A Geographic Journey: Exploring Yosemite National Park’s Location
Related Articles: A Geographic Journey: Exploring Yosemite National Park’s Location
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Journey: Exploring Yosemite National Park’s Location. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Geographic Journey: Exploring Yosemite National Park’s Location
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Geographic Journey: Exploring Yosemite National Park’s Location
- 3.1 Yosemite’s Place in the World
- 3.2 Navigating Yosemite’s Geographic Context
- 3.3 Exploring Yosemite’s Geographic Importance
- 3.4 Yosemite’s Significance Beyond Geography
- 3.5 Understanding Yosemite’s Location: A Key to Exploration
- 3.6 FAQs on Yosemite National Park’s Location:
- 3.7 Tips for Visiting Yosemite National Park:
- 3.8 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
A Geographic Journey: Exploring Yosemite National Park’s Location

Yosemite National Park, a jewel of the Sierra Nevada, holds a captivating allure for nature enthusiasts and adventure seekers alike. Its towering granite cliffs, cascading waterfalls, and ancient sequoia groves evoke a sense of awe and wonder. Understanding the park’s location within the broader context of the western United States is crucial for appreciating its geographical significance and planning a visit.
Yosemite’s Place in the World
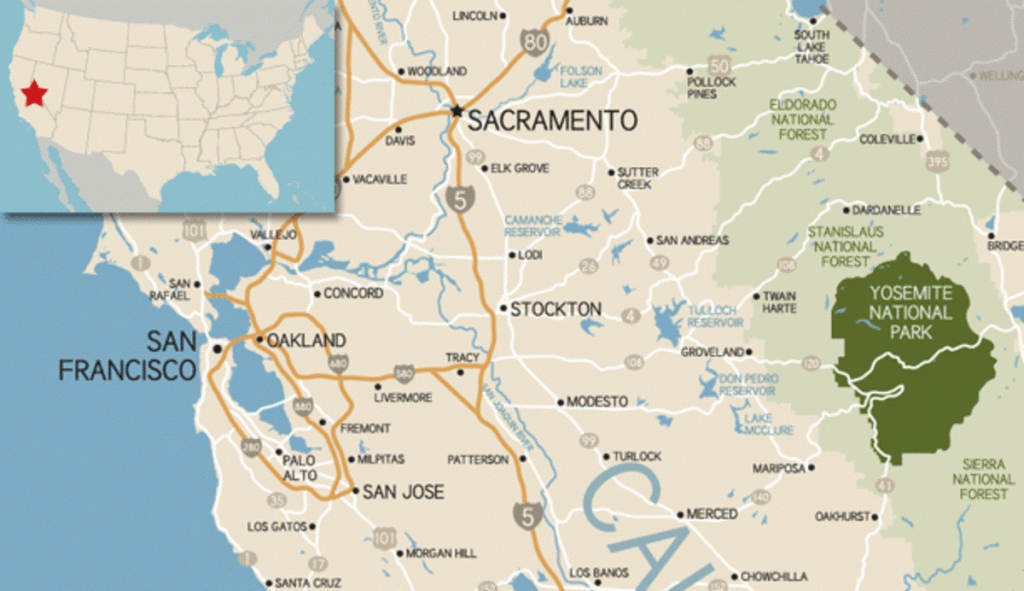
Yosemite National Park is situated in the western United States, specifically within the Sierra Nevada mountain range of California. This mountain range, stretching for over 400 miles, forms the eastern boundary of California’s Central Valley and houses some of the state’s highest peaks, including Mount Whitney, the tallest mountain in the contiguous United States.
Figure 1: Map of Yosemite National Park in California
[Insert a map of California with Yosemite National Park highlighted]
Yosemite’s location within the Sierra Nevada is crucial to its unique characteristics. The park’s dramatic topography, sculpted by glacial activity over millennia, has resulted in the iconic granite cliffs, deep valleys, and cascading waterfalls that define its landscape. The Sierra Nevada’s elevation and its position within the rain shadow of the Pacific Coast create a distinct climate for Yosemite, characterized by dry summers and snowy winters. This unique climate contributes to the park’s diverse flora and fauna, including giant sequoia trees, black bears, and the elusive Sierra Nevada red fox.
