A Geographic Overview of India’s Neighbors: Understanding the Importance of India’s Surroundings
Related Articles: A Geographic Overview of India’s Neighbors: Understanding the Importance of India’s Surroundings
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Overview of India’s Neighbors: Understanding the Importance of India’s Surroundings. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Overview of India’s Neighbors: Understanding the Importance of India’s Surroundings
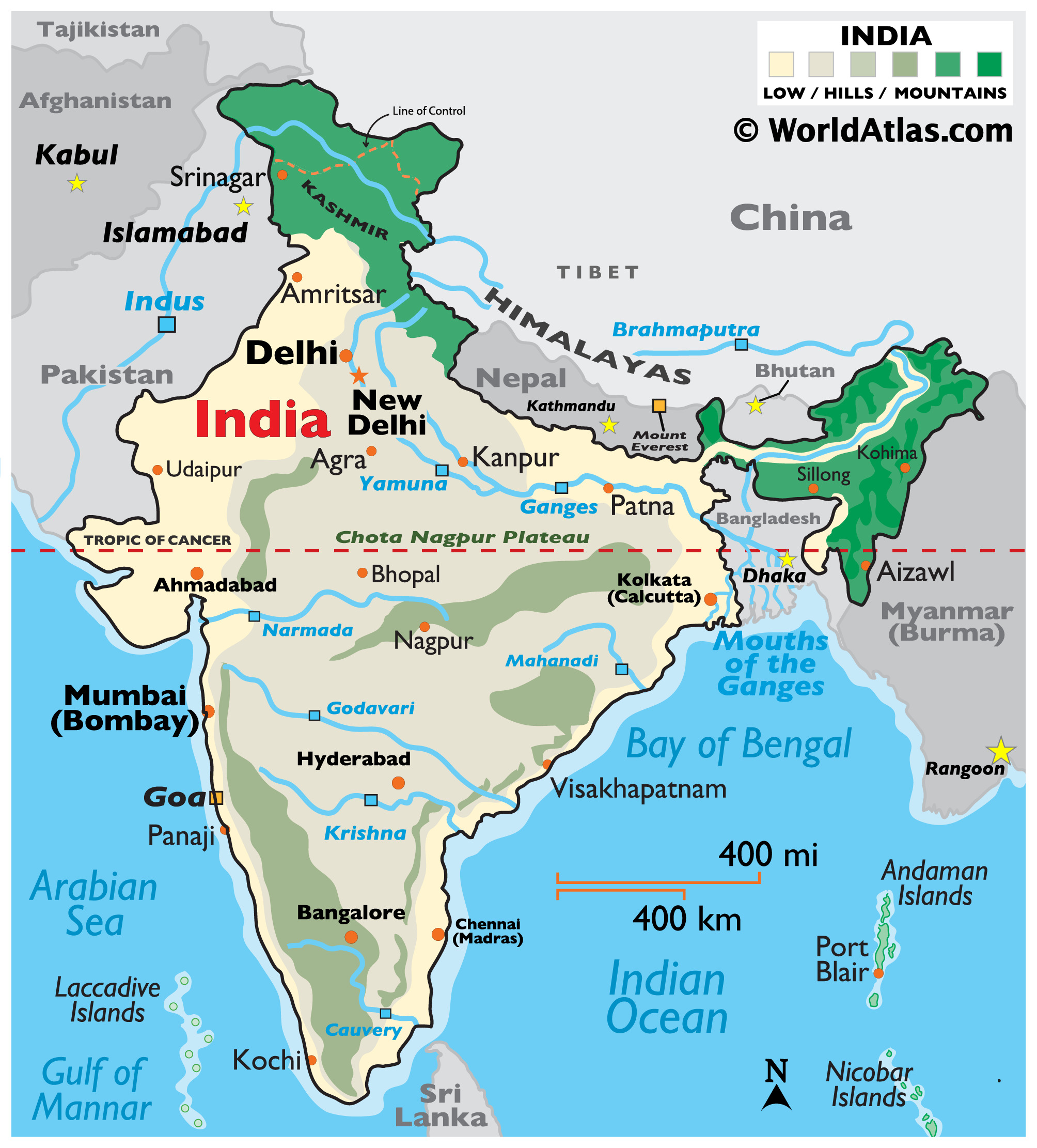
India, a vast subcontinental nation, is geographically positioned in a region of immense historical, cultural, and political significance. Understanding the countries that surround India is crucial for comprehending the nation’s past, present, and future. This article delves into the geographic landscape of India’s neighbors, exploring their diverse characteristics, shared histories, and the multifaceted relationships that bind them.
