A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator, North Pole, and South Pole: Understanding Our Planet’s Geometry
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator, North Pole, and South Pole: Understanding Our Planet’s Geometry
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator, North Pole, and South Pole: Understanding Our Planet’s Geometry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator, North Pole, and South Pole: Understanding Our Planet’s Geometry

The Earth, our home planet, is a dynamic and complex sphere. Its surface is not uniform, but rather exhibits a diverse range of geographical features, climates, and ecosystems. To understand and navigate this intricate world, we rely on a system of lines and points that define its geometry. Among these, the equator, the North Pole, and the South Pole hold significant importance, serving as fundamental reference points for understanding Earth’s shape, orientation, and global positioning.
The Equator: A Line of Zero Latitude
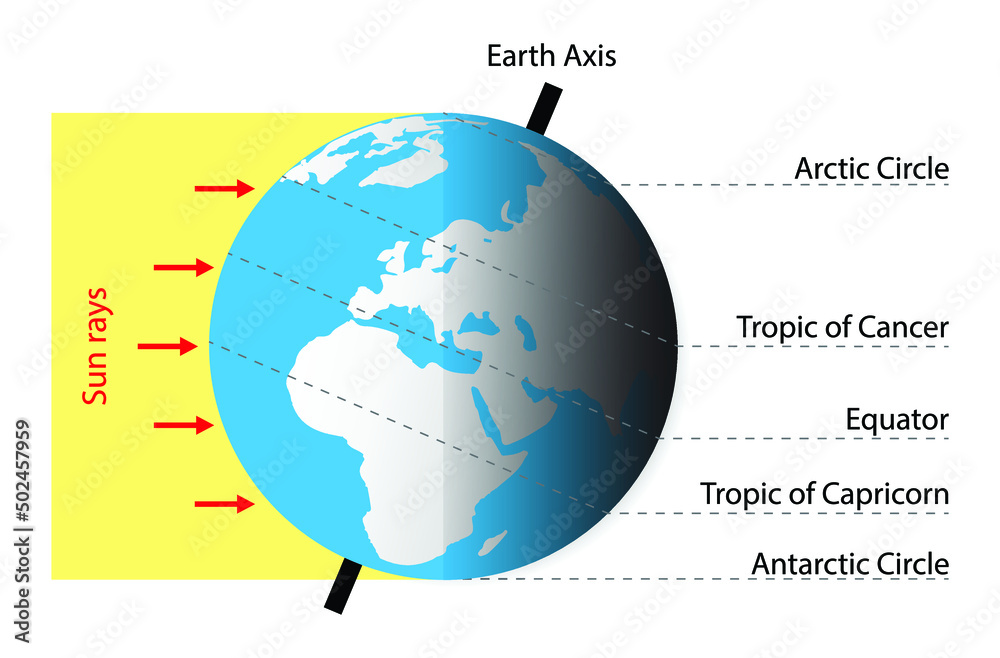
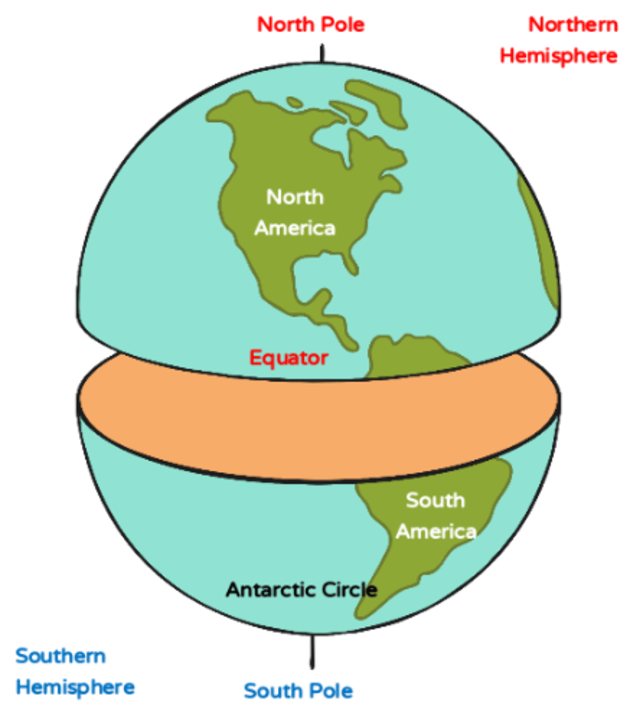
The equator is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude. It is the largest circle of latitude on the planet, dividing it into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The equator is equidistant from both the North Pole and the South Pole, and it represents the point where the Earth’s circumference is the greatest.
