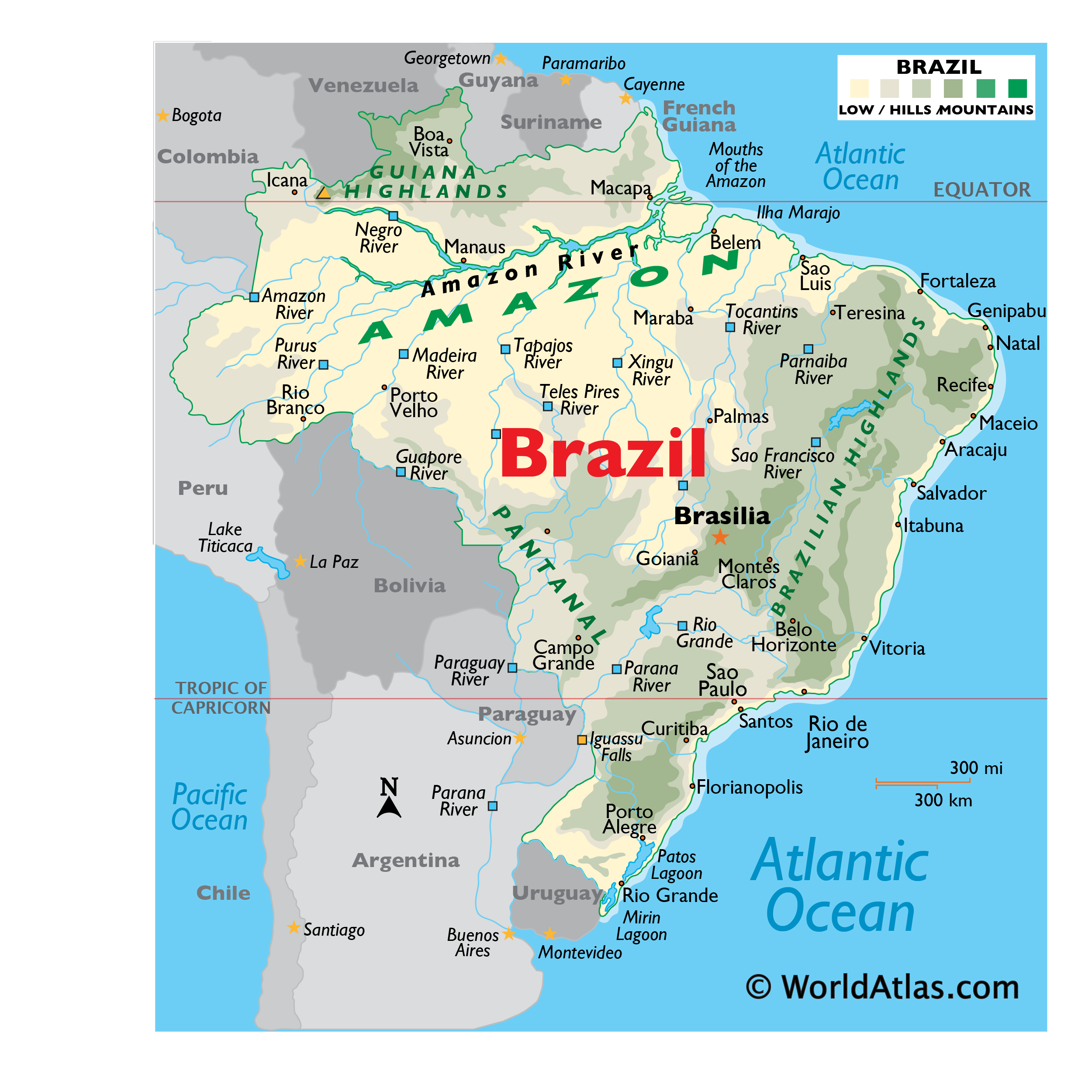
The Earth’s equator, an imaginary line that circles the globe at zero degrees latitude, is a significant geographical feature that divides the planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. In South America, the equator traverses a substantial portion of Brazil, effectively bisecting the country and creating a unique geographic divide. This article delves into the significance of the equator in Brazil, exploring its impact on the country’s climate, biodiversity, and cultural landscape.
The Equator’s Influence on Brazil’s Climate
The equator’s presence has a profound impact on Brazil’s climate, primarily due to the consistent exposure to direct sunlight throughout the year. This constant solar radiation translates into consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall, particularly in the Amazon rainforest, which stretches across much of northern Brazil.
The equatorial climate is characterized by:
- High Temperatures: The equator experiences consistent high temperatures throughout the year, with average temperatures ranging from 25°C to 30°C (77°F to 86°F).
- High Humidity: The constant exposure to sunlight and the presence of extensive bodies of water lead to high humidity levels, making the air feel heavy and muggy.
- Abundant Rainfall: The equatorial climate is characterized by high rainfall, with some regions receiving over 2,000 millimeters (80 inches) of rain annually. This rainfall fuels the lush vegetation and diverse ecosystems of the Amazon rainforest.