The Indian Subcontinent: A Mosaic of Nations
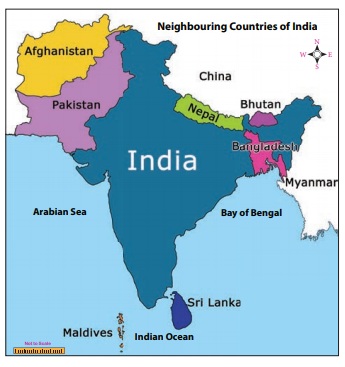
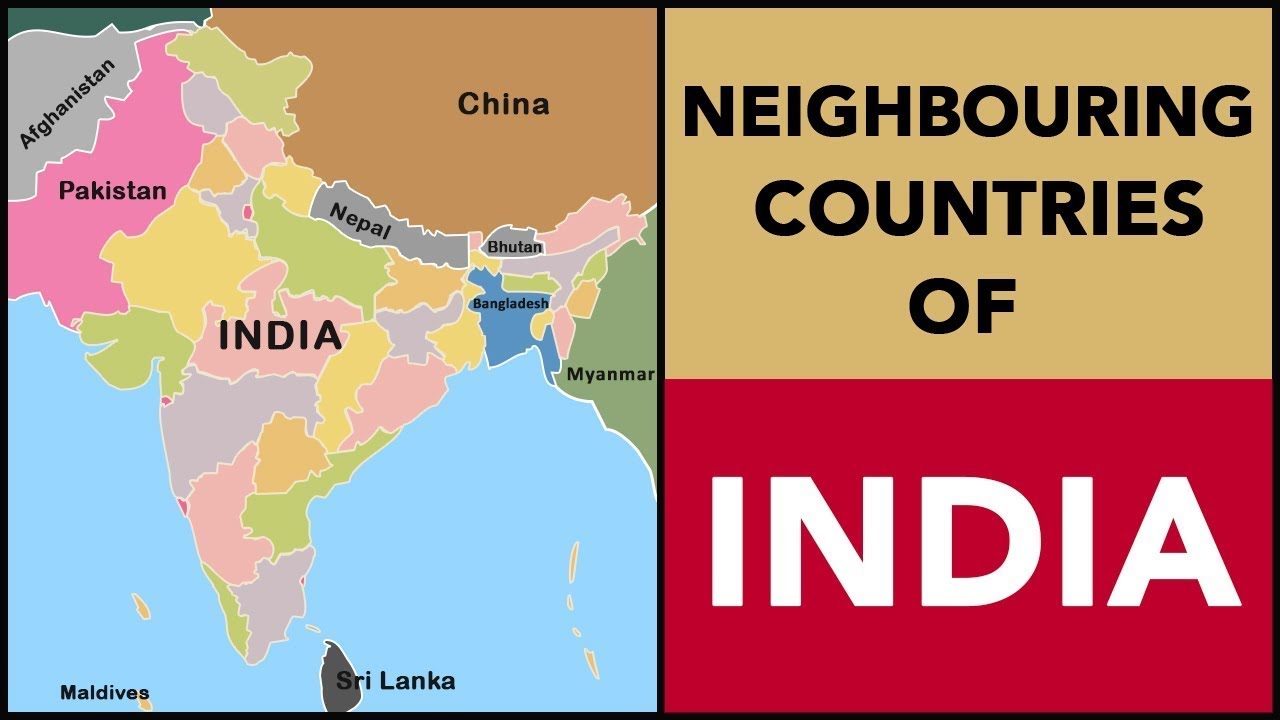
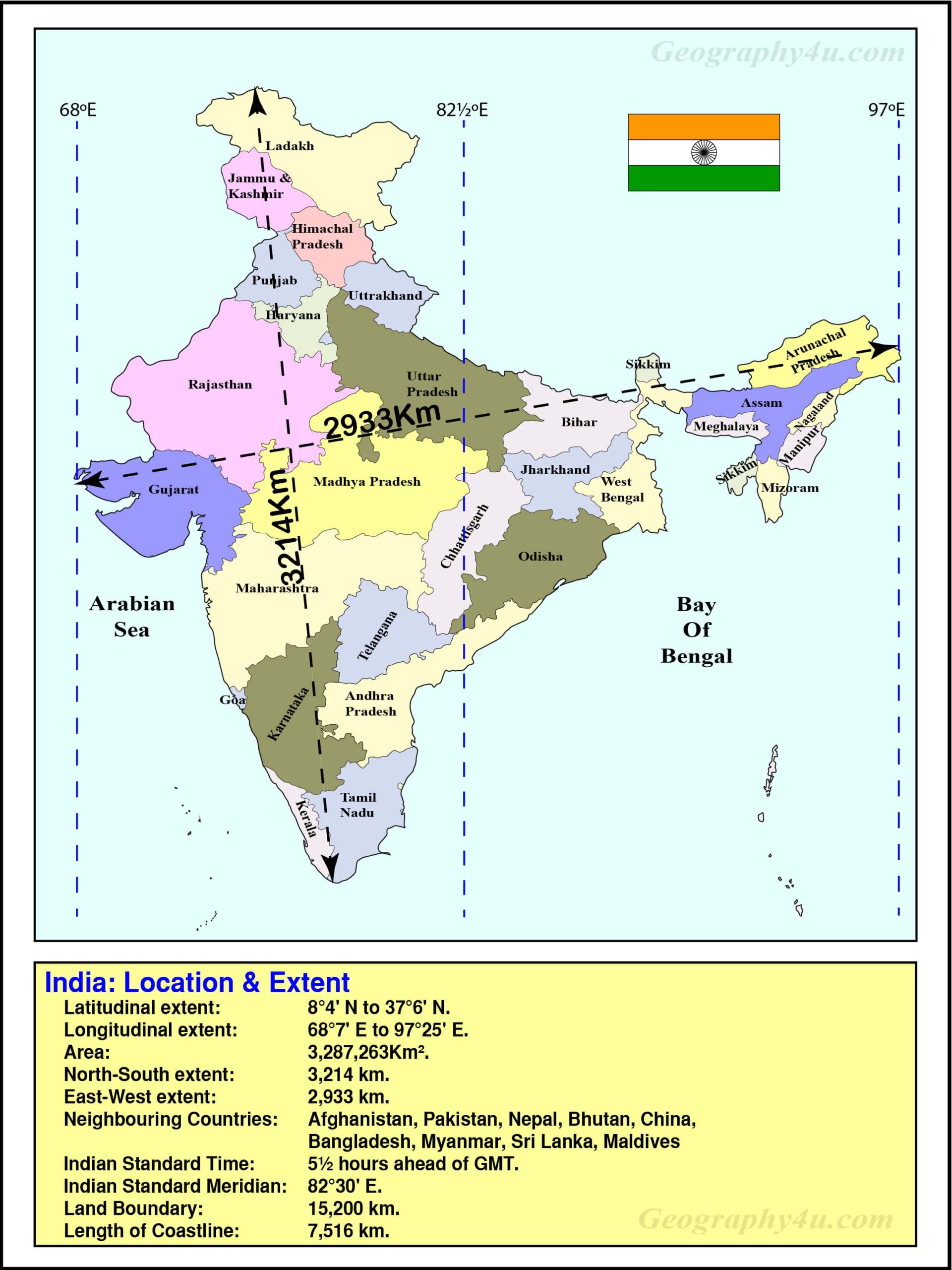
India’s geographical position, nestled within the Indian subcontinent, is a defining factor in its history and contemporary relationships. The subcontinent, encompassing India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives, is a melting pot of cultures, religions, and languages.