Significance of the Equator:
- Climate: The equator experiences the most intense solar radiation due to its direct exposure to the sun’s rays. This leads to a consistently warm climate with high humidity and abundant rainfall.
- Time Zones: The equator is the basis for the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) system, which divides the world into 24 time zones. Each time zone covers 15 degrees of longitude, starting from the Prime Meridian, which passes through Greenwich, England.
- Navigation: The equator serves as a crucial reference point for navigation, particularly for ships and airplanes. It allows for accurate determination of position and direction.
- Global Distribution: The equator plays a role in understanding the distribution of various natural resources, including rainforests, biodiversity, and mineral deposits.
The North Pole: The Northernmost Point
The North Pole is the northernmost point on Earth, located at 90 degrees North latitude. It is situated in the Arctic Ocean, covered by a thick layer of ice. The North Pole experiences 24 hours of daylight during the summer solstice and 24 hours of darkness during the winter solstice.
Significance of the North Pole:
- Geomagnetic Pole: The North Pole is close to the Earth’s geomagnetic north pole, which is where the Earth’s magnetic field lines converge. This magnetic field protects us from harmful solar radiation.
- Climate Change: The North Pole is particularly vulnerable to climate change, experiencing rapid melting of sea ice and rising sea levels.
- Research and Exploration: The North Pole is a hub for scientific research, with numerous expeditions studying climate change, ocean currents, and biodiversity.
- Cultural Importance: The North Pole holds cultural significance for indigenous communities in the Arctic region, who have lived in harmony with the environment for centuries.
The South Pole: The Southernmost Point
The South Pole is the southernmost point on Earth, located at 90 degrees South latitude. It is situated on the continent of Antarctica, covered by a vast ice sheet. Similar to the North Pole, the South Pole experiences 24 hours of daylight during the summer solstice and 24 hours of darkness during the winter solstice.
Significance of the South Pole:
- Geographic South Pole: The South Pole is the geographic south pole, representing the point where all lines of longitude converge.
- Ice Sheet: The South Pole is home to the largest ice sheet on Earth, containing approximately 70% of the world’s freshwater.
- Research and Exploration: The South Pole is a major site for scientific research, with numerous stations studying climate change, astronomy, and geology.
- International Cooperation: The South Pole is governed by the Antarctic Treaty System, which promotes international cooperation and scientific collaboration.
The Equator, North Pole, and South Pole Map: A Visual Representation of Earth’s Geometry
A map depicting the equator, North Pole, and South Pole is crucial for understanding the Earth’s geometry and global positioning. It provides a visual representation of the key reference points that define our planet’s shape and orientation.
Key Features of the Map:
- Equator: The equator is typically depicted as a thick, solid line that encircles the globe at 0 degrees latitude.
- North Pole: The North Pole is marked as a point at the top of the map, representing 90 degrees North latitude.
- South Pole: The South Pole is marked as a point at the bottom of the map, representing 90 degrees South latitude.
- Lines of Latitude and Longitude: The map may also include lines of latitude and longitude, forming a grid system for precise location identification.
- Continents and Oceans: The map may depict the continents and oceans, providing context for the positioning of the equator, North Pole, and South Pole.
Benefits of Using an Equator, North Pole, and South Pole Map:
- Visualization: The map offers a clear visual representation of the Earth’s geometry, helping to understand the concept of latitude and longitude.
- Global Perspective: It provides a global perspective, enabling the visualization of the relative positions of different countries and continents.
- Navigation: It assists in navigation by providing a reference point for determining direction and location.