Navigating Yosemite’s Geographic Context
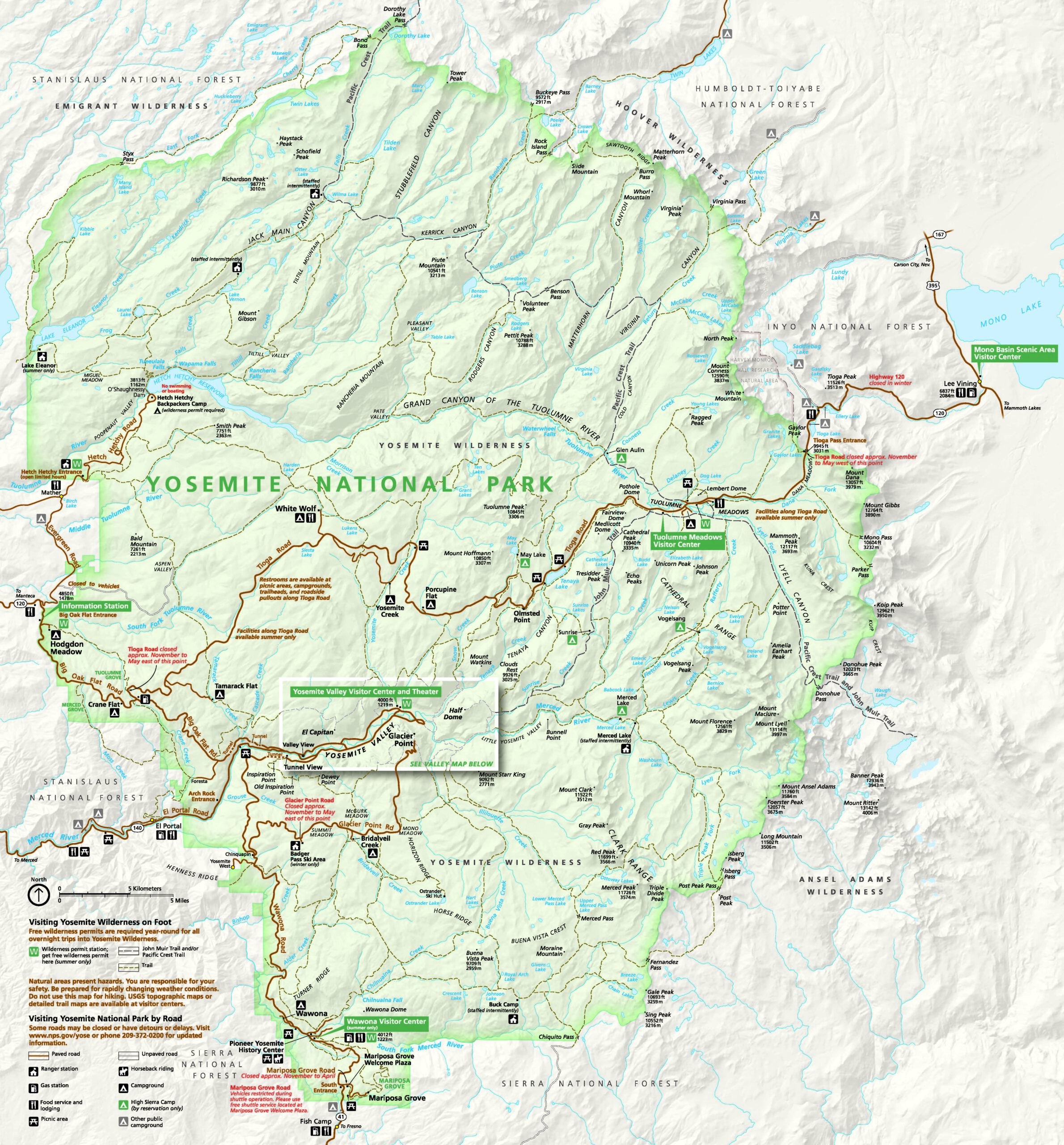
Yosemite National Park is located in the central Sierra Nevada, approximately 180 miles east of San Francisco and 200 miles north of Los Angeles. It covers an area of over 1,165 square miles, encompassing a diverse range of ecosystems, from alpine meadows to deep forests.