The Northern Frontier: A Tapestry of Mountains and Plateaus
The Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range, form a formidable natural barrier along India’s northern border. This imposing landscape houses three countries:
- Nepal: Situated in the heart of the Himalayas, Nepal is a landlocked nation known for its stunning mountain scenery, including Mount Everest, and its rich cultural heritage.
- Bhutan: Nestled in the eastern Himalayas, Bhutan is a landlocked kingdom renowned for its pristine environment and unique Buddhist culture.
- China: The vast and powerful Asian giant shares a long and complex border with India, marked by the towering Himalayas. The two nations have a history of territorial disputes, adding a layer of complexity to their bilateral relationship.
The Western Border: A History of Partition and Conflict
India’s western border is marked by the presence of Pakistan, a nation born out of the partition of British India in 1947. The partition led to widespread violence and displacement, leaving a lasting legacy of mistrust and conflict between the two countries.
- Pakistan: This Islamic republic shares a turbulent history with India, marked by wars, border disputes, and ongoing political tensions. The two nations have been engaged in a long-standing dispute over the Kashmir region, a source of constant friction.
The Eastern Border: A Shared History and Cultural Exchange
India’s eastern border is defined by its relationship with Bangladesh, a nation that emerged from the 1971 liberation war against Pakistan.
- Bangladesh: This South Asian nation shares a strong cultural and linguistic connection with India, making it a close neighbor with deep historical ties. The two nations cooperate on a range of issues, including trade, development, and security.
The Southern Shores: Islands of Diversity
India’s southern coast overlooks the Indian Ocean, where two island nations lie:
- Sri Lanka: This island nation, separated from India by the Palk Strait, has a long and complex history with its mainland neighbor. The two countries share cultural and linguistic connections, but have also faced periods of political tension and conflict.
- Maldives: This archipelago nation, located in the Indian Ocean, is known for its stunning beaches and luxurious resorts. Though geographically distant, the Maldives maintains close diplomatic and economic ties with India.
The Importance of Understanding India’s Neighbors
Understanding the geography and relationships between India and its neighbors is crucial for several reasons:
- Regional Stability: India’s strategic location in South Asia makes its relationships with neighboring countries vital for regional stability. The peaceful resolution of border disputes and the promotion of cooperation are essential for maintaining peace in the region.
- Economic Development: India’s economic growth is closely linked to its relationship with its neighbors. Trade, investment, and infrastructure development are crucial for fostering economic prosperity in the region.
- Cultural Exchange: The diverse cultures of India and its neighbors have a rich history of exchange and interaction. This cultural exchange enriches the lives of people in the region and fosters mutual understanding.
- Security Concerns: India faces a number of security challenges, including terrorism, separatism, and the proliferation of weapons. Understanding the dynamics of its neighbors is essential for addressing these challenges.
FAQs
Q1: What are the major challenges facing India’s relations with its neighbors?
A1: India’s relations with its neighbors are marked by a complex interplay of factors, including historical grievances, territorial disputes, political differences, and economic competition. Some of the major challenges include:
- Border Disputes: India faces unresolved border disputes with China, Pakistan, and Nepal. These disputes often escalate tensions and threaten regional stability.
- Terrorism: India has faced a long-standing threat from terrorism emanating from neighboring countries, particularly Pakistan. This has strained relations and created a climate of mistrust.
- Economic Competition: India’s economic rise has led to increased competition with some of its neighbors, particularly Pakistan and China. This competition can sometimes translate into political tensions.
Q2: How is India working to improve its relations with its neighbors?
A2: India has adopted a multifaceted approach to improve its relations with its neighbors:
- Diplomacy: India engages in regular diplomatic dialogue with its neighbors, seeking to resolve disputes through peaceful means.