- Education: It is a valuable tool for educational purposes, helping students understand the Earth’s shape, orientation, and geographical features.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Equator, North Pole, and South Pole Map:
Q: Why is the equator important?
A: The equator is important because it serves as a reference point for understanding the Earth’s geometry, climate, time zones, navigation, and the distribution of natural resources.
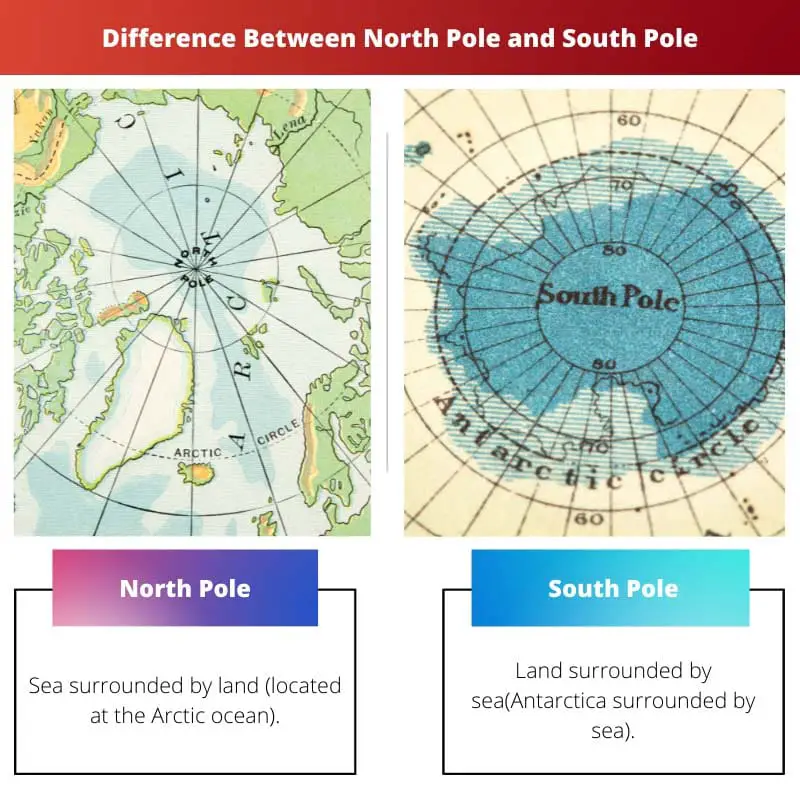
Q: What is the difference between the North Pole and the South Pole?
A: The North Pole is located in the Arctic Ocean, covered by ice, while the South Pole is located on the continent of Antarctica, also covered by ice. The North Pole is close to the Earth’s geomagnetic north pole, while the South Pole is the geographic south pole.
Q: What is the significance of the lines of latitude and longitude on the map?
A: Lines of latitude and longitude form a grid system that allows for precise location identification on the Earth’s surface. Lines of latitude run horizontally, measuring distance north or south of the equator, while lines of longitude run vertically, measuring distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
Q: How can I use an equator, North Pole, and South Pole map for navigation?
A: By using the map, you can determine your current location by identifying the intersecting lines of latitude and longitude. You can then use this information to navigate to a desired destination.
Tips for Using an Equator, North Pole, and South Pole Map:
- Choose a reliable map: Ensure that the map you use is accurate and up-to-date.
- Familiarize yourself with the key features: Understand the meaning of the equator, North Pole, South Pole, and lines of latitude and longitude.
- Practice using the map: Use the map to locate different countries, continents, and points of interest.
- Consider using a digital map: Digital maps offer interactive features, such as zooming, panning, and searching, which can enhance your understanding and navigation experience.
Conclusion:
The equator, North Pole, and South Pole are fundamental reference points that define the Earth’s geometry and global positioning. Understanding these key features is essential for comprehending our planet’s shape, orientation, and geographical features. A map depicting these points provides a visual representation of the Earth’s geometry, offering a global perspective and assisting in navigation and education. By using an equator, North Pole, and South Pole map, we gain a deeper understanding of our planet’s intricate structure and the interconnectedness of its diverse ecosystems.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator, North Pole, and South Pole: Understanding Our Planet’s Geometry. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!