A Circumnavigation of the Globe: Exploring the Countries Crossed by the Equator
Related Articles: A Circumnavigation of the Globe: Exploring the Countries Crossed by the Equator
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Circumnavigation of the Globe: Exploring the Countries Crossed by the Equator. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Circumnavigation of the Globe: Exploring the Countries Crossed by the Equator
The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, serves as a fundamental geographical marker, dividing the planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. This invisible line bisects a diverse array of countries, each contributing unique cultural, geographical, and ecological elements to the equatorial landscape. Understanding the countries traversed by the equator provides a fascinating insight into the Earth’s diversity and the interconnectedness of its inhabitants.
Navigating the Equatorial Belt: A Journey Through Diverse Lands
The equator’s journey around the globe begins in the Atlantic Ocean, traversing the westernmost point of Africa in Sao Tome and Principe. This island nation, renowned for its volcanic landscapes and rich biodiversity, serves as a gateway to the equatorial belt.
Moving eastward, the equator crosses the vast continent of Africa, traversing several countries, each with its own distinct character.
- Gabon, known for its dense rainforests and abundant wildlife, is a haven for nature enthusiasts.
- Republic of the Congo, a country rich in natural resources, boasts a diverse ecosystem, including the vast Congo Basin rainforest.
- Democratic Republic of the Congo, the second-largest country in Africa, is home to the iconic Mount Nyiragongo, a volcano with a lava lake.
- Uganda, a landlocked nation, is famous for its breathtaking landscapes, including the Rwenzori Mountains and the source of the Nile River.
- Kenya, renowned for its iconic wildlife safaris and the Great Rift Valley, offers a glimpse into the heart of Africa.
- Somalia, a country located on the Horn of Africa, possesses a rich history and culture, with a coastline facing the Indian Ocean.
After traversing Africa, the equator enters Asia, passing through:
- Maldives, a tropical archipelago known for its pristine beaches and luxurious resorts.
- Indonesia, the world’s largest archipelago, boasts a diverse landscape ranging from volcanic mountains to lush rainforests.
- Kiribati, a nation comprised of numerous islands in the Pacific Ocean, is a key player in the fight against climate change.
Continuing its westward journey, the equator crosses the vast Pacific Ocean, reaching the South American continent.
- Ecuador, the country named after the equator, is home to the Galapagos Islands, a UNESCO World Heritage Site renowned for its unique wildlife.
- Colombia, a nation with diverse landscapes, including the Amazon rainforest and the Andes Mountains, is a cultural melting pot.
- Brazil, the largest country in South America, boasts a vibrant culture, diverse ecosystems, and the iconic Amazon River.
Finally, the equator returns to the Atlantic Ocean, completing its circumnavigation of the globe.
The Importance of the Equator: A Tapestry of Life and Climate
The equator’s significance extends far beyond its geographical position. It plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s climate, influencing weather patterns, and supporting a diverse range of ecosystems.
- Tropical Climate: Countries located along the equator experience a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures and abundant rainfall. This climate fosters the growth of lush rainforests, teeming with biodiversity.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The equatorial region is considered a biodiversity hotspot, home to a vast array of plant and animal species. This rich ecosystem provides crucial services, including carbon sequestration and regulation of the global climate.
- Global Trade and Connectivity: The equator’s strategic location has facilitated global trade and connectivity for centuries. The movement of goods and people along the equatorial belt has fostered cultural exchange and economic development.
FAQs: Unveiling the Secrets of the Equator
1. What is the significance of the equator?
The equator is a fundamental geographical marker that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s climate, influencing weather patterns, and supporting a diverse range of ecosystems.
2. How many countries does the equator pass through?
The equator passes through a total of 14 countries, spanning across four continents.
3. What are the major geographical features located on the equator?
The equator passes through various significant geographical features, including the Amazon rainforest, the Congo Basin, the Galapagos Islands, and the Great Rift Valley.
4. What are the challenges faced by countries located on the equator?
Countries located on the equator face challenges related to climate change, deforestation, and biodiversity loss. They also struggle with poverty, inequality, and political instability.
5. How does the equator influence the climate of the Earth?
The equator receives the most direct sunlight, leading to high temperatures and abundant rainfall. This creates a tropical climate that supports the growth of lush rainforests and diverse ecosystems.
Tips for Exploring the Equator
- Plan your trip during the dry season: The equatorial region experiences heavy rainfall during certain periods. Planning your trip during the dry season ensures a more enjoyable experience.
- Respect the local culture: Equatorial countries boast a rich diversity of cultures. Respect local customs and traditions.
- Support sustainable tourism: Choose eco-friendly accommodation and tours that minimize their environmental impact.