- Economic Cooperation: India has launched initiatives to promote economic cooperation with its neighbors, including infrastructure development projects and trade agreements.
- Cultural Exchange: India actively promotes cultural exchange programs with its neighbors, fostering people-to-people connections and mutual understanding.
Q3: What is the significance of India’s "Neighborhood First" policy?
A3: India’s "Neighborhood First" policy is a strategic framework that prioritizes strengthening relations with its immediate neighbors. This policy emphasizes economic cooperation, security cooperation, and cultural exchange as key pillars of its foreign policy.
Tips
- Engage in critical thinking: Analyze the historical, political, and economic factors that influence the relationships between India and its neighbors.
- Seek diverse perspectives: Explore different viewpoints on the challenges and opportunities facing India’s regional relationships.
- Stay informed: Keep up with current events and developments in the region to understand the evolving dynamics of India’s foreign policy.
Conclusion
India’s geographical location and its relationships with its neighbors are crucial for its national security, economic prosperity, and cultural development. Understanding the diverse landscape of India’s surroundings, from the towering Himalayas to the islands of the Indian Ocean, is essential for comprehending the complexities of the region and the importance of fostering peaceful and cooperative relations. By engaging in thoughtful analysis, seeking diverse perspectives, and staying informed, we can gain a deeper understanding of the multifaceted dynamics that shape India’s interactions with its neighbors.
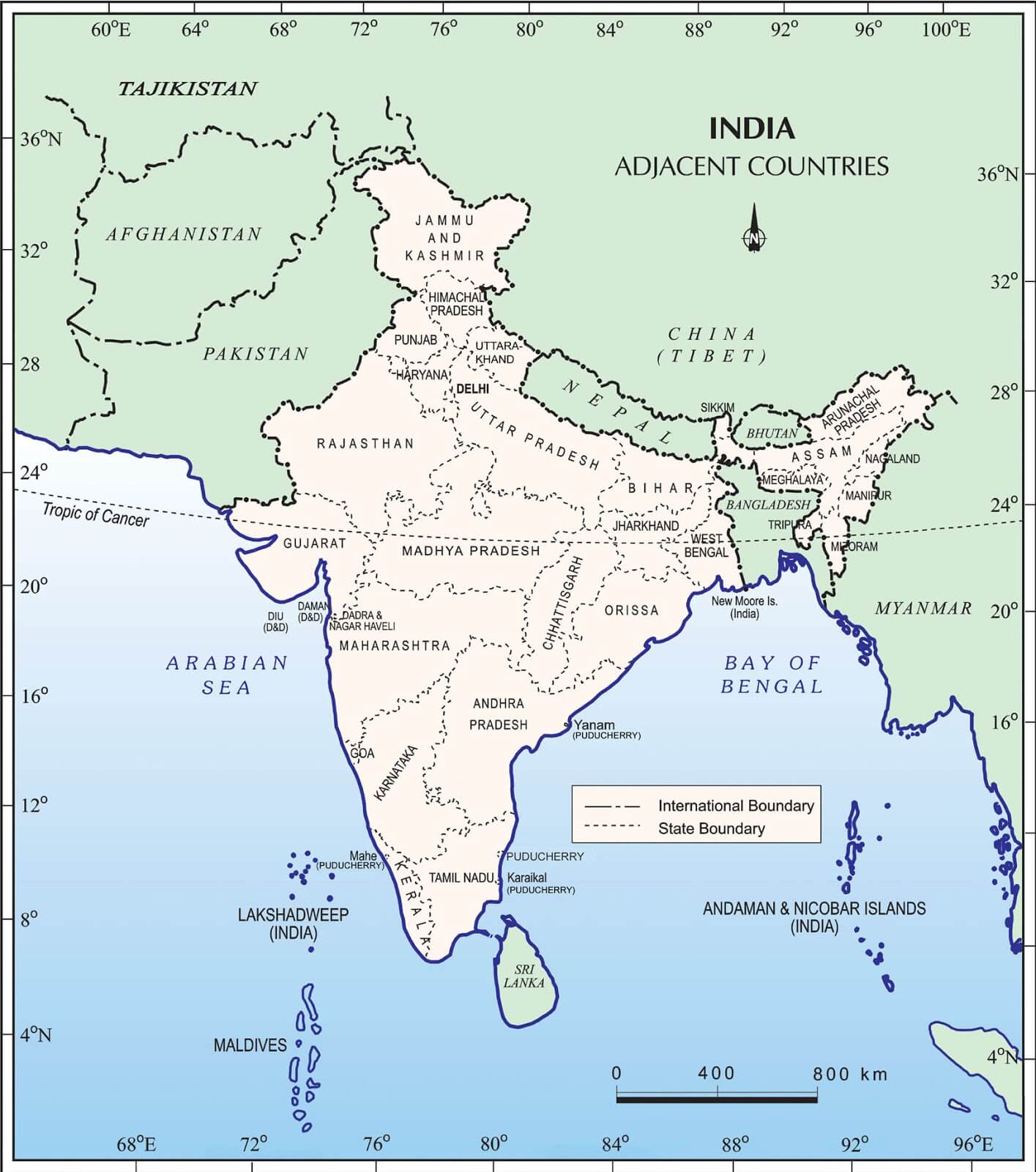
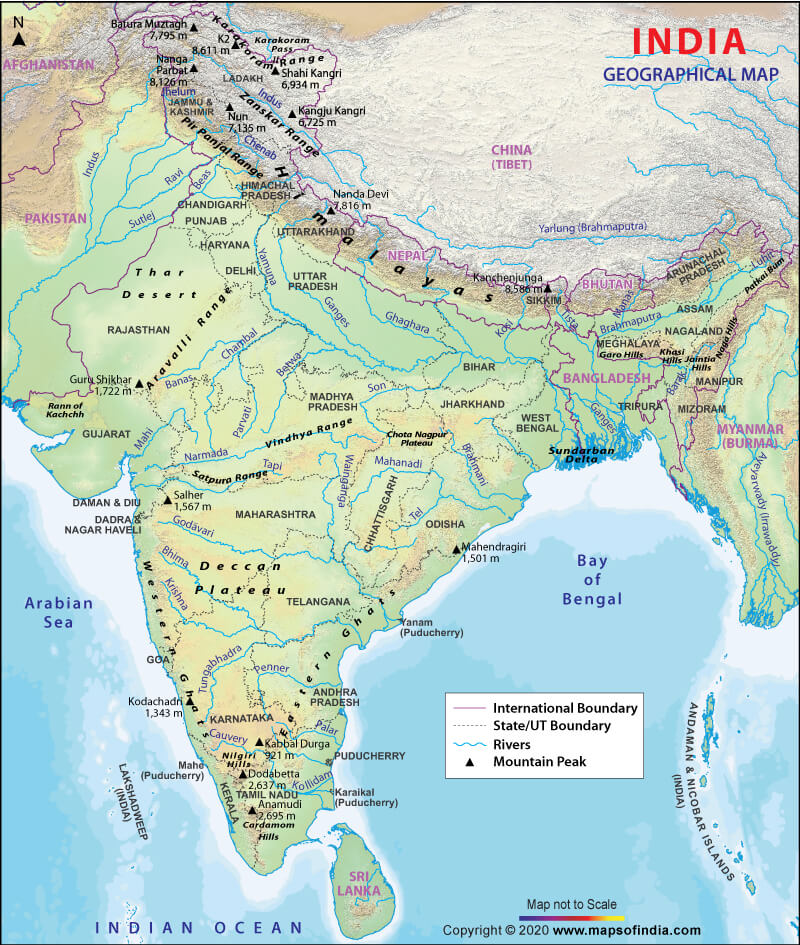
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Overview of India’s Neighbors: Understanding the Importance of India’s Surroundings. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!