A Geographic Perspective: Understanding South America’s Equator Crossing
Related Articles: A Geographic Perspective: Understanding South America’s Equator Crossing
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Perspective: Understanding South America’s Equator Crossing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Perspective: Understanding South America’s Equator Crossing
South America, a continent renowned for its diverse landscapes, rich cultures, and vibrant ecosystems, is uniquely positioned on the globe. The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0° latitude, intersects South America, dividing the continent into two distinct hemispheres: the Northern and Southern hemispheres. This intersection has profound implications for South America’s climate, biodiversity, and cultural development.
The Equatorial Line: A Defining Feature
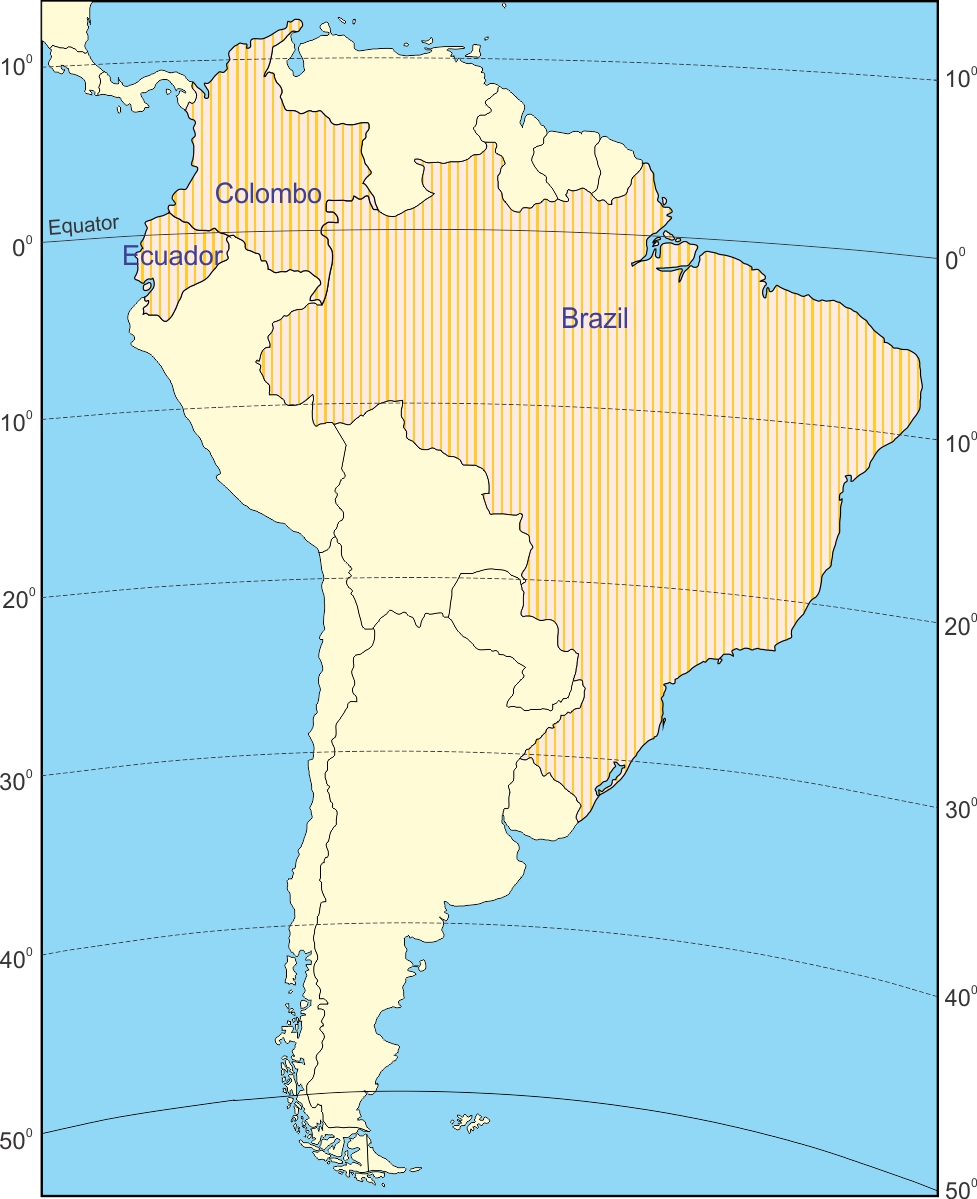
The equator’s passage through South America is a significant geographical feature. It runs through the northern parts of Colombia, Ecuador, and Brazil, influencing the climate and ecosystems of these regions. The equatorial belt, encompassing the area around the equator, experiences consistent solar radiation throughout the year, leading to a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall. This consistent warmth and moisture create ideal conditions for the flourishing of diverse ecosystems, including lush rainforests, vast savannas, and fertile agricultural lands.
Climate and Biodiversity: Equatorial Influence
The equator’s presence profoundly shapes South America’s climate and biodiversity. The equatorial belt, encompassing the area around the equator, experiences consistent solar radiation throughout the year, leading to a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall. This consistent warmth and moisture create ideal conditions for the flourishing of diverse ecosystems, including lush rainforests, vast savannas, and fertile agricultural lands.
-
The Amazon Rainforest: The Amazon rainforest, the largest rainforest in the world, is a prime example of the equatorial influence. This vast ecosystem, spanning across several South American countries, thrives on the abundant rainfall and consistent warmth provided by the equatorial climate. It is home to an unparalleled diversity of plant and animal life, representing a significant portion of the world’s biodiversity.
-
The Andes Mountains: The Andes Mountains, running along the western edge of South America, are another notable example of the equator’s influence. While the Andes experience a variety of climates, the equatorial region of the mountains, particularly in Ecuador, is home to unique ecosystems, including cloud forests and páramos, characterized by high altitudes and unique plant and animal life.
Cultural and Economic Significance
The equator’s influence extends beyond the natural environment, shaping the cultural and economic landscape of South America.
-
Indigenous Cultures: The equatorial regions of South America have been home to indigenous cultures for millennia. These cultures, adapted to the tropical climate and rich ecosystems, have developed unique traditions, languages, and knowledge systems. Their relationship with the environment is deeply intertwined with their cultural identity, highlighting the importance of understanding and respecting their role in the preservation of biodiversity.
-
Agriculture and Resources: The equatorial regions of South America are vital for the continent’s agricultural production. The fertile soils and abundant rainfall support a wide range of crops, including coffee, cacao, bananas, and rice. These agricultural products are essential for both domestic consumption and international trade, contributing significantly to the economies of these countries.
-
Tourism and Conservation: The equatorial regions of South America are also increasingly popular tourist destinations. The unique ecosystems, diverse wildlife, and vibrant cultures attract visitors from around the world. However, this tourism must be managed sustainably to preserve the delicate balance of these ecosystems and support the local communities.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the equator’s influence brings numerous benefits, it also presents challenges. The equatorial regions are vulnerable to climate change, deforestation, and other environmental threats.
-
Climate Change: The equatorial regions are particularly susceptible to the impacts of climate change, such as rising temperatures, changes in rainfall patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events. These changes can threaten the delicate balance of ecosystems, impact agriculture, and displace communities.
-
Deforestation: The Amazon rainforest, a critical carbon sink and home to immense biodiversity, is facing increasing deforestation due to agricultural expansion, logging, and mining. This deforestation not only destroys valuable ecosystems but also contributes to climate change.
-
Sustainable Development: Sustainable development is crucial for balancing economic growth with environmental conservation in the equatorial regions. This requires collaboration between governments, communities, and international organizations to promote responsible resource management, protect biodiversity, and ensure the well-being of local populations.
Exploring the Equator: A Journey of Discovery
Understanding the equator’s intersection with South America offers a unique perspective on the continent’s geography, climate, biodiversity, and cultural heritage. It highlights the intricate relationship between humans and the environment, underscoring the importance of sustainable development and conservation efforts.
FAQs
1. What is the equator, and why is it important?
The equator is an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0° latitude, dividing the planet into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is important because it influences the climate, biodiversity, and cultural development of regions that it intersects.
2. How does the equator influence South America’s climate?
The equator’s consistent solar radiation leads to a tropical climate in the equatorial regions of South America, characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall. This creates ideal conditions for diverse ecosystems, including rainforests and savannas.
3. What are some examples of equatorial ecosystems in South America?
The Amazon rainforest, the largest rainforest in the world, is a prime example of an equatorial ecosystem. The Andes Mountains, particularly in Ecuador, also have unique equatorial ecosystems, including cloud forests and páramos.
4. How does the equator impact South America’s culture and economy?
The equatorial regions are home to indigenous cultures with unique traditions and knowledge systems. They are also vital for agriculture, producing essential crops for both domestic consumption and international trade. Furthermore, the equatorial regions are popular tourist destinations, attracting visitors from around the world.
5. What are the challenges facing the equatorial regions of South America?
The equatorial regions are vulnerable to climate change, deforestation, and other environmental threats. These challenges require sustainable development strategies to balance economic growth with environmental conservation.
Tips for Further Exploration
- Visit the Equator Monument: Several countries in South America have monuments marking the equator, offering a unique opportunity to stand on the line that divides the world.
- Explore the Amazon rainforest: Embark on a guided tour to witness the incredible biodiversity and cultural richness of the Amazon rainforest.
- Visit the Andes Mountains: Explore the diverse ecosystems of the Andes Mountains, including cloud forests and páramos, and experience the unique cultural heritage of the Andean communities.
- Support sustainable tourism: Choose eco-friendly accommodations and tours that prioritize environmental conservation and support local communities.
- Learn about indigenous cultures: Engage with local indigenous communities to understand their traditions, knowledge systems, and perspectives on environmental conservation.
Conclusion
The equator’s intersection with South America is a defining feature of the continent, shaping its climate, biodiversity, and cultural landscape. Understanding this intersection is crucial for appreciating the continent’s unique geography and for developing sustainable strategies for its future. As we navigate the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, the equator serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of the Earth and the importance of responsible stewardship of our planet.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Perspective: Understanding South America’s Equator Crossing. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!