- Distinct Wet and Dry Seasons: While the equator experiences high rainfall year-round, some areas exhibit distinct wet and dry seasons. These variations are influenced by the movement of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a band of low atmospheric pressure that shifts north and south throughout the year.
The Equator’s Impact on Brazil’s Biodiversity
The equatorial climate plays a crucial role in supporting Brazil’s extraordinary biodiversity. The Amazon rainforest, located north of the equator, is the largest and most biodiverse rainforest on Earth, harboring a staggering number of plant and animal species. This biodiversity is attributed to:
- Abundant Rainfall and Sunlight: The consistent rainfall and sunlight provide ideal conditions for plant growth, fostering a dense and diverse forest canopy.
- Stable Climate: The equatorial climate’s relatively stable temperatures and rainfall patterns create a predictable environment that allows species to thrive and diversify.
- Rich Soils: The Amazon rainforest’s soils, though poor in nutrients, are rich in organic matter, providing essential nutrients for plant growth.
- Geographic Isolation: The Amazon rainforest’s vast expanse and isolation have created unique evolutionary pressures, leading to the development of a wide range of endemic species found nowhere else on Earth.
Cultural Diversity and the Equator’s Influence
The equator’s presence has also shaped the cultural landscape of Brazil, contributing to the country’s rich and diverse cultural heritage.
- Indigenous Cultures: The Amazon rainforest has been home to indigenous communities for millennia, and their cultures are deeply intertwined with the natural environment. Their traditional knowledge and practices demonstrate a profound understanding of the rainforest’s ecosystem and its resources.
- Afro-Brazilian Culture: The slave trade brought people of African descent to Brazil, particularly to the coastal regions, where they contributed to the development of unique musical genres, dance forms, and culinary traditions.
- European Influence: European colonization introduced new cultural influences to Brazil, including language, religion, and architectural styles. The interaction of these influences has created a unique cultural blend that reflects the country’s diverse history.
The Equator as a Geographic Divide
The equator’s presence in Brazil has created a distinct geographic divide, separating the country into two distinct regions:
- Northern Brazil: Located north of the equator, this region is characterized by the Amazon rainforest, its humid climate, and its diverse indigenous communities.
- Southern Brazil: Located south of the equator, this region experiences a more temperate climate, with distinct seasons and a diverse landscape that includes grasslands, forests, and mountains.
This geographic divide is reflected in the country’s cultural, economic, and social landscapes. The Amazon rainforest region is home to a significant portion of Brazil’s indigenous population, while the southern region has a more diverse population with a strong European influence.
Exploring the Equator in Brazil: Key Locations and Experiences
For those seeking to experience the equator’s influence in Brazil, several key locations offer unique opportunities:
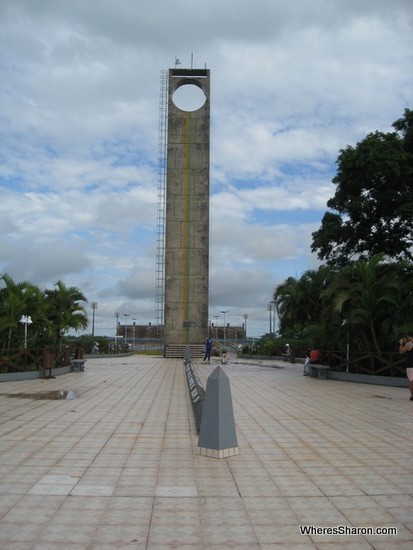
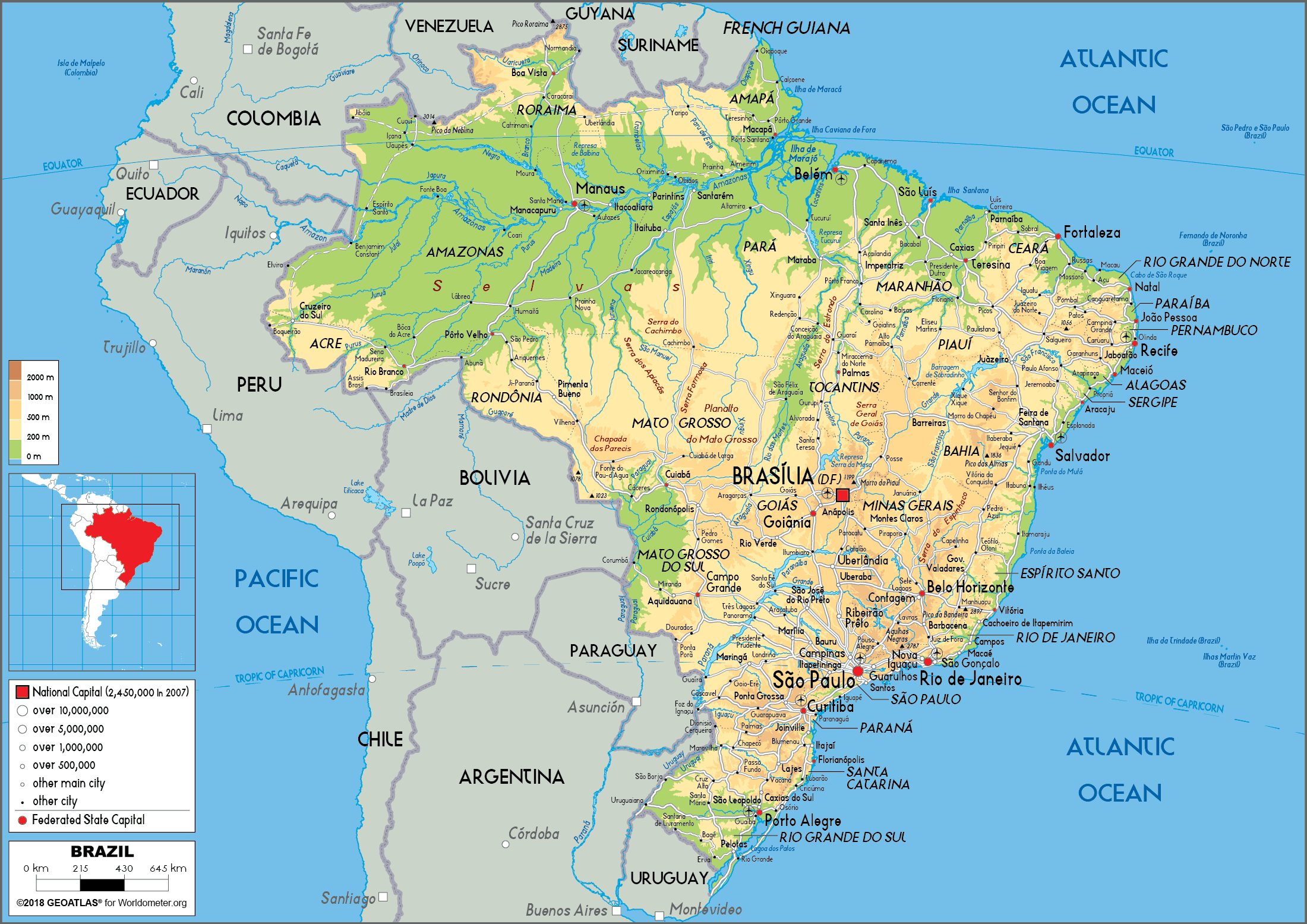
- Macapá, Amapá: Located on the northern coast of Brazil, Macapá is the closest major city to the equator. The city is known for its diverse ecosystems, including the Amazon rainforest and the coastal mangroves. Visitors can visit the Marco Zero do Equador, a monument marking the precise location of the equator.
- Manaus, Amazonas: Situated deep within the Amazon rainforest, Manaus is a bustling city known as the "Gateway to the Amazon." Visitors can embark on boat trips to explore the rainforest, encounter diverse wildlife, and experience the vibrant indigenous culture of the region.
- Belém, Pará: Located on the mouth of the Amazon River, Belém is a historical city with a rich cultural heritage. The city is known for its vibrant markets, colonial architecture, and its proximity to the Amazon rainforest.
FAQs about the Equator in Brazil
- Q: What is the significance of the equator in Brazil?
A: The equator plays a crucial role in shaping Brazil’s climate, biodiversity, and cultural landscape. It influences the country’s tropical climate, supports the Amazon rainforest’s diverse ecosystems, and has shaped the cultural heritage of Brazil’s indigenous and Afro-Brazilian communities.
- Q: What are the main differences between northern and southern Brazil?
A: Northern Brazil, located north of the equator, is characterized by the Amazon rainforest, its humid climate, and its diverse indigenous communities. Southern Brazil, located south of the equator, experiences a more temperate climate, with distinct seasons and a diverse landscape that includes grasslands, forests, and mountains.
- Q: What are some of the best places to experience the equator in Brazil?
A: Macapá, Amapá, Manaus, Amazonas, and Belém, Pará are all excellent locations to experience the equator’s influence on Brazil’s climate, biodiversity, and culture.
Tips for Visiting the Equator in Brazil
- Plan your trip during the dry season: The best time to visit Brazil’s equatorial regions is during the dry season, which typically runs from June to September.
- Pack lightweight clothing: The equatorial climate is hot and humid, so pack lightweight, breathable clothing.
- Bring insect repellent: The Amazon rainforest is home to a variety of insects, so bring insect repellent to protect yourself from bites.
- Respect local customs and traditions: When visiting indigenous communities, it is essential to respect their customs and traditions.
- Support sustainable tourism: Choose tour operators and accommodations that prioritize sustainability and environmental conservation.
Conclusion
The equator’s presence in Brazil has had a profound impact on the country’s climate, biodiversity, and cultural landscape. From the lush Amazon rainforest to the diverse ecosystems of the southern region, Brazil’s geographic divide is a testament to the equator’s influence. By understanding the equator’s significance, we can appreciate the unique and diverse nature of Brazil and its place in the global landscape.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Across the Equator: Exploring the Significance of Brazil’s Geographic Divide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!