Figure 2: Map of Yosemite National Park with Key Locations
[Insert a map of Yosemite National Park with key locations like Yosemite Valley, Mariposa Grove, and Tioga Pass marked]
The park’s main entrance is located in the west, accessible via Highway 140. Visitors can also enter from the south via Highway 41 or the east via Highway 120 (Tioga Pass).
Exploring Yosemite’s Geographic Importance
Yosemite’s location within the Sierra Nevada is not merely a geographical fact; it is a testament to the park’s ecological significance. The park serves as a vital habitat for numerous species, including the iconic giant sequoia, which thrives in the unique conditions of the Sierra Nevada. The park’s diverse ecosystems also play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the surrounding region, contributing to water resources, air quality, and biodiversity.
Yosemite’s Significance Beyond Geography
Yosemite’s geographical location has shaped its cultural and historical significance. Native American tribes, including the Ahwahneechee, have called this land home for centuries, leaving behind a rich legacy of traditions and stories. The park’s breathtaking landscapes have also inspired artists, writers, and photographers, solidifying its place in American culture.
Understanding Yosemite’s Location: A Key to Exploration
Understanding Yosemite’s location within the Sierra Nevada is essential for any visitor planning to explore its diverse landscapes and experience its natural beauty. By appreciating the park’s geographic context, visitors can better understand its unique characteristics, plan their itinerary, and appreciate the intricate relationship between the park’s environment, history, and culture.
FAQs on Yosemite National Park’s Location:
Q1: How far is Yosemite National Park from San Francisco?
A1: Yosemite National Park is approximately 180 miles east of San Francisco.
Q2: What is the best time of year to visit Yosemite National Park?
A2: The best time to visit Yosemite National Park depends on your interests. Spring (April-May) and Fall (September-October) offer pleasant weather and fewer crowds. Summer (June-August) brings warm temperatures and the opportunity to hike to higher elevations. Winter (November-March) provides a unique experience with snow-covered landscapes and opportunities for snowshoeing and cross-country skiing.
Q3: Are there any major roads leading to Yosemite National Park?
A3: Yes, there are three major roads leading to Yosemite National Park: Highway 140 (west entrance), Highway 41 (south entrance), and Highway 120 (Tioga Pass, east entrance).
Q4: What are some of the most popular attractions within Yosemite National Park?
A4: Some of the most popular attractions within Yosemite National Park include Yosemite Valley, Half Dome, El Capitan, Yosemite Falls, Mariposa Grove of Giant Sequoias, and Glacier Point.
Q5: What are the elevation changes within Yosemite National Park?
A5: Yosemite National Park experiences significant elevation changes, ranging from approximately 2,000 feet in Yosemite Valley to over 13,000 feet at the summit of Mount Lyell.
Tips for Visiting Yosemite National Park:
1. Book Accommodations in Advance: Yosemite National Park is a popular destination, especially during peak season. Booking accommodations in advance is highly recommended to ensure availability.
2. Pack for Varying Weather Conditions: Yosemite’s weather can be unpredictable, even during the summer months. Pack layers of clothing, including rain gear and warm clothing for evenings and higher elevations.
3. Respect Wildlife: Yosemite is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including black bears. Store food properly in bear-resistant containers and maintain a safe distance from all animals.
4. Be Prepared for Hiking: Many of Yosemite’s attractions require hiking. Wear appropriate footwear and pack plenty of water and snacks.
5. Purchase a Park Pass: A park pass is required for entry to Yosemite National Park. Passes can be purchased online or at park entrances.
Conclusion:
Yosemite National Park’s location within the Sierra Nevada is a testament to its unique natural beauty, rich cultural heritage, and ecological significance. Its dramatic landscapes, diverse ecosystems, and iconic landmarks attract visitors from around the world, offering a glimpse into the grandeur of the American West. By understanding Yosemite’s geographic context, visitors can better appreciate its unique characteristics, plan their exploration, and contribute to the preservation of this treasured national park.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Journey: Exploring Yosemite National Park’s Location. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!