- Learn about the local wildlife: The equatorial region is home to a vast array of wildlife. Take the opportunity to learn about the unique flora and fauna.
- Embrace the adventure: The equatorial region offers a unique and unforgettable travel experience. Be open to exploring new cultures and landscapes.
Conclusion: A Global Tapestry Woven by the Equator
The equator, a line of latitude that circles the Earth at 0 degrees, serves as a powerful symbol of the planet’s interconnectedness. It weaves together diverse cultures, landscapes, and ecosystems, creating a global tapestry of life and beauty. Understanding the countries crossed by the equator provides a profound appreciation for the Earth’s diversity and the importance of preserving its natural wonders for future generations.

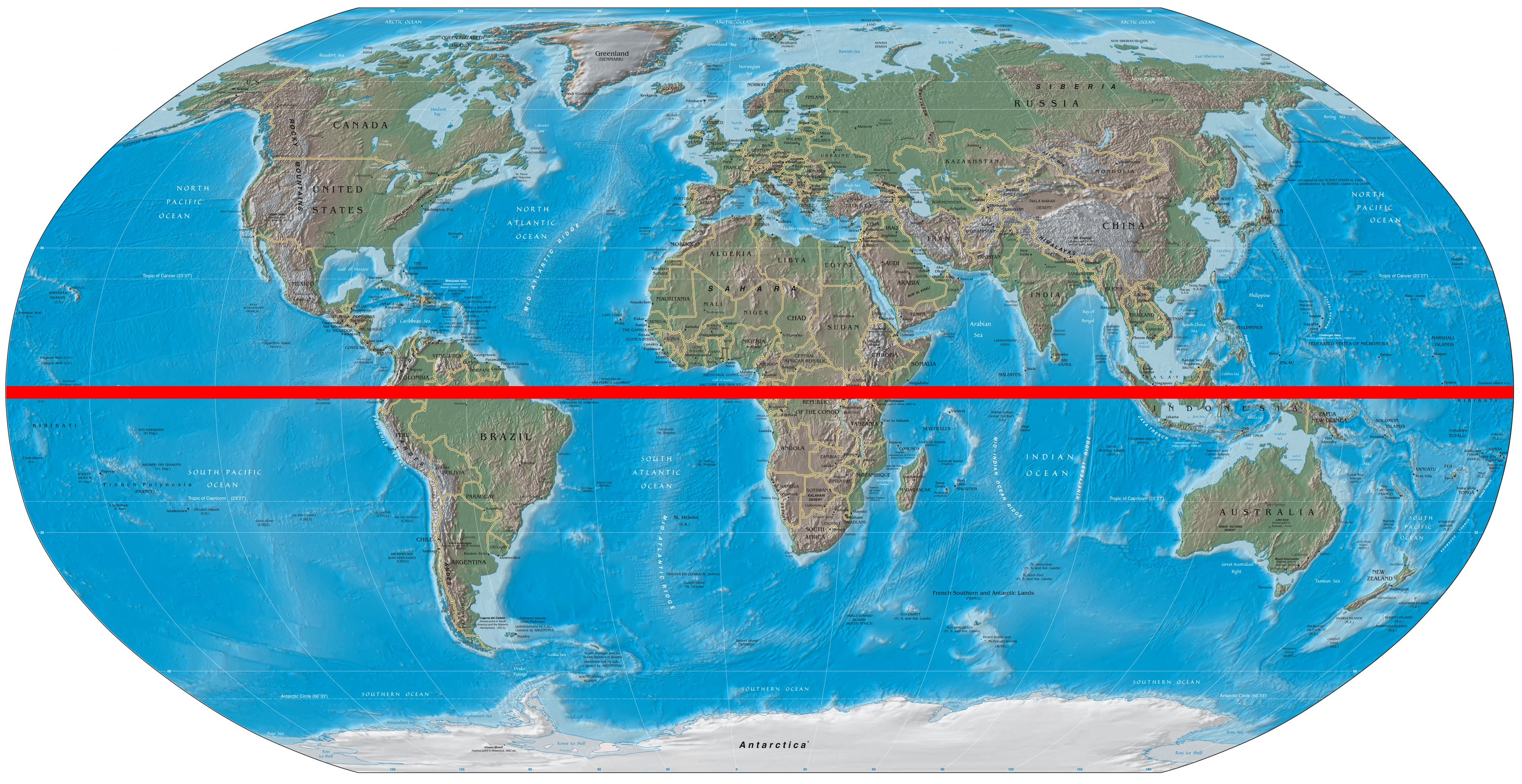




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Circumnavigation of the Globe: Exploring the Countries Crossed by the Equator